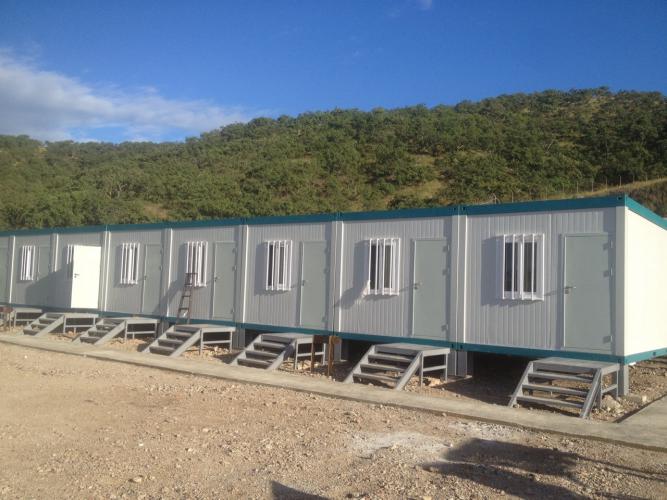
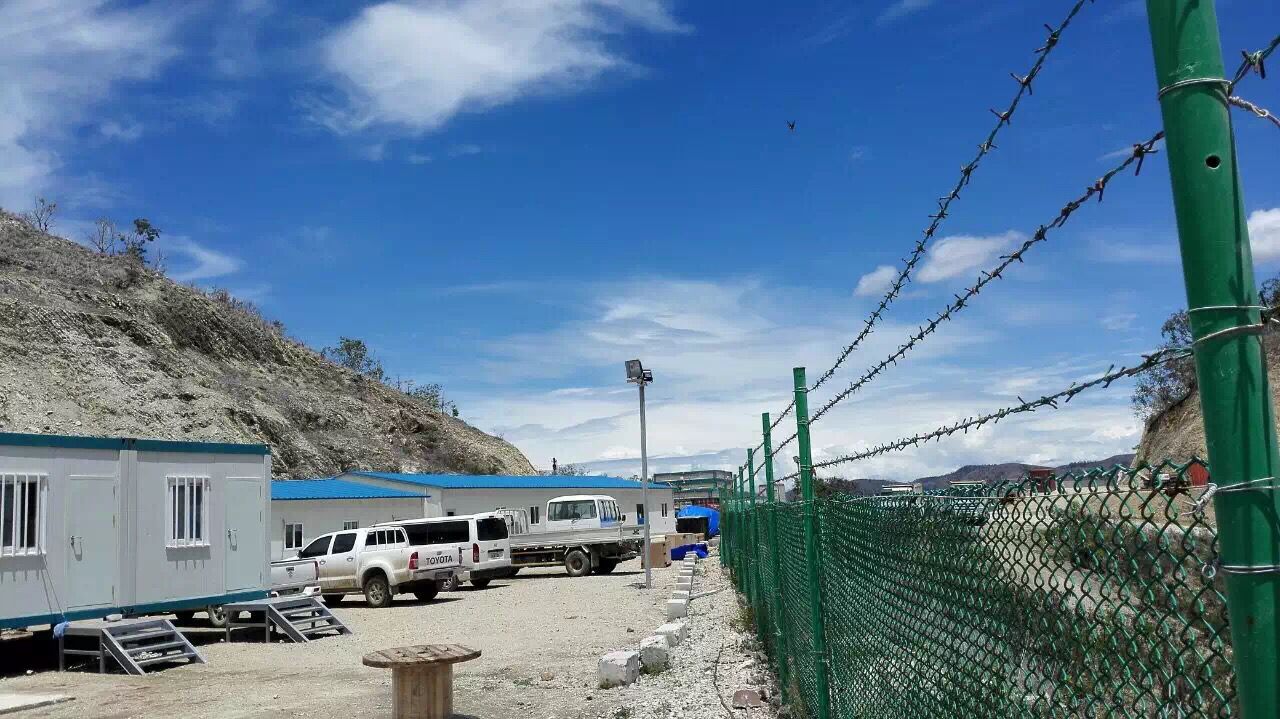
Introduction
The global construction industry faces unprecedented challenges: tight project timelines, labor shortages, environmental concerns, and the need for cost-effective solutions. Modular building companies have emerged as game-changers, offering innovative prefabrication technologies that address these pain points directly. Unlike traditional construction methods that require months or even years to complete, modular buildings can be designed, manufactured, and deployed in a fraction of the time.
Modular construction represents a fundamental shift in how we approach temporary and semi-permanent structures. These buildings are manufactured off-site in controlled factory environments, ensuring superior quality control, reduced waste, and faster installation. From remote mining camps in Africa to infrastructure projects across Southeast Asia, modular buildings are transforming how organizations support their workforce and manage project-based accommodations.
This comprehensive guide explores the modular building industry, its key players, technological innovations, and real-world applications that demonstrate why modular construction has become the preferred choice for engineering camps, construction sites, and emergency accommodations worldwide.

Understanding Modular Building Solutions
What Are Modular Buildings?
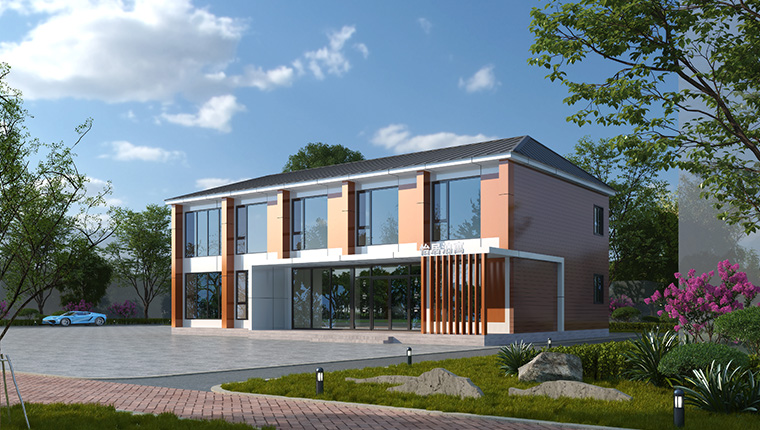
Modular buildings are prefabricated structures manufactured in a controlled factory setting and transported to the project site for assembly. Unlike traditional construction, which happens on-site with on-site material delivery, labor coordination, and weather dependencies, modular buildings arrive substantially completed, requiring only final installation and connection.
The fundamental advantage of modular construction lies in its modular design philosophy—standardized components that can be combined horizontally and vertically to create complex layouts suited to specific project requirements. This flexibility allows a single modular unit to serve as a dormitory, office, medical facility, or kitchen depending on internal configuration and equipment integration.
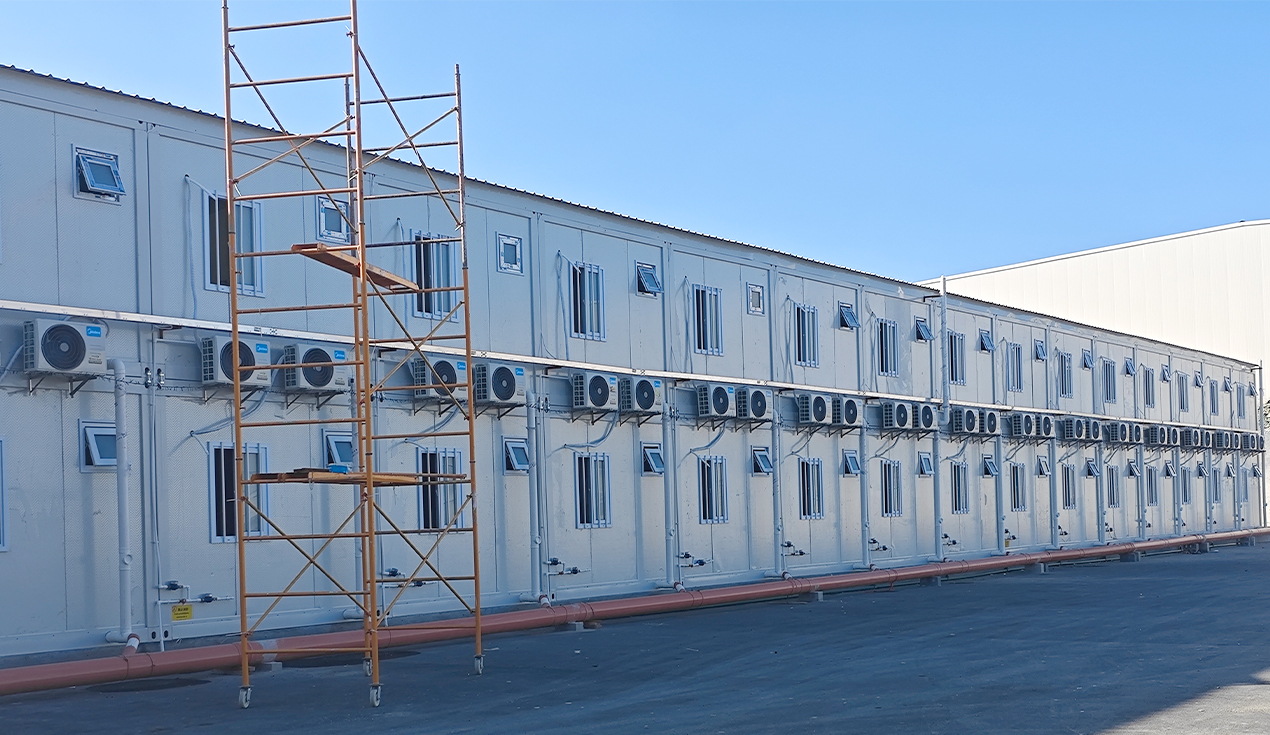

Core Product Categories
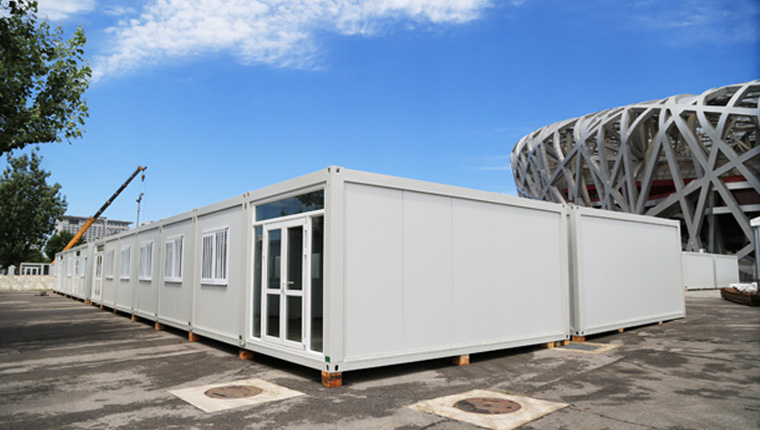
Container Houses
Container houses utilize standard shipping containers as the structural foundation. Steel container frames are reinforced with corner castings and can be stacked up to three layers high. Interior spaces feature composite maintenance boards, comprehensive insulation systems (typically 100mm of rock wool or fiberglass), and all necessary utilities pre-installed. The advantage: low transportation costs (five container houses fit into a standard 20-foot container), structural stability, and rapid deployment.
Prefab Houses
Prefab houses employ a steel frame connected by composite maintenance boards to create a stable building system. These structures offer superior environmental adaptability and excellent anti-corrosion, sealing, and thermal insulation properties. Prefab construction allows for targeted layout design and detailed interior-exterior customization based on specific project demands.
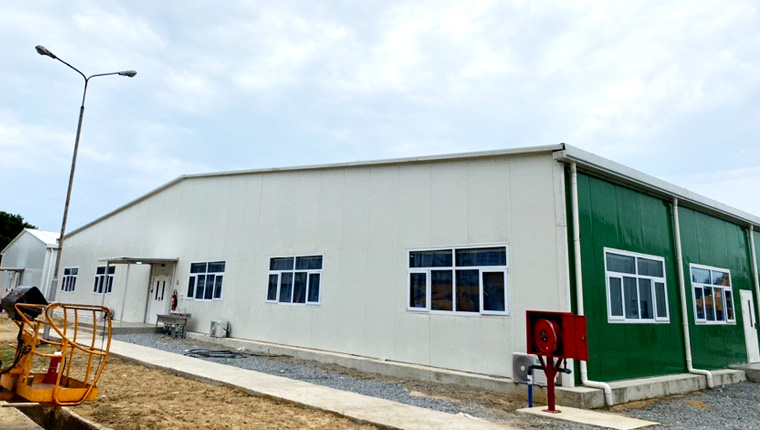
Light Steel Structures
Developed to address limitations of traditional H-shaped steel structures, light steel buildings use cold-formed, mechanically mass-produced materials. They significantly reduce self-weight, processing time, and comprehensive transportation costs—critical advantages for remote engineering camps. These structures excel in warehouse, workshop, and production facility applications.
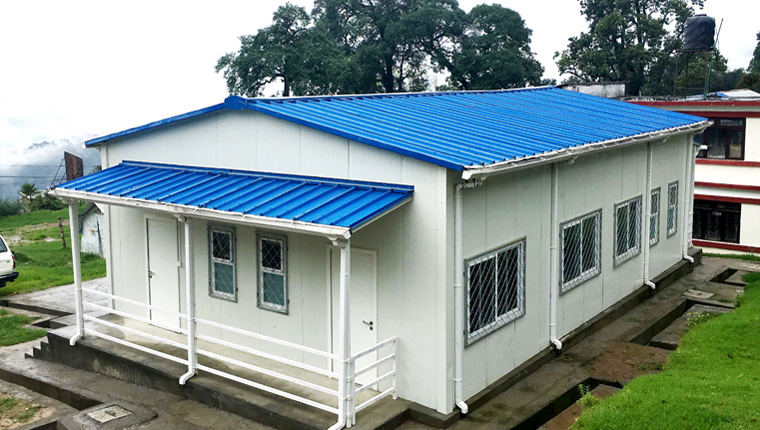
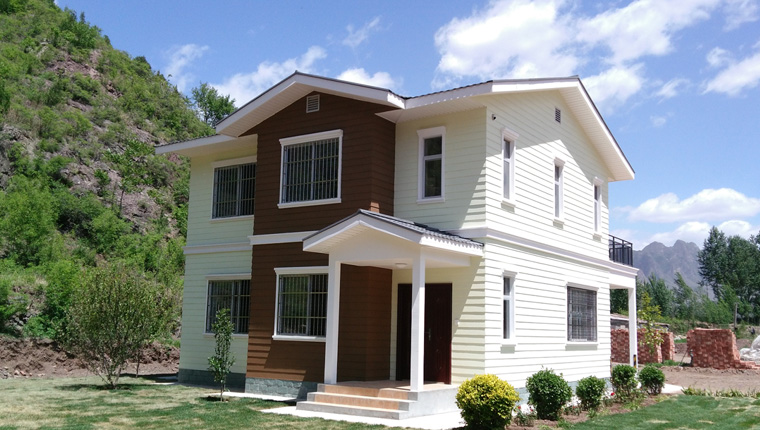
Light Steel Villas
Representing the high-end segment of modular housing, light steel villas serve as semi-permanent buildings with construction cycles dramatically shorter than traditional villas. They are customizable in design stage and perform exceptionally well across diverse climate regions, reducing on-site environmental pollution while maintaining architectural sophistication.
ZA Type Houses
ZA type houses feature cold-formed, hot-dip galvanized steel structures with patent-protected designs. These innovative products withstand Category 11 winds and, with special treatment, can endure Category 17 hurricanes. They offer flexible, customizable layouts suitable for dormitories, offices, restaurants, and recreational spaces, with excellent performance in high-temperature, high-cold, Gobi, and coastal environments.
The Modular Building Industry Landscape
Market Context and Growth Drivers
The global modular construction market is experiencing robust growth driven by multiple convergent factors:
Project Timeline Pressure: Major infrastructure, mining, energy, and construction projects demand rapid accommodation solutions for hundreds or thousands of workers. Traditional site-based construction cannot meet these timelines.
Labor Efficiency: Factory production of modular units reduces on-site labor requirements by up to 40% compared to traditional construction, partially offsetting global labor shortages.
Quality Assurance: Factory environments enable rigorous quality control, standardized manufacturing processes, and reduced defect rates compared to variable on-site conditions.
Sustainability: Modular construction generates significantly less waste, reduces site disturbance, and enables full recyclability and reusability when projects conclude.
Global Expansion: The Belt and Road Initiative, infrastructure development in emerging markets, and large-scale resource extraction projects drive demand for modular housing across Africa, Asia, Latin America, and beyond.
Industry Leaders and Market Positioning
The modular building industry includes specialized manufacturers serving different market segments:
International Scale Operators: Companies like Algeco Scotsman (the world's largest modular building producer) operate hundreds of offices and manage fleets exceeding 94,000 units globally. Their focus spans office space, portable classrooms, and storage solutions serving 24,000+ customers.
Specialized Engineering Camp Providers: Beijing Chengdong International Modular Housing Corporation exemplifies the specialist provider category, focusing exclusively on engineering camp construction and modular housing. With facilities across multiple Chinese provinces (Sichuan, Xinjiang, Wuhan, Shaanxi, Hainan, Hebei) and international operations spanning more than 100 countries, Chengdong represents the emerging class of Chinese manufacturers capturing global market share through specialization and project excellence.
Regional and Niche Providers: Companies including Triumph Modular, BOXX Modular, and Mobile Modular focus on North American markets with emphasis on temporary and permanent modular construction, portable classrooms, and custom solutions.
CDPH: A Case Study in Specialization
Beijing Chengdong International Modular Housing Corporation (CDPH) exemplifies how specialization drives market leadership. Founded in 1998, Chengdong has evolved from a domestic supplier to a global engineering camp expert, completing over 1,000 projects across 100+ countries.
Operational Infrastructure: Chengdong operates through a network of specialized subsidiaries—Chengdong Camp (Sichuan), Chengdong Camp (Xinjiang), Chengdong Integrated House (Wuhan), Shaanxi Heye Construction Engineering, CDPH (Hainan), Chengdong Integrated House Hebei, and the North China Storage and Transportation Center. This distributed manufacturing and logistics network enables rapid response to global project demands.
Manufacturing Capacity: With a container house annual production capacity of 40,000 units and manufacturing facilities strategically located across China, Chengdong maintains flexibility to serve projects across diverse geographic regions and climatic conditions.
Certifications and Standards: CDPH holds ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), OHSAS 18001 (Occupational Safety), CE certifications for steel structures (EN1090) and sandwich panels (EN14509), CSA Standard W47.1 for Canadian market manufacturing, and Chinese High-Tech Enterprise status. These certifications validate manufacturing quality and enable market access across regulated jurisdictions.
Key Technological Innovations
Modular Design and Standardization
Modern modular buildings employ fixed-dimension design parameters that enable flexible combination and customization. Standard container houses, for example, feature external dimensions of 6,055mm × 2,990mm × 2,896mm with interior net sizes of 5,845mm × 2,780mm × 2,500mm. This standardization allows unlimited horizontal combinations and up to three-layer vertical stacking while maintaining structural integrity.
Advanced Materials and Insulation
Thermal performance is critical for global deployment across diverse climates. Contemporary modular buildings incorporate:
Roof insulation: 100mm glass fiber wool rolls with thermal transfer coefficients (k-values) of 0.46-0.64 W/mK
Floor insulation: 100mm glass fiber wool with k-values of 0.46 W/mK, providing protection against ground heat loss
Wall systems: 75mm rock wool/glass wool composite boards (k-value: 0.47 W/mK) with optional 50-100mm configurations for extreme climate applications
For cold-resistant applications, advanced variants feature 150-190mm roof insulation and 160mm floor insulation, achieving k-values as low as 0.25 W/mK—critical for sub-zero environments ranging from -10°C to -50°C operational zones.
Structural Systems and Safety
Modern modular buildings employ hot-dip galvanized steel profiles providing multi-layer corrosion protection essential for diverse environmental conditions. Structural systems achieve:
Wind load capacity: 0.5-0.6 KN/m² standard configuration; enhanced systems withstand Category 11-17 winds through special reinforcement
Seismic performance: Interior column reinforcement with exterior floor-to-floor connections provides earthquake resistance
Connection methodology: Bolt connections throughout eliminate on-site welding, reducing installation time and enabling rapid disassembly without structural loss
Integrated Building Systems
The "Nine Systems" approach pioneered by companies like Chengdong represents sophisticated systems integration:
Building System: Core accommodation and functional structures
Water and Drainage System: Supply, treatment, and wastewater management
Electrical System: Power distribution, transformation, and backup generation
Low-voltage System: Telecommunications, data, and lighting networks
Fire Suppression System: Automatic sprinklers, alarms, and emergency protocols
Security System: Access control, surveillance, intrusion detection
Transportation Infrastructure: Road networks, parking, pedestrian pathways
Camp Environmental System: Landscaping, recreation, waste management
Environmental Protection System: Wastewater treatment and ecological preservation
This comprehensive approach ensures complete camp functionality without requiring external infrastructure.
Real-World Applications and Project Impact
Mining and Resource Extraction Camps
In global mining operations—from African copper mines to Canadian oil sands developments—modular buildings provide rapid accommodation for hundreds or thousands of workers in remote locations where traditional construction is impractical. A single large coal mining project might require dormitory-type engineering camps for 500+ miners, technicians, and managers. Modular buildings deliver fully-equipped dormitories with integrated furniture (beds, desks, chairs) and optional private bathrooms, enabling workers to maintain productivity through comfortable rest environments. One-time setup transforms raw camp sites into functional communities in 120 days—a timeline impossible with conventional construction.
Infrastructure and Transportation Projects
Railway electrification, highway expansion, and airport development projects spanning 2-5 years require sustained worker accommodation throughout extended construction phases. Modular buildings enable project management to establish permanent or semi-permanent communities supporting projects like Kenya's Mombasa-Nairobi Railway, enabling seamless workforce management without conventional site construction delays. These projects typically exceed 10,000-person camp populations, demonstrating scalability that justifies capital investment in modular infrastructure.
Educational and Commercial Applications
Schools requiring rapid expansion, such as Antilles Primary School in Curaçao, leverage modular construction for safety and aesthetic advantages. Improved yellow-structured container houses enhance visual appeal while meeting strict educational building codes—impossible to achieve through traditional temporary structures. Commercial applications span sports events, where modular design enables modular room separation or connection into viewing corridors meeting broadcasting and spectator requirements, through military assistance, where standard modular housing reduces from multiple units to single 20-foot containers, enabling rapid deployment and transport cost minimization.
Emergency and Humanitarian Response
Modular buildings demonstrate humanitarian value in disaster response contexts. China's 2018 provision of 1,000 modular houses to Myanmar's Rakhine State represented rapid humanitarian intervention enabling displaced persons' accommodation and dignified resettlement during refugee crises.
Comparative Advantages: Modular vs. Traditional Construction
| Factor | Modular Buildings | Traditional Construction |
| Construction Timeline | 60-120 days | 12-36 months |
| Weather Dependency | Minimal (factory-based) | High (site-dependent) |
| Labor Intensity | 40% reduction vs. traditional | Baseline |
| Quality Control | Standardized factory processes | Variable on-site conditions |
| Site Disruption | Minimal (integrated units) | Significant (material delivery, waste) |
| End-of-Life Recyclability | Complete disassembly and reuse | Partial or difficult demolition |
| Customization | Flexible within modular framework | Extensive but time-intensive |
| Transportation Cost | Optimized packing (5 units per 20' container) | Standard cargo handling |
Logistics and Supply Chain Excellence
Modular building deployment demands sophisticated logistics integration addressing challenges traditional construction never faces: international transportation, customs documentation, port handling, and integration across multiple supply chain partners.
Professional modular building providers employ specialized logistics expertise including:
Customs Classification: Class A customs rating enabling priority declaration, inspection, and processing (critical advantage held by established manufacturers)
Regional Expertise: Deep understanding of commercial regulations in target markets (Chile, Argentina, Southeast Asia, Africa) enabling rapid clearance
Maritime Transportation: Partnerships with multiple shipping lines optimizing container utilization and transit timing
Last-Mile Coordination: Integration with local transportation networks in destination countries, ensuring delivery to often-remote project sites
Documentation Management: Expert handling of certificates of origin, quality certifications, and regulatory compliance documentation required for international trade
Efficient logistics reduce project delivery timelines by 4-8 weeks compared to inefficient providers, directly improving project economics.
Sustainability and Environmental Performance
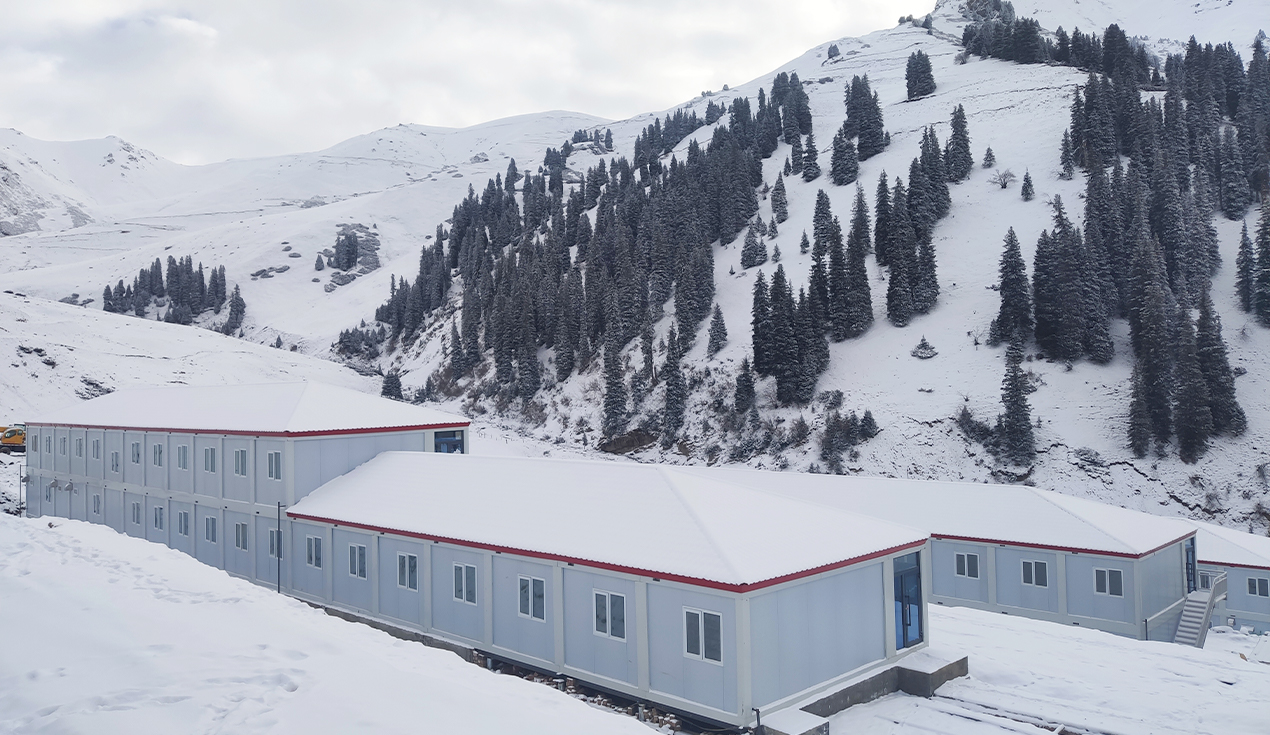

Modular building construction delivers measurable environmental advantages:
Waste Reduction: Factory production generates 75-90% less construction waste than site-based building, with remaining waste managed through established recycling streams.
Transportation Efficiency: Optimized container packing (five modular houses per standard 20-foot container) reduces per-unit transportation carbon footprint by 40-60% compared to partial or standard shipments.
Reusability: Upon project completion, modular units can be disassembled without loss and relocated to new projects, extending product lifecycle 20-30 years and amortizing manufacturing environmental cost across multiple applications.
Thermal Performance: Advanced insulation systems (k-values of 0.25-0.64 W/mK) reduce operational energy consumption 30-40% compared to traditional structures, delivering cost savings over multi-year deployment periods.
Integrated Environmental Systems: Wastewater treatment, recycled water systems, and ecological landscaping design ensure modular camps achieve near-zero environmental impact, critical for projects in sensitive environments (coastal zones, protected forests, archaeological sites).
The Future of Modular Construction
The modular building industry is advancing toward:
Digitalization and BIM Integration: Computer-aided design tools enabling real-time project visualization, supply chain tracking, and predictive maintenance scheduling.
Sustainable Materials: Development of bio-based insulation materials, recycled steel components, and low-carbon manufacturing processes addressing climate change imperatives.
Automation and Robotics: Factory automation increasing manufacturing efficiency, reducing labor costs, and enabling economies of scale at lower production volumes.
Smart Building Integration: IoT sensors for environmental monitoring, occupancy detection, and predictive maintenance enabling data-driven camp management.
Distributed Manufacturing: Regional production facilities in key markets (Africa, Southeast Asia, Latin America) reducing international transportation and enabling faster response to local project demand.
Selecting a Modular Building Provider
Organizations evaluating modular building partnerships should assess:
Track Record: Completed projects in target regions, client references, and demonstrated expertise in similar project types
Manufacturing Certifications: ISO 9001, ISO 14001, regional certifications (CE, CSA, etc.) validating quality and standards compliance
Logistics Capability: In-house customs expertise, regional transportation partnerships, and supply chain resilience
Customization Flexibility: Ability to modify standard designs for specific project requirements without extended timelines
After-Sales Support: Warranty coverage, maintenance services, and technical support during multi-year project deployment
Sustainability Credentials: Environmental certifications, waste minimization practices, and circular economy approaches
Conclusion
Modular building companies have fundamentally transformed how organizations support global projects. By combining factory precision, streamlined logistics, environmental responsibility, and operational flexibility, modular buildings deliver superior value compared to traditional construction approaches. Whether supporting mining operations across three continents, enabling infrastructure development in emerging markets, or responding to humanitarian emergencies, modular builders stand as essential partners enabling modern project execution.
The evolution from niche solution to industry standard reflects underlying economic and operational realities: modular construction delivers faster timelines, superior quality, lower costs, and environmental benefits that traditional methods cannot match. As projects grow more complex, timelines tighten, and sustainability becomes non-negotiable, modular building companies will continue expanding their market share and technological sophistication.
For organizations managing large-scale, time-sensitive projects across global markets, partnering with established, certified modular building providers represents the strategic choice delivering measurable competitive advantage. The future of construction—temporary and permanent, local and global, industrial and humanitarian—belongs to modular building innovators transforming how humanity builds.
About CDPH
Beijing Chengdong International Modular Housing Corporation (CDPH) represents a leading example of modular construction excellence. With over two decades of specialized experience, CDPH operates manufacturing facilities across China, maintains a global project footprint spanning more than 100 countries, and holds certifications validating quality and regulatory compliance across international markets. The company specializes in engineering camp design, planning, construction, and operation for large-scale infrastructure, mining, and resource extraction projects worldwide.
For more information about modular building solutions and engineering camp expertise, visit: https://www.cdph.net/



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More



























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





