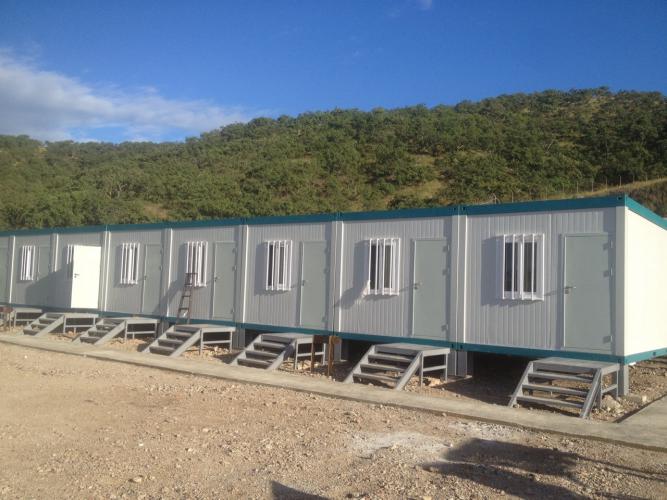
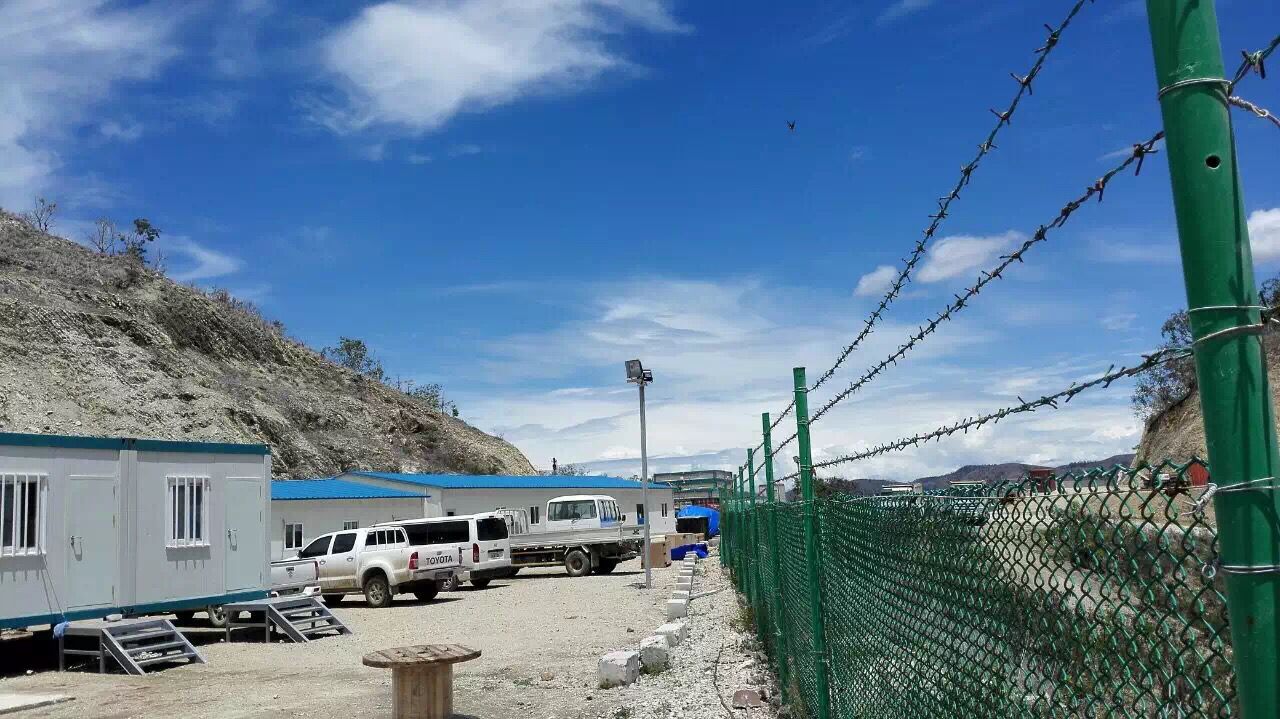
When choosing between prefab houses vs modular houses, many prospective houseowners find themselves weighing cost, value, and long-term worth. While both options promise faster construction and lower costs than traditional stick-built houses, their differences can have a real impact on your budget and future resale prospects. Let’s dive into a detailed comparison that unpacks upfront costs, savings, resale trends, customization, and real-world case studies—helping you make an informed decision.
Prefabricated Houses
Prefabricated Houses consist of individually manufactured components—walls, floors, roofs, doors, and windows—produced in a factory and then shipped to the site for assembly.
Factory production ensures consistent parts and efficient quality inspections.
On-site assembly involves structural erection and connection of utilities (plumbing, electrical).
Typical timeline: 4–6 weeks of factory production plus 1–2 weeks of on-site assembly.
Modular Houses
Modular Houses break the structure into complete, self-contained modules—bedrooms, living rooms, kitchen units—that arrive at the site with interior finishes and major inspections already complete.
Each module is effectively move-in ready upon delivery.
On-site work is limited to joining modules, sealing interfaces, and exterior finishing.
Typical timeline: 6–8 weeks of factory production plus 2–3 weeks of on-site erection and finishing.
Performance and Quality Comparison
| Performance Metric | Modular Houses | Prefab Houses |
| Quality Control | Full-module acceptance tests; tighter tolerances | Component-level inspections in a centralized factory |
| Energy Efficiency | Factory-installed seals and finishes deliver uniform insulation and soundproofing | Optional high-performance insulation; site sealing |
| Seismic and Fire Safety | Whole modules undergo seismic and fire-rating tests; higher fire-resistance at joints | Lightweight structures require reinforced connections |
| Insulation & Acoustics | Consistent, factory-applied insulation and sound barriers | Flexible choice of insulation and soundproofing layers |
| Customization | Standardized modules limit floorplan and facade options but accelerate delivery | Flexible component selection for bespoke layouts |
Understanding Upfront Costs
One of the biggest draws of prefab houses vs modular houses is the lower upfront cost compared to conventional builds. But costs can vary widely depending on type, finishes, location, and site conditions.
For modular houses, expect to pay $40–80 per square foot for the base structure. Fully installed, including transport, crane placement, and finish work, this often rises to $100–200 per square foot. For a typical 1,800 ft² modular house, you’re looking at $180,000–360,000 all-in.
Manufactured houses, a popular prefab option, tend to be cheaper, averaging $40–50 per square foot. However, the savings can shrink once you factor in site prep—land purchase, foundations, transport, and crane costs can add up quickly, sometimes closing the gap with modular options.
Cost Savings vs Stick-Built Construction
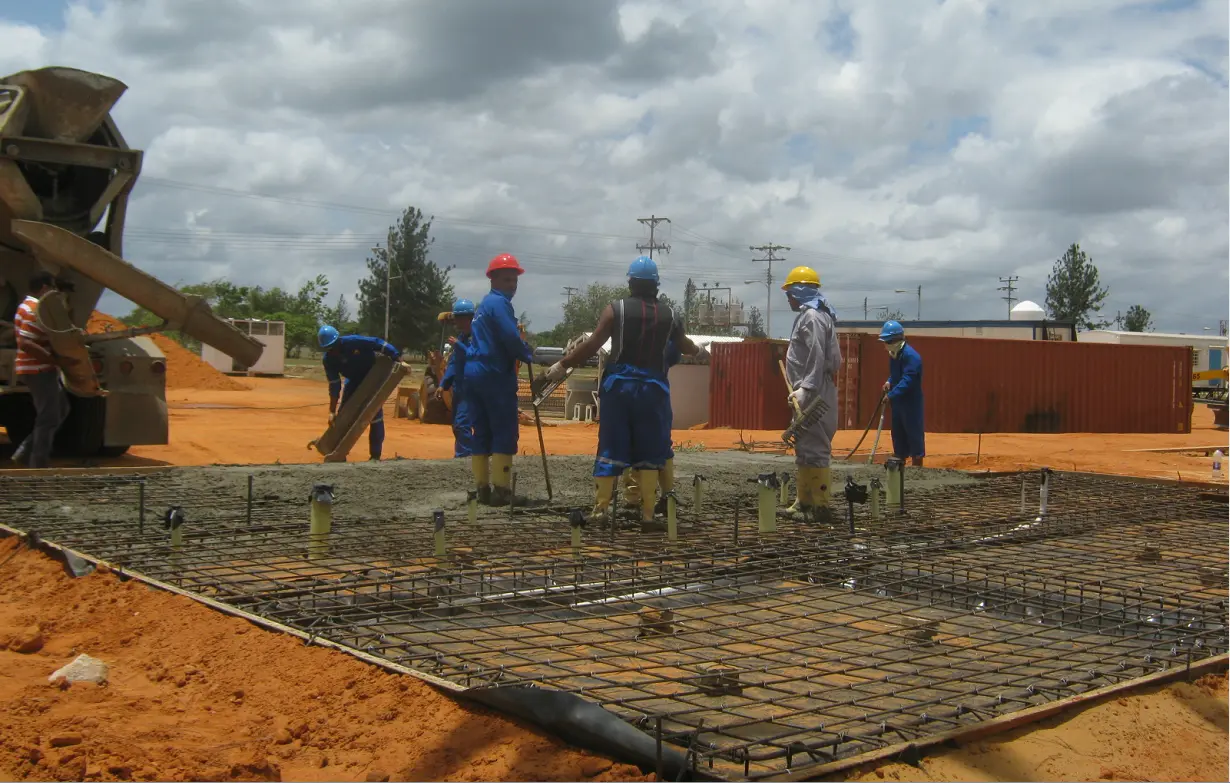

When comparing prefab houses vs modular houses to stick-built houses, savings become clearer. Modular builds are generally 10–25% cheaper per square foot, partly because they cut construction timelines by 20–50%. This speed comes from simultaneous factory fabrication and site prep—a significant advantage over traditional builds that depend on good weather and on-site coordination.
Panelized and kit systems also reduce labor costs. Manufactured houses can cost as little as 56–61% of a conventional site-built house, though this affordability comes with trade-offs in value retention and financing.
Appreciation and Resale Value
A big question in the prefab houses vs modular houses debate is how these structures perform in the housing market years down the line.
Modular houses tend to appreciate much like traditional houses. Built to the same codes, they qualify for standard mortgages and often carry no stigma in resale value—lenders and buyers generally treat them the same as stick-built properties.
Manufactured houses, meanwhile, often depreciate over time, similar to vehicles. Unless permanently affixed to land with a foundation, they can lose 30% of their value in just five years. If you plan to move or refinance, this depreciation is a crucial factor.
Total Costs Over Time
Upfront savings are just part of the story. Let’s look at the total cost of ownership (TCO) when comparing prefab houses vs modular houses.
Modular houses are known for better energy efficiency and durability, which can translate into lower maintenance and repair bills over time. The quality control in factory conditions reduces waste, weather delays, and construction errors—saving money for decades.
Financing is another factor. Modular houses qualify for traditional mortgages with competitive rates. Manufactured houses, by contrast, often require chattel or FHA loans with higher interest, since they’re sometimes treated more like personal property than real estate.
Add depreciation into the mix, and modular houses again tend to deliver better lifetime value.
Speed and Project Timeline
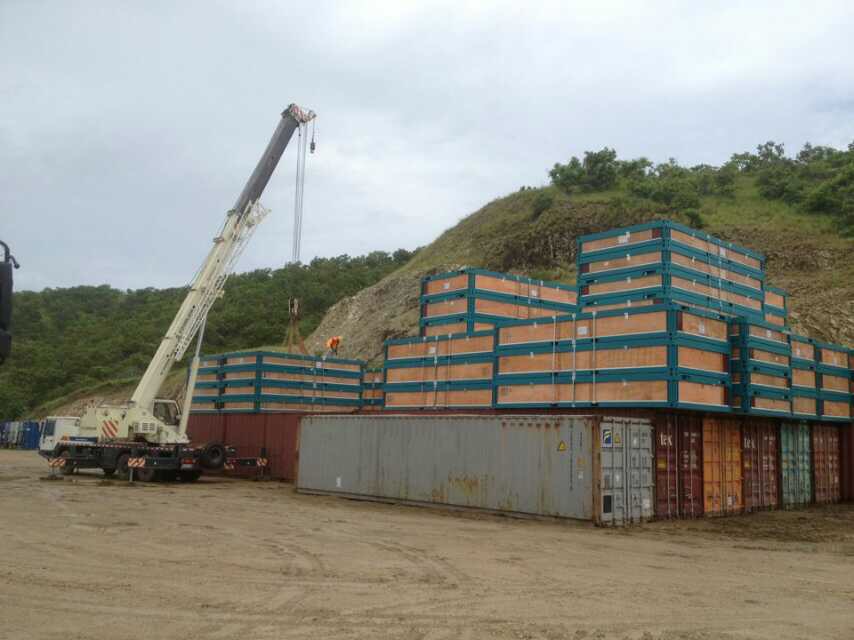

One undeniable advantage of prefab houses vs modular houses compared to traditional builds is speed.
Modular houses are usually built in climate-controlled factories while your site is prepped. Once ready, they’re shipped and assembled quickly, minimizing weather risks. Many modular projects wrap up in 2–6 months, cutting total build time by nearly half compared to stick-built projects.
Manufactured and panelized prefab options are even faster but can vary based on site readiness and utility hookups.
Customization and Quality
A common misconception is that prefab houses vs modular houses lack customization. The reality is quite the opposite, especially for modular builds.
Modern modular houses are highly customizable—buyers can tweak floor plans, finishes, and architectural styles to suit their taste, all while meeting or exceeding local building codes. They’re built strong enough to withstand transport and assembly, often resulting in better durability than stick-built houses.
In contrast, manufactured houses and basic prefab kits offer fewer customization options and may not meet the same standards for extreme weather durability.
Summary Comparison Table
| Aspect | Modular houses | Manufactured Prefab houses |
| Upfront Cost | $100–200/ft² installed | $40–50/ft² |
| Total Cost Savings | 10–25% cheaper than stick-built | 40–60% cheaper than stick-built |
| Appreciation | Retains value like stick-built | Often depreciates over time |
| Financing | Standard mortgages available | Chattel/FHA loans, higher rates |
| Timeline | 2–6 months | 1–4 months |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Limited customization |
| Durability | Meets local codes, high quality | Less durable if not permanently fixed |
Real-World Example: CDPH Prefab and Modular Expertise
Companies like CDPH—Chengdong Prefabricated Housing highlight how large-scale modular and prefab manufacturing can push costs down and value up.
Operating multiple standard factories across 70,000 m² with an annual output of 40,000 units, CDPH leverages bulk production and vertical integration to slash per-unit costs by 10–30% compared to traditional construction.
Their bolt-assembled steel-frame modules can be disassembled and reused multiple times, extending lifespan to 15–50 years, sometimes even longer in steel villa applications.
CDPH’s approach—simultaneous factory production and site prep—delivers projects 40–60% faster than conventional methods. Plus, their CE and ISO certifications enable compliance with strict international codes, securing standard mortgage eligibility and strong resale potential.
For buyers wanting factory-direct efficiency, global compliance, and proven longevity, CDPH illustrates why modular houses often win the prefab houses vs modular houses debate.
Chile Modular Exhibition Pavilion
At Chengdong’s inaugural modular House exhibition in Santiago, a reception hall, model suite, and office zone were fully assembled on-site in just five days after delivery, generating widespread media interest.
Tata Steel Plant Camp, India
For Tata Steel’s Phase II expansion, Chengdong supplied typhoon-resistant office and dining modules. Each unit passed stringent wind-load and anti-corrosion testing, ensuring long-term durability under extreme weather.
Worker Dormitories, Somalia
In a 90-day timeframe, Chengdong delivered 3,000 m² of temporary dormitories and office facilities for an oil development project, complete with private bathrooms and air-conditioning, significantly enhancing on-site living standards.
Chengdong Modular Housing Solutions Core Advantages
Factory Standardization for Superior Quality
Each module is fabricated in a controlled environment where structural framing, utility pre-installation, and interior finishes undergo precise dimension checks and stringent inspections. Compared to traditional on-site builds, Chengdong modules exhibit minimal tolerances and have passed professional tests for seismic resistance, fire safety, and thermal/acoustic performance.
Accelerated Delivery, Shortened Timelines
Parallel production and site preparation enable a typical schedule of 6–8 weeks for factory manufacturing and just 2–3 weeks for on-site craning and integration. For example, Chengdong’s first overseas showcase in Santiago, Chile, moved from design to fully operational exhibition pavilion in under six months, attracting extensive local media coverage.
Flexible Customization for Diverse Applications
Standardized modules can be combined in countless configurations and finished in multiple façade styles. Whether for residential complexes, boutique hotels, corporate offices, or temporary camps, modules adapt to mountainous terrain, coastal settings, or cold-climate regions with optional high-insulation, thermal barrier, or weatherproof units.
Green and Energy-Efficient Construction
By using recyclable steel frames and eco-friendly composite panels with CNC-precision cutting, Chengdong minimizes material waste. Modular buildings achieve a 20–30% improvement in overall thermal performance, meeting or exceeding green building certification standards.
Seamless Service Process
Needs Assessment & Design
Field surveys inform a tailored modular scheme aligned with operational requirements and local environment.
Factory Fabrication & Quality Assurance
Modules undergo raw-material inspection, welding verification, and structural load testing.
Logistics & On-Site Crane Assembly
End-to-end transport management and specialized lifting equipment ensure safe, rapid delivery.
Interface Sealing & Final Finishes
Modules are joined, utilities connected, façades completed, and systems tested before handover.
Prefab Houses vs Modular Houses: What Should You Choose?
Choosing between prefab houses vs modular houses comes down to priorities. For buyers wanting long-term value, easy resale, and customization, modular houses are the clear winner. They balance lower costs with higher quality, conventional financing, and future market value.
If upfront price is your only concern and you need a temporary or highly affordable option, manufactured prefab houses may fit the bill—just be mindful of their potential to depreciate and the higher cost of chattel loans.
Either way, do your housework on local land costs, permits, and site preparation. These “hidden” expenses can tip the scales.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between prefab houses vs modular houses?
Prefab is a broad term for any factory-built housing, including modular, panelized, and manufactured. Modular specifically means pre-built, code-compliant modules assembled onsite.
Are modular houses cheaper than prefab houses?
Not always. Manufactured prefab houses can be cheaper upfront, but modular houses deliver better long-term value and lower depreciation.
Do modular houses appreciate in value?
Yes. Modular houses typically appreciate like stick-built houses because they meet the same codes and qualify for standard mortgages.
Can I customize a prefab house?
You can, but options vary. Modular houses are very customizable, while manufactured or kit houses may have limited design flexibility.
What’s the difference between prefab and modular construction?
Prefab Houses deliver individual components (walls, floors, roofs) to the site for assembly, offering design flexibility and lower part costs. Modular Houses ship fully finished modules that are craned into place, providing tighter tolerances, uniform quality, and faster overall delivery.
How long does a Chengdong modular House project take?
Typical timelines are 6–8 weeks for factory fabrication and 2–3 weeks for on-site craning, sealing, and final finishes, depending on project scale and site conditions.
Can I customize floor plans and finishes?
Yes. Chengdong’s modular system supports a wide range of layouts and exterior styles. Clients choose from standardized module types and specify interior finishes, cladding materials, and color palettes.
How energy-efficient are Chengdong modules?
Chengdong modules use recyclable steel frames and high-performance composite panels. Factory-applied insulation delivers a 20–30% improvement in thermal performance over conventional builds, helping achieve green certification.
What support is provided after delivery?
Post-handover, Chengdong offers warranty coverage, maintenance guidance, and optional training for facility managers. Spare parts and service teams are available for rapid response.
Conclusion
Prefab houses vs modular houses: both promise faster builds and lower upfront costs than traditional construction. But only modular houses consistently deliver the trifecta of affordability, quality, and resale value. Whether you’re buying your first house, downsizing, or adding a rental unit, weigh your budget, financing, and long-term plans carefully—your future self will thank you.
Ready to Get Started?
Chengdong modular housing solutions empower clients worldwide with efficient, safe, and sustainable prefab construction. Contact us today to explore product offerings, request custom quotes, and receive comprehensive on-site support—making your next project faster, superior, and greener.
Contact our experts today at info@chengdong.com or call +86 400-123-4567 to turn your vision into reality.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More


























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





