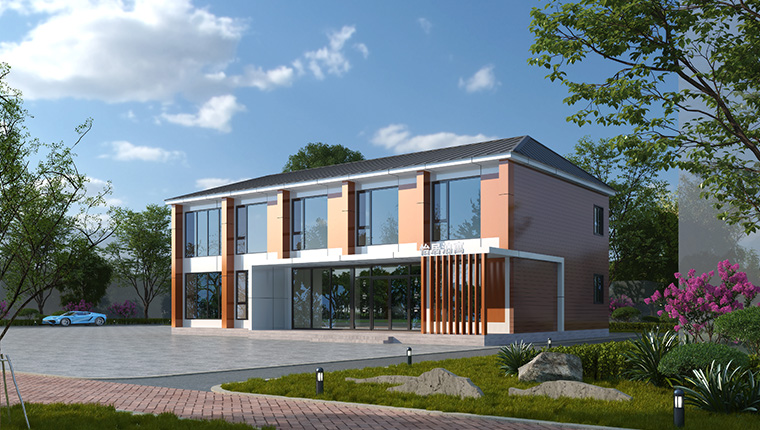
In an era where environmental consciousness drives consumer choices, the Eco-friendly modular house stands at the forefront of sustainable architecture. Combining green building principles with off-site construction efficiencies, these homes offer homeowners an attractive way to minimize their carbon footprint, reduce utility bills, and enjoy healthier indoor environments. This comprehensive article will explore the benefits, design considerations, materials, certifications, and real-world examples that make Eco-friendly modular houses the future of residential living.
Why Choose an Eco-Friendly Modular House?

Eco-friendly modular houses redefine sustainable construction by merging two powerful trends:
Modular Construction: Factory-built, pre-finished modules delivered to your site for quick assembly.
Green Building: Use of low-impact materials, energy-efficient systems, and waste-reducing processes.
Key advantages include:
Faster build times (30–60% quicker than traditional on-site construction).
Lower costs due to streamlined factory workflows and bulk materials purchasing.
Superior quality control, as modules are built under controlled conditions.
Less on-site waste and reduced environmental disturbance.
Optimized energy performance through integrated systems and high-performance envelopes.
By choosing an Eco-friendly modular house, homeowners benefit from cost-effective construction and a commitment to environmental stewardship.
Core Principles of Eco-friendly Modular Housing
Off-Site Prefabrication
A cornerstone of Eco-friendly modular house construction is off-site prefabrication. Building modules in a factory enables:
Precise material cutting, reducing off-cuts and waste.
Efficient labor deployment, lowers energy use per unit.
Weather-independent workflows, preventing schedule delays and material spoilage.
Factories can recycle leftover materials—wood scraps, metal trimmings, and packaging—minimizing landfill contributions and supporting circular-economy practices.
Sustainable Materials
Sourcing eco-friendly materials is essential for truly green modular homes. Common choices include:
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) and sustainably harvested wood for structural panels.
Recycled Steel frames, providing durability with lower embodied carbon.
Bamboo Flooring and cabinetry—fast-growing, renewable, and aesthetically pleasing.
Hempcrete and straw-bale insulation, offering superior thermal and acoustic performance.
Low-VOC Paints and adhesives to improve indoor air quality.
Pairing renewable materials with recycled content reduces resource depletion and supports healthier living spaces.
High-Performance Building Envelope
The building envelope of an Eco-friendly modular house is engineered for maximum thermal efficiency:
Advanced Insulation: Closed-cell spray foam, rigid foam boards, or vacuum insulation panels achieve U-values as low as 0.15 W/m²K.
Airtightness: Precision factory assembly minimizes air leakage, preventing drafts and heat loss.
Thermal Breaks: Composite materials and insulated connections reduce thermal bridging at panel joints.
Reflective Roofing: Cool-roof coatings deflect solar heat, reducing cooling loads.
An optimized envelope slashes heating and cooling demands, delivering comfort and significant energy savings.
Renewable Energy Integration
Eco-friendly modular houses often come pre-wired and plumbed for renewable systems:
Solar Photovoltaics (PV) panels installed on rooftops or carports.
Battery Storage for load-shifting and backup power during grid outages.
Solar Thermal collectors for domestic hot water, cutting gas or electric water-heater usage.
Ground-Source Heat Pumps or mini-split heat pumps for efficient heating and cooling.
Integrating renewables reduces reliance on fossil fuels, drives down utility bills, and often qualifies homeowners for incentives or net-metering programs.
Water Efficiency and Waste Reduction
To further environmental goals, Eco-friendly modular houses incorporate water-saving and waste-minimizing features:
Low-Flow Fixtures: Faucets, showerheads, and toilets that use 30–60% less water.
Rainwater Harvesting systems with filtration for irrigation and non-potable uses.
Greywater Recycling to reuse gentle wastewater from sinks and showers for landscaping.
Composting Toilets or on-site septic systems designed to reduce sewage output.
These strategies conserve water resources and lower utility expenses, reflecting a holistic approach to sustainable living.
Design Considerations for Eco-friendly Modular Houses

Site-Specific Planning
Before construction, rigorous site analysis informs module orientation, passive-solar strategies, and foundation design. Key factors include:
Solar path and shading to maximize daylighting and passive heating.
Prevailing winds for natural ventilation and cooling.
Topography and soil conditions to determine optimal foundation type.
Access routes for transport trucks and crane placement.
A thoughtful approach ensures modules deliver peak performance and integrate seamlessly with the landscape.
Flexible Floor Plans
Eco-friendly modular houses cater to diverse lifestyles. Popular configurations include:
Single-Story Open Plans: Ideal for small families or retirees, emphasizing flow and accessibility.
Two-Story Stackable Modules: Maximizing living area on compact sites.
Multiplex Designs: Attached modules creating duplexes or townhouses for multi-family living.
Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs): Backyard studios or guest houses that expand living space.
Factory-built modules allow clients to customize layouts—adding balconies, lofts, or multi-use flex spaces—without compromising efficiency.
Indoor Environmental Quality
Healthy indoor environments are vital in Eco-friendly modular homes:
Ventilation Systems: Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR) ensures fresh air while preserving thermal energy.
Natural Light and Views: Large factory-cut openings, clerestory windows, and skylights reduce electric lighting needs.
Non-Toxic Finishes: Low-VOC materials, formaldehyde-free cabinetry, and toxin-free sealants improve occupant well-being.
Acoustic Insulation: High-density panels and resilient channels minimize noise transmission between modules.
Prioritizing indoor environmental quality supports occupant health and productivity.
Certifications and Standards
Earning recognized building certifications validates the eco credentials of modular homes:
| Certification | Description |
| LEED | Green building rating emphasizing energy, water, and material efficiency. |
| Passive House | Stringent standard focused on ultra-low energy use and airtightness. |
| Living Building | Holistic framework demanding net-positive energy, water, and materials. |
| WELL | Concentrates on occupant health and wellness metrics like air and light. |
Manufacturers and builders align with these frameworks, guiding material selection, performance targets, and post-occupancy monitoring.
Real-World Examples
The GreenBox Home (USA)
Developed by a leading modular manufacturer, the GreenBox Home combines CLT panels, spray-foam insulation, and rooftop solar arrays. Delivered in kit form, homeowners assembled modules in four days. The home achieved a 70% reduction in heating energy and received a LEED Platinum certification.
EcoStack Apartments (Europe)
A five-story, 25-unit apartment building in Germany used recycled steel containers retrofitted with high-performance envelopes. Modules were craned into place in a single weekend, and the project earned Passive House certification, boasting an annual heating demand of just 15 kWh/m².
Bamboo Grove Retreat (Asia-Pacific)
Situated on a tropical hillside, this bespoke four-bedroom house features CLT modules, hemp-fiber insulation, and operable louvered facades for natural ventilation. A rainwater catchment system supplies 80% of the household’s water needs, and solar thermal panels provide hot water.
Cost Considerations and ROI
While initial Eco-friendly modular house costs can be comparable to conventional builds—ranging from $200 to $300 per square foot—long-term savings in energy, water, and maintenance often yield a positive return on investment within 5–10 years. Factors influencing cost include:
Level of prefabrication (shell-only vs. turnkey).
Choice of high-end sustainable materials.
Renewable energy system capacity.
Site access complexities and local labor rates.
Incentives—such as federal tax credits for solar installations or local rebates for water-efficiency upgrades—further enhance affordability.
Future Trends in Eco-friendly Modular Housing
Looking ahead, innovation continues to drive Eco-friendly modular homes forward:
Digital Design and BIM: Integrated building-information modeling supports real-time energy simulations and clash detection.
Robotic Assembly: Automated module construction promises faster cycle times and lower labor costs.
Advanced Materials: Graphene-infused panels, transparent solar glass, and self-healing concrete will elevate performance.
Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chains: Transparent material provenance tracking ensures ethical sourcing and circularity.
Community-Scale Modular Neighborhoods: Clustered modular homes sharing microgrids, communal gardens, and shared amenities.
These advancements will make Eco-friendly modular houses more accessible, efficient, and appealing to a broader market.
Conclusion
Eco-friendly modular houses represent a paradigm shift in residential construction, offering speed, quality, and sustainability in one package. By leveraging factory efficiencies, green materials, high-performance envelopes, and renewable energy, these homes minimize environmental impact while delivering superior comfort. As certifications, technologies, and consumer awareness evolve, Eco-friendly modular housing will continue its ascent—transforming how we build, live, and coexist with our planet. Embrace this future of sustainable living by choosing an Eco-friendly modular house that reflects your values and elevates your lifestyle.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More


























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





