Prefab houses, with their advantages of fast construction, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, have become a preferred choice in engineering camps, emergency rescue, and other fields. However, many users are confused about whether prefab houses require a foundation. The answer is not absolute—it depends on the type of prefab house, usage scenario, and environmental conditions. As a professional enterprise deeply engaged in the integrated housing industry, Beijing Chengdong has rich experience in global projects, and its product system covers various prefab types with distinct foundation requirements. This article will detail the foundation rules for different prefab houses, combined with practical application cases.
Overview of Prefab Houses and Foundation Significance
Prefab houses refer to buildings whose key components such as walls, roofs, and floors are prefabricated in factories and then transported to the construction site for assembly. They are characterized by modular design, steel structure application, and versatile scenarios. Foundations, as the bearing structure of buildings, play a crucial role in stabilizing the house, resisting external forces such as wind and earthquakes, and extending service life.
For prefab houses, the rationality of the foundation directly affects their safety and usability. A suitable foundation can adapt to local geological and climatic conditions, avoid problems such as house tilt and deformation, and ensure the building meets usage requirements in both short-term and long-term scenarios. Beijing Chengdong adheres to the concept of "providing overall solutions for global engineering camps" and designs targeted foundation schemes based on different product characteristics and market demands, ensuring product reliability in various environments.
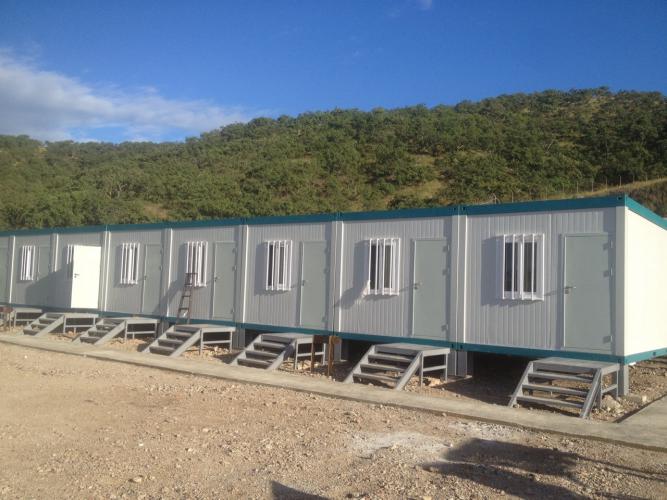
Container houses are a type of modular house, mainly targeting developed countries and high-end customers. They are movable, reusable, and can be stacked up to 3 layers vertically. Due to their relatively heavy weight and high stability requirements for multi-layer stacking, container houses generally require a foundation.
The common foundation forms include concrete strip foundations and concrete piers. For single-layer container houses used as temporary offices or dormitories, simple concrete piers can meet the requirements—they are easy to construct and cost-effective. For multi-layer combinations or long-term use scenarios (such as permanent engineering camp dormitories), concrete strip foundations are more suitable, as they can evenly distribute the weight of the building and enhance overall stability. Beijing Chengdong's container houses have been applied in coal mine camp projects and overseas engineering camps, with foundation schemes tailored to local geological conditions, ensuring stable use even in harsh environments.
Prefab House (Non-modular Activity Board House)
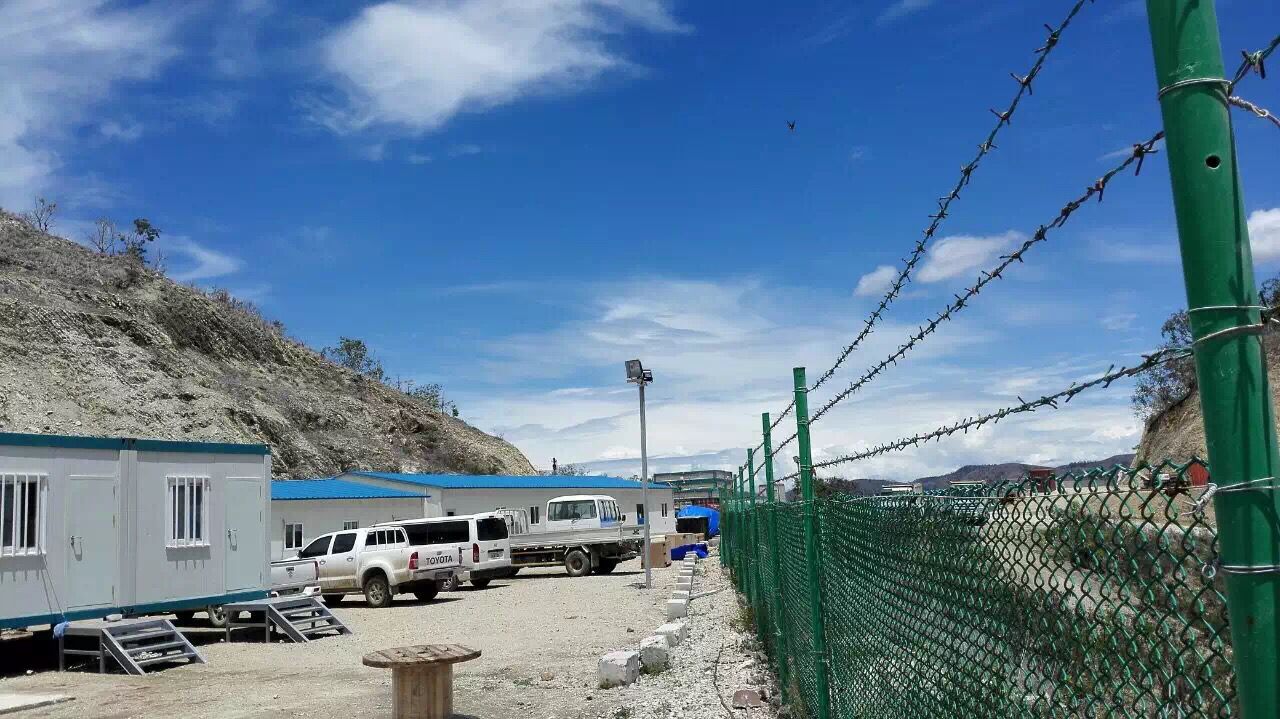
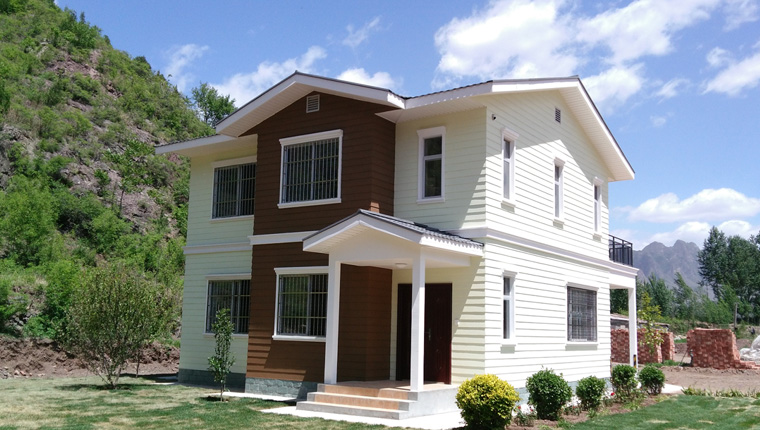
Prefab houses belong to non-modular activity board houses, mainly targeting underdeveloped regions such as Africa and Southeast Asia. They feature high prefabrication, stable steel frame structures, and strong environmental adaptability, with good corrosion resistance and thermal insulation performance.
Due to their lightweight characteristics and mostly single-layer use, prefab houses have relatively low foundation requirements. In areas with flat terrain and stable soil quality, simple ground leveling plus gravel paving or concrete slabs can be used as the foundation, which greatly reduces construction costs and shortens the construction cycle. In regions with poor geological conditions (such as soft soil or uneven terrain), simple strip foundations can be adopted to improve stability. Beijing Chengdong's assembled houses are widely used in overseas mining areas and rural public service projects, with foundation schemes adjusted according to local conditions to ensure adaptability and practicality.
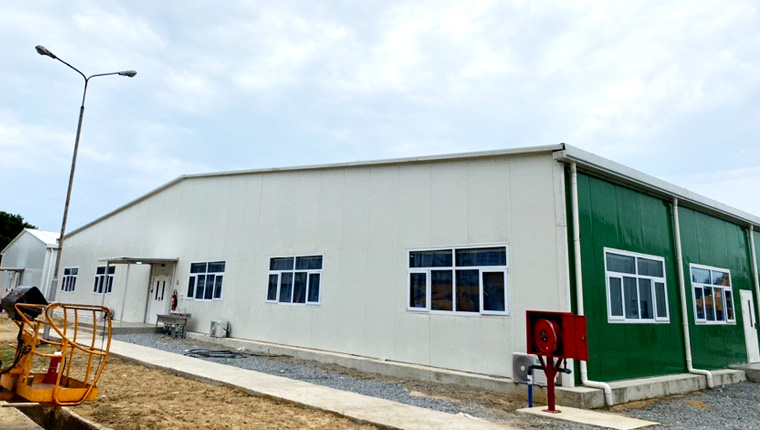
Steel structure (Large Functional Space)
Steel structure are developed by Beijing Chengdong's R&D team for the needs of overseas camp production facilities. They address the problems of heavy traditional H-steel structures and high transportation costs, using cold-formed materials for mechanized mass production. They are mainly used as large functional spaces such as factories, warehouses, and canteens in overseas camps.
Due to their large span and heavy load-bearing requirements, Steek structure must be equipped with stable foundations. Usually, reinforced concrete strip foundations or independent foundations are adopted to ensure the building can withstand the weight of equipment and materials and resist wind and seismic forces. In overseas oil and gas field camps and mining area projects, Beijing Chengdong's ZM series houses have achieved successful applications, with foundation designs combined with local seismic intensity and wind load data to ensure structural safety.
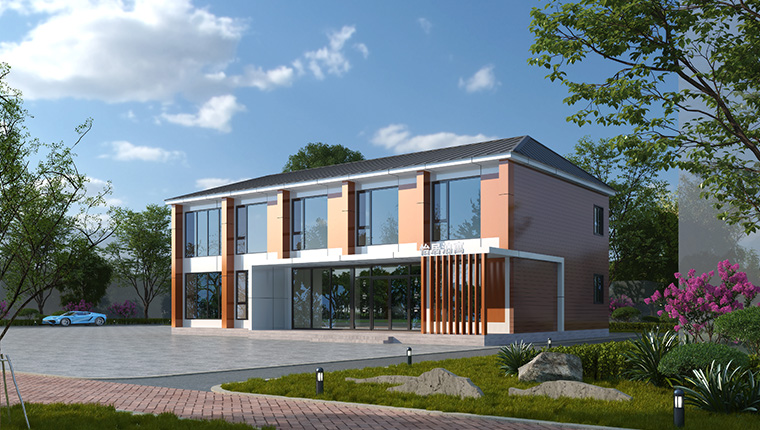
Equipment Box (Special Scenario Customization)
Equipment boxes are customized modular houses for special scenarios, such as equipment rooms for special equipment or residences in extreme environments (high temperature, cold, aridity). They integrate various equipment and instruments, with highly customized configurations.
Their foundation requirements depend on the usage scenario and equipment weight. For mobile equipment boxes that need to be moved frequently, simple adjustable supports or temporary concrete piers can be used as the foundation, facilitating disassembly and transfer. For fixed equipment boxes in extreme environments, stable strip foundations or pile foundations are required to resist harsh natural conditions. Beijing Chengdong's equipment boxes have been applied in polar scientific research stations and desert oilfield projects, with foundation schemes designed according to the specific needs of the equipment and the environment, ensuring reliable operation of the equipment and comfortable living for personnel.
Key Factors Affecting Foundation Selection for Prefab Houses
Usage Scenario and Service Life
Temporary scenarios such as emergency rescue and short-term engineering camps can adopt simple foundations (such as gravel paving, concrete slabs) to prioritize construction speed and cost control. For long-term scenarios such as permanent residences and industrial facilities, stable and durable foundations (such as reinforced concrete strip foundations, raft foundations) are necessary to ensure service life.
Building Height and Load-bearing Capacity
Single-layer prefab houses have low load requirements and can use simple foundations. Multi-layer stacked buildings (such as container houses stacked 2-3 layers) or large-span buildings (such as ZM series warehouses) have higher load-bearing requirements, requiring reinforced foundations to avoid structural risks.
Geological and Climatic Conditions
In regions with stable soil quality and mild climates, the foundation requirements are relatively loose. In areas with complex geological conditions (soft soil, sand dunes) or harsh climates (strong winds, earthquakes, heavy rains), the foundation needs to be strengthened—such as anti-seismic reinforcement, wind resistance design, and moisture-proof treatment. Beijing Chengdong's global projects cover the Middle East (high temperature and sandstorms), South America (earthquakes and floods), Indonesia (tsunamis and volcanic activities), and other regions, with foundation schemes fully adapted to local environmental characteristics.
Beijing Chengdong's Foundation Solutions and Project Cases
Beijing Chengdong is a private enterprise specializing in the integrated housing industry, with the vision of "providing overall solutions for global engineering camps" and the goal of becoming a global engineering camp expert. It has a global layout covering more than 100 countries, with a leading market position in the Middle East, South America, Indonesia, and other regions.
In domestic key projects, such as the Wenchuan earthquake-resistant engineering housing, the 50th National Day military parade village, the 2008 Olympic Games and Paralympic Games venues, and the 2022 Winter Olympic Games housing, Beijing Chengdong's prefab houses adopted targeted foundation designs according to different scenarios, ensuring the safety and stability of the buildings. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the company's prefab houses were used in many mobile cabin hospitals, with simple and efficient foundation schemes realizing rapid deployment.
In overseas projects, such as Middle East oilfield camps, South American mining camps, and Indonesian disaster relief sites, Beijing Chengdong's foundation solutions fully adapt to local conditions. For example, in Middle East oilfield camps with high temperatures and sandstorms, container houses adopt reinforced concrete strip foundations with wind-resistant reinforcement; in South American seismic-prone areas, assembled houses use flexible foundation connections to improve seismic performance. These cases fully verify the rationality and reliability of the company's foundation solutions.
Summary
Whether prefab houses need a foundation depends on multiple factors such as product type, usage scenario, and environmental conditions. Different prefab houses have distinct foundation requirements—container houses and ZM series houses generally require stable foundations to meet load-bearing and stability needs, while assembled houses can adopt simple foundations to balance cost and efficiency. Light steel villas and equipment boxes need customized foundation schemes according to service life and special requirements.
As a professional integrated housing solution provider, Beijing Chengdong integrates product characteristics and global project experience to provide customers with scientific and reasonable foundation designs, ensuring prefab houses achieve optimal performance in safety, durability, and cost-effectiveness. When choosing a prefab house, customers should cooperate with professional enterprises to formulate suitable foundation schemes based on actual needs, so as to maximize the value of the product.
If you need to know more about the foundation matching schemes for specific prefab house products or want to obtain customized solutions for overseas projects, you can contact Beijing Chengdong for detailed consultation. The company's professional team will provide you with full-process support from design to constructionhttps://www.cdph.net/contact-us.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More
























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





