
- Home
-
About Us
Social Responsibility
Contact Us
Corporate Culture
Regulated Enterprise
Listed on the New Third Board in 2015, stock code: 832789
Free Design
Free scheme design and quotation
Global Footprint
Covering 100+ countries
Factory Direct Sales
Self-owned standard factory
Customization
Customize product size and matching according to needs
Cost-effective
Lowest comprehensive cost
Our Achievements
128,000
㎡Factory Area
85,000
UnitAnnual Production Capacity
4000+
Project Experience
75+
Patent
Free service hotline
Contact usTel / Whatsapp:+86 18001125785 Email:chengdong@cdph.com.cn
-
Products

Modular House
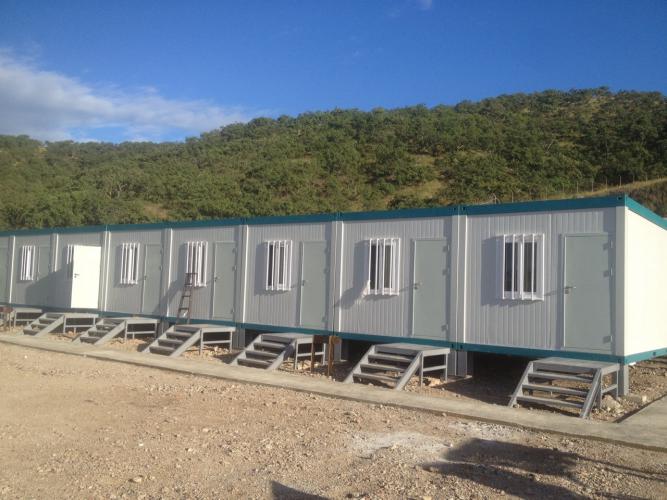
The container house is a movable and reusable building product. This kind of house adopts modular design and factory prefabrication production. It uses the container frame as the basic unit and can be used alone. It can also be used through different combinations of horizontal and vertical directions to form a spacious use space. The vertical direction can be stacked with 3 layers. The box unit structure is a standard component welded with special steel. The containers are connected by bolts. Its structure is stable, easy and fast to install, and is favored by most users.
More

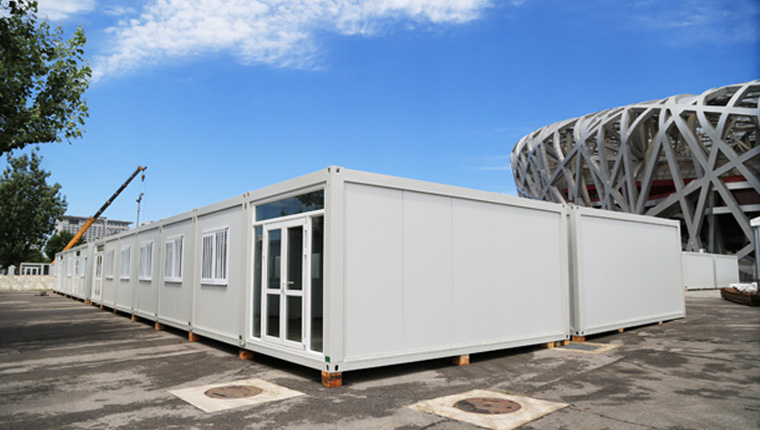
Prefab House
The prefab house is highly prefabricated, which is closely connected by a steel frame and a composite maintenance board to form a stable building system, allowing for targeted layout design and interior and exterior decoration according to actual needs. The prefab house is highly adaptable to the environment and has good anti-corrosion, sealing and thermal insulation properties.
More
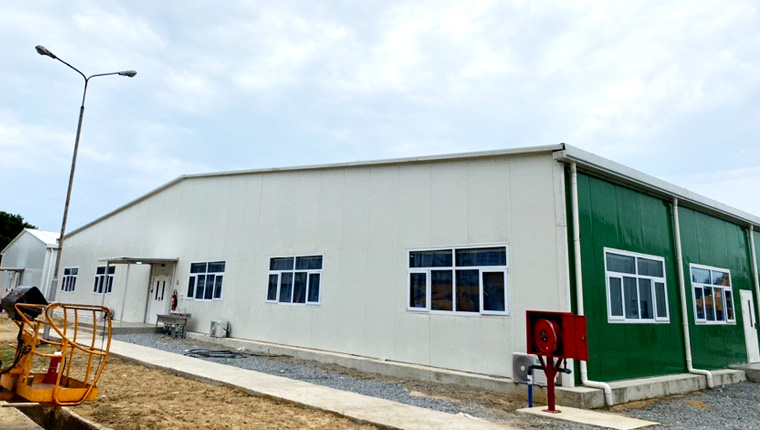

Steel Structure
In the construction project of engineering camps, not only accommodation and office buildings are needed, but also some production buildings. Due to the relatively large self-weight of the traditional H-shaped steel structure, the long processing cycle, and the relatively high comprehensive cost of long-distance transportation. The R & D team of Chengdong Camp has developed a light steel structure that is cold-formed and can be mass-produced mechanically on the basis of the traditional portal frame. After several technical improvements, it has finally been finalized into our product introduction. At present, this product is widely used in large functional buildings such as workshops, storerooms, and restaurants in the construction of engineering camps.
More
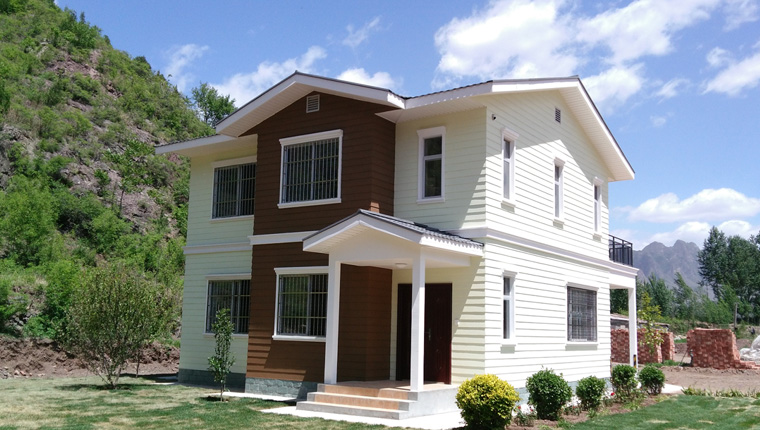

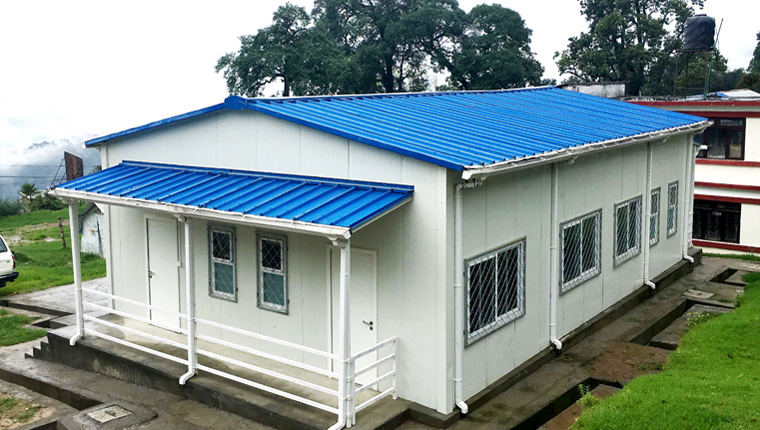
Light Steel Villa
Light steel villas are currently the application direction of high-end housing in camp construction and future civil buildings. They can be used as semi-permanent buildings. According to the individual needs of customers, the layout and decoration style can be customized in the design stage. For construction scenarios in different climate regions, building materials can be selected in a targeted manner. Compared with traditional villas, it greatly reduces the construction cycle and greatly reduces the environmental pollution on the construction site.
More
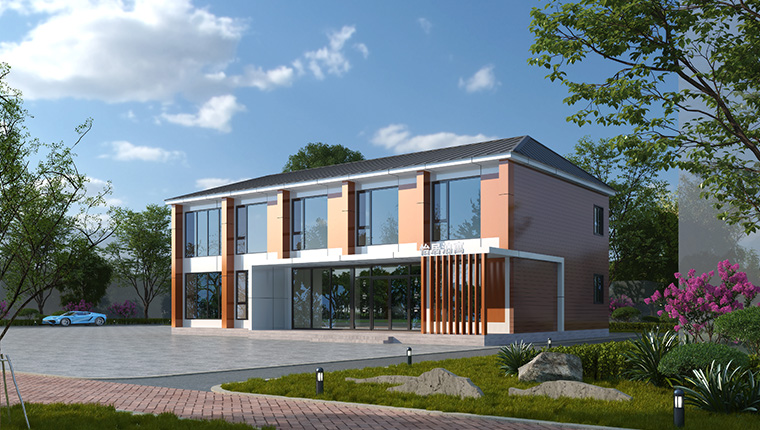

Light steel module products
Light steel module products adopt a sheet-type module system. Through the through-column design, the structural stress performance is more reasonable. The light steel integrated wall adopts an integrated modular design concept, making installation simple and fast.
According to the application scenarios, the products can be fully prefabricated in the factory and hoisted on site, or semi-prefabricated and assembled on site. They have the advantages of modular design, earthquake resistance, wind resistance, fire resistance, heat insulation, and short construction period. They are mainly used in scenarios such as apartments, hotels, commercial buildings, and offices.More
-
Case Center
Engineering Camps Culture and Tourism Education Commerce Emergency and Events Event Military and Assistance Mining, Oil & GasGlobal Footprint
We have covered 100+ countries
4000+ camp construction projectsLearn More






- Support
- News
- Contact Us


















![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





