Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of the construction industry, modular construction has emerged as a transformative approach. But what exactly does modular construction mean? This article aims to demystify the concept, exploring its definition, components, and the far - reaching implications it holds for the future of building.
Defining Modular Construction
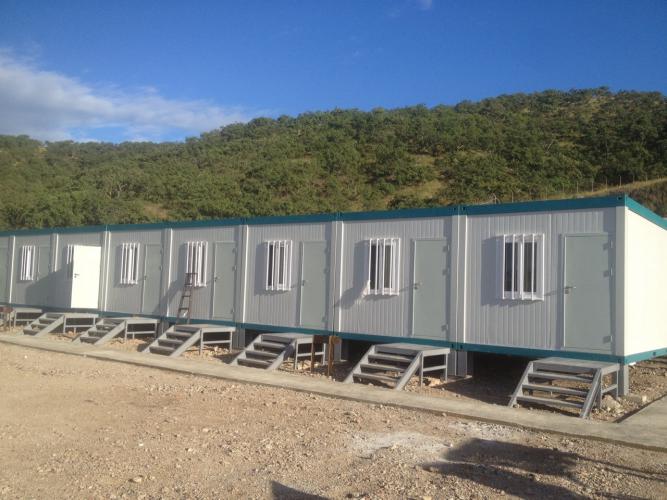
Modular construction refers to the process of building structures by assembling pre - fabricated modules. These modules are sections of a building that are manufactured off - site, typically in a factory environment. Once fabricated, they are transported to the building site and joined together to create the final structure. It's a departure from traditional on - site construction methods, where most of the building work is carried out directly at the location where the structure will stand.
Key Components of Modular Construction
Prefabricated Modules
Manufacturing Process
Prefabricated modules are the heart of modular construction. They are built in a factory using a combination of automated and manual processes. The factory environment allows for precise control over the manufacturing process, ensuring consistent quality. For example, in a modular house factory, the walls, floors, and ceilings of each module are constructed with high - precision cutting and joining techniques. The use of advanced machinery enables accurate measurements, resulting in components that fit together seamlessly.
Levels of Completion
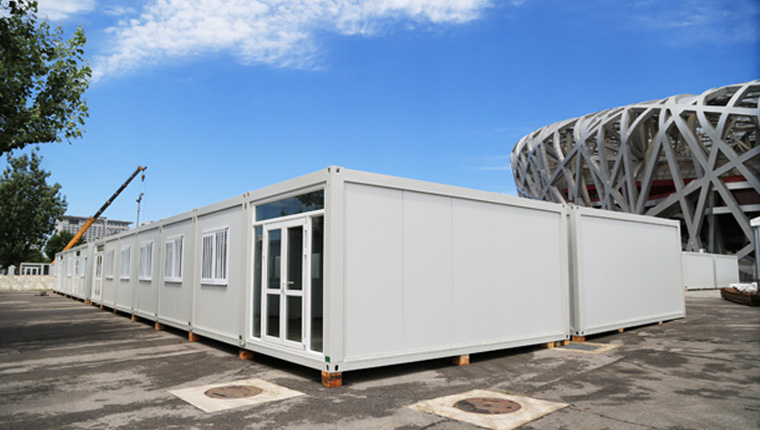
Modules can be manufactured to different levels of completion. Some may be "shell - only" modules, consisting of just the basic structural framework, including the outer walls, floor, and roof. Others can be fully - finished modules, equipped with interior finishes, plumbing, electrical systems, and even furniture. For instance, in the case of modular office buildings, a fully - finished module might come with pre - installed desks, cubicles, and lighting fixtures, ready for immediate occupancy upon assembly.
Transportation and Assembly
Transportation Considerations
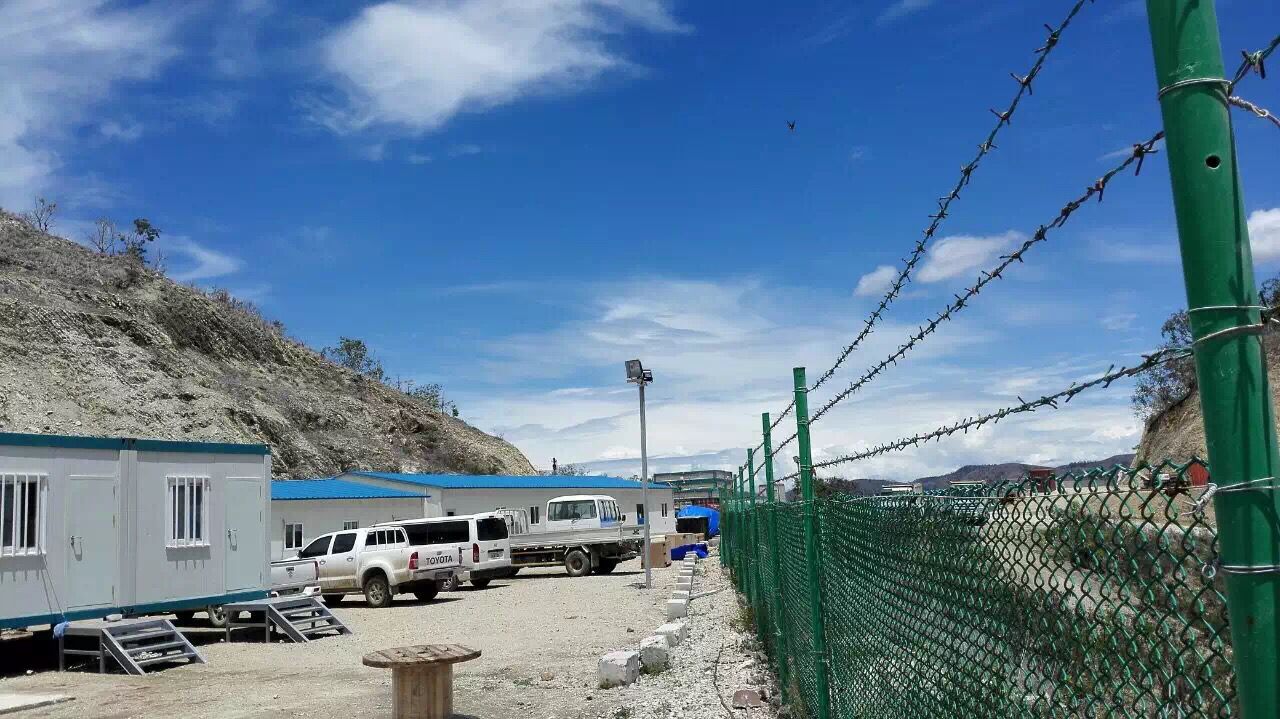
Once the modules are manufactured, they need to be transported to the building site. This requires careful planning, as the size and weight of the modules can be significant. Specialized transport vehicles are often used to ensure safe and efficient transportation. For large - scale modular projects, such as multi - story apartment buildings, the modules may need to be carefully routed to avoid low - hanging bridges, narrow roads, or weight - restricted routes. Additionally, proper securing of the modules during transit is crucial to prevent damage.
On - site Assembly
On - site assembly is a crucial stage in modular construction. The modules are typically lifted into place using cranes or other heavy - lifting equipment. Once in position, they are joined together using various connection methods, such as bolts, welding, or specialized connectors. The assembly process is relatively quick compared to traditional construction, as the modules are designed to fit together easily. For example, a modular hotel can be assembled in a matter of weeks, with the modules being rapidly connected to form the complete building structure.
Advantages of Modular Construction
Speed of Construction
Parallel Processes
One of the most significant advantages of modular construction is the ability to carry out multiple processes simultaneously. While the modules are being manufactured in the factory, site - preparation work can be taking place at the building location. This includes tasks such as land clearing, foundation pouring, and utility connections. This parallel approach significantly reduces the overall construction time. For example, a traditional building project might take 12 months to complete, while a modular construction of the same size and complexity could be finished in as little as 6 months.
Efficient Assembly
The pre - fabricated nature of the modules allows for efficient on - site assembly. Since the modules are pre - built and designed to fit together precisely, the time required for construction on - site is minimized. There is less time spent on tasks such as framing, plumbing rough - ins, and electrical wiring, as these are often completed in the factory. This speed is particularly beneficial for projects with tight deadlines, such as emergency housing or commercial developments that need to open for business quickly.
Quality Control
Factory - Controlled Environment
The factory environment in modular construction provides a high level of quality control. In a factory, the manufacturing process is subject to strict quality standards and inspections at every stage. Workers are trained to follow standardized procedures, ensuring that each module meets the required specifications. For example, in a modular bathroom factory, every unit can be tested for leaks and proper functionality before it is shipped to the site. This level of quality control is often more difficult to achieve in traditional on - site construction, where weather, worker availability, and other factors can affect the quality of the work.
Reduced Defects
The combination of precise manufacturing and quality control measures in modular construction results in fewer defects. Since the modules are built in a controlled environment, issues such as uneven walls, leaky roofs, or electrical problems are less likely to occur. This not only improves the overall quality of the building but also reduces the need for costly repairs and rework after the building is completed.
Cost - Effectiveness
Economies of Scale
Modular construction often benefits from economies of scale. Factories can purchase materials in bulk, resulting in lower costs per unit. Additionally, the standardized manufacturing process allows for greater efficiency, reducing labor costs. For example, a modular house manufacturer can buy lumber at a discounted rate because of the large quantities they purchase. The streamlined production process also means that fewer workers are needed to produce each module, further reducing labor expenses.
Predictable Costs
The nature of modular construction makes cost prediction more accurate. Since the manufacturing process is standardized, there are fewer unexpected expenses compared to traditional construction. For instance, weather - related delays, which can add significant costs to a traditional project, are minimized in modular construction. Owners and project managers can get a more precise estimate of the total cost upfront, making it easier to plan and budget for the project.
Applications of Modular Construction
Residential Construction
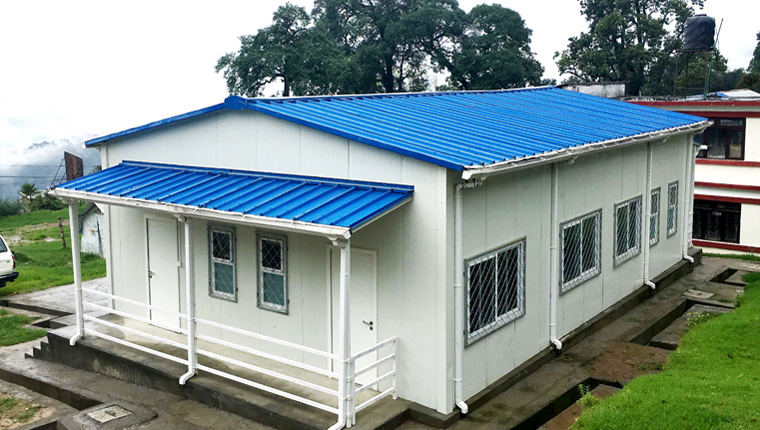
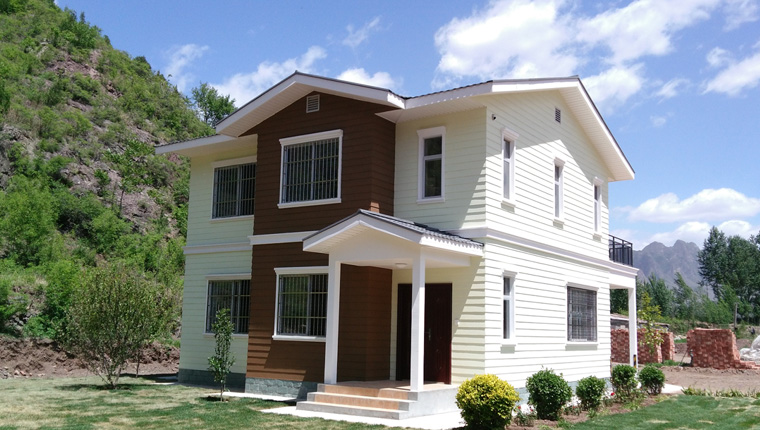
Modular construction is increasingly popular for building single - family houses. Buyers can choose from a variety of pre - designed modular house plans or work with manufacturers to customize a design. Modular houses offer the advantage of quick construction, allowing families to move into their new houses faster. They also provide a high level of quality and energy efficiency, with many modular house manufacturers using advanced insulation and energy - efficient appliances.
In the multi - family housing sector, modular construction is being used to build apartment buildings, condominiums, and townhouses. The speed of construction is a major advantage, as it allows developers to bring projects to market more quickly. Modular multi - family housing can also be designed to meet high - density living requirements, with well - planned layouts and shared amenities. For example, a modular apartment complex can be built with a central courtyard, fitness center, and parking facilities.
Commercial Construction
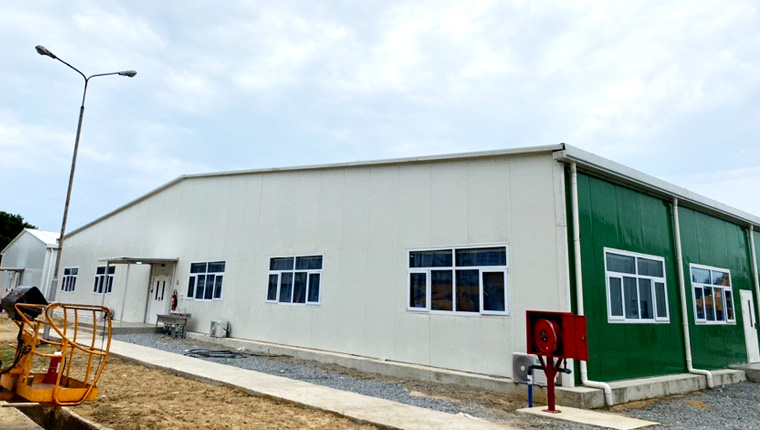
Modular construction is well - suited for office buildings. It offers the flexibility to create open - plan or partitioned office spaces, depending on the needs of the business. The quick construction time means that companies can start operating in their new offices sooner. Additionally, modular office buildings can be designed with modern, energy - efficient features, such as large windows for natural light and advanced ventilation systems.
In the retail and hospitality industries, modular construction is being used to build stores, restaurants, hotels, and resorts. The ability to customize the design and the speed of construction are key advantages. For example, a chain of restaurants can use modular construction to quickly open new locations with a consistent brand image. Modular hotels can be built in popular tourist destinations in a relatively short time, meeting the high demand for accommodation.
Challenges and Considerations in Modular Construction
Transportation and Logistics
Size and Weight Limitations
The size and weight of modular components can pose challenges in transportation. There are legal restrictions on the dimensions and weight of vehicles on public roads. This may require special permits or the use of oversized transport vehicles. In some cases, modules may need to be designed in a way that they can be disassembled into smaller, more transport - friendly sections. For example, a large modular building module may need to be split into two parts for transportation and then reassembled on - site.
Delivery Scheduling
Coordinating the delivery of modules to the building site is crucial. Delays in transportation can disrupt the on - site assembly process, leading to additional costs. It's important to work with reliable transportation partners and have a detailed delivery schedule. Additionally, the building site needs to be prepared to receive the modules on time, with proper storage and handling facilities in place.
Regulatory and Design Constraints
Building Codes and Standards
Modular construction must comply with local building codes and standards. While many regions are adapting their codes to accommodate modular construction, there may still be some areas where the regulations are not fully developed. This can require extra effort from manufacturers and builders to ensure compliance. For example, some building codes may have specific requirements for the connection of modular components, which need to be carefully addressed.
Design Compatibility
When using modular construction, the design of the building needs to be carefully planned to ensure compatibility between the modules. The modules must fit together seamlessly, and the overall design should meet the aesthetic and functional requirements of the project. This may require close collaboration between architects, engineers, and modular manufacturers to create a cohesive design.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is modular construction more expensive than traditional construction?
In many cases, modular construction can be cost - effective. The economies of scale, reduced labor costs, and predictable cost structure often make it a more affordable option. However, the cost can vary depending on factors such as the level of customization, the location of the project, and the complexity of the design. In some situations, highly customized modular projects may be more expensive, but overall, modular construction can offer significant cost savings.
How durable are modular buildings?
Modular buildings are generally very durable. The factory - controlled manufacturing process ensures high - quality construction. The use of strong materials and proper connection techniques makes modular buildings capable of withstanding various environmental conditions. They are often built to the same or higher standards as traditional buildings, providing long - term durability and structural integrity.
Can modular construction be used for large - scale, complex projects?
Yes, modular construction can be used for large - scale and complex projects. In fact, many large - scale commercial and residential developments, such as high - rise apartment buildings and multi - story office complexes, are being built using modular construction techniques. The key is to have a well - planned design, efficient manufacturing process, and proper on - site assembly procedures to ensure the success of the project.
Conclusion
Modular construction represents a significant shift in the way we build structures. With its numerous advantages in terms of speed, quality, and cost - effectiveness, it has the potential to revolutionize the construction industry. However, like any construction method, it also comes with its own set of challenges that need to be carefully addressed. As technology and regulations continue to evolve, modular construction is likely to become an even more prominent and widely - adopted approach in the future of building.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More
























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





