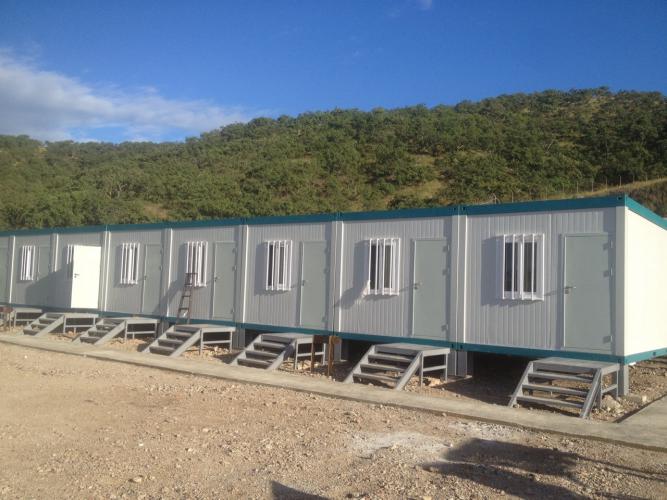
Modular construction is rapidly reshaping the global building industry, offering fast, high-quality, cost-effective, and environmentally responsible alternatives to traditional methods. By shifting much of the construction process into a controlled factory environment, this innovative approach delivers superior projects on accelerated timelines.
What Is Modular Construction?

What is a modular construction? It is a process where a building is broken down into individual, complete units—or "modules"—such as rooms, corridors, or equipment spaces, which are prefabricated in a factory. Unlike traditional building, where all work happens on-site, a significant portion of the structural, electrical, plumbing, and finishing work is completed in a controlled workshop. These finished modules are then transported to the building site, connected, sealed, and commissioned to form the final, complete structure.
Think of it as adult-sized LEGO: expertly crafted pieces are manufactured off-site and then simply snapped together on location to create a complete structure .
Core Advantages: Speed, Quality, and Value
Modular methods offer four primary benefits that drive their adoption:
Rapid Delivery: Factory prefabrication and on-site foundation work happen simultaneously. This parallel process typically cuts overall construction time by 30–50%. For example, a project that might take over six months traditionally could be completed in just 120 days using modular construction.
Superior Quality: The controlled factory environment eliminates major site variables like adverse weather, moisture issues, and inconsistent labor. This leads to higher precision, ensuring watertight walls, level floors, and perfectly aligned piping, which significantly reduces defects and costly rework.
Cost Efficiency: Standardization and bulk production lead to savings in labor and a dramatic reduction in material waste. Furthermore, quick transport and installation, combined with minimal on-site debris, lower cleanup and finishing costs.
Flexibility & Sustainability: Modules can be configured in countless ways to suit homes, apartments, schools, hospitals, or temporary camps. The sustainability advantage is key: at the end of a project's life, modules can often be disassembled and reused, directly supporting circular economy goals.
Applications and Expertise
What is a modular construction used for? Its speed and flexibility make it ideal for a diverse range of projects:
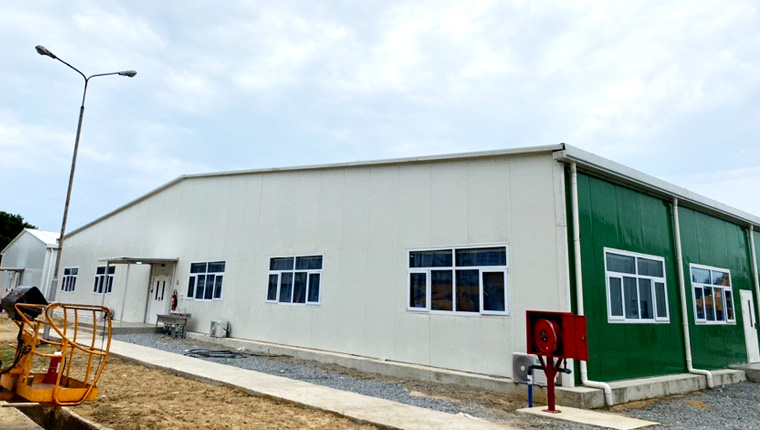
Remote Camps & Emergency Facilities: Quickly providing housing, offices, and clinics for remote operations like oil fields, mines (e.g., El Teniente copper mine project), and rail lines, accelerating project startups.
Education & Healthcare: Allowing for the rapid expansion of classrooms, labs, or community clinics, often delivered between semesters or in response to health emergencies without disrupting existing services.
Residential & Commercial: Standardized production is highly efficient for large-scale apartment buildings, hotels, and resorts, while still allowing for customization of exterior finishes and interior décor.
Case Study: Chengdong Modular Construction
Chengdong Modular Construction exemplifies industry best practices, operating state-of-the-art facilities that deliver high-precision steel frames, insulated panels, and fully integrated MEP systems. Their expertise is proven globally, adapting modules for harsh environments and navigating complex local building codes. Projects like Chile's first Flatpack modular exhibition hall and a 1,700-bed mining camp demonstrate their ability to provide turnkey logistics and rapid, reliable solutions.
The Five-Step Modular Implementation Process
Implementing a modular project is a systematic, phased approach:
Requirements & Design: Define functional zones, layout, and develop detailed floor plans and elevations for each module.
Factory Prefabrication: The actual construction—assembling the steel frames, wall panels, ceilings, plumbing, and finishes—occurs entirely within the controlled workshop.
Foundation Works: In parallel with factory work, site foundations, footings, and utility connections are prepared on-location. What is a modular construction's key time-saver? This simultaneous work!
Transportation & Assembly: Modules are transported (by road or sea), lifted by cranes, and joined on-site. Seams are sealed, and the structure is secured.
Commissioning & Handover: All systems (electrical, plumbing, HVAC) are tested, a final quality inspection is performed, and the completed building is handed over to the client.
Key Best Practices for Success
To maximize the benefits of modular building, consider these best practices:
Select a Proven Manufacturer: Rigorously evaluate a manufacturer's factory capacity, production expertise, quality management systems, and track record.
Develop a Total-Cost Model: Look beyond the initial unit price. Include prefabrication, transport, installation, and lifecycle maintenance costs for a true apples-to-apples comparison with traditional construction.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Verify that all designs (structural, seismic, fire-safety, energy-efficiency) meet local building codes before manufacturing begins.
Plan Site Logistics Carefully: Coordinate site access, crane positioning, and module delivery sequence to prevent costly on-site bottlenecks.
Design for Future Expansion: Incorporate connection points and utility reserves into the initial design to allow for easy module addition or interior reconfiguration later.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
| Question | Answer |
| 1. Is modular construction the same as a manufactured or mobile home? | No. What is a modular construction is distinct from manufactured or mobile homes. Modular buildings are constructed to the same International Building Codes (IBC) or local state codes as traditional, site-built properties. They are placed on permanent foundations and are treated as real property for financing, insurance, and resale. Manufactured homes (sometimes called mobile homes) are built to a different federal standard (HUD code) and are built on a non-removable steel chassis. |
| 2. Are there any disadvantages or limitations to modular construction? | The primary challenges include: Transportation Costs & Risk for the modules, which can be expensive and logistically complex; Front-Loaded Design, requiring most design decisions to be finalized before fabrication begins (changes are difficult once production starts); and potentially Complex Approval Processes, as some local jurisdictions may have less familiarity with modular methods than traditional ones. |
| 3. How are modular construction projects typically financed? | Financing for modular construction is generally similar to financing a traditional custom-built home. For new construction, this involves a Construction Loan which covers the costs of factory production and site work. Once the building is complete and set on its permanent foundation, the construction loan is typically converted into a standard Permanent Mortgage (like a conventional, FHA, or VA loan). Lenders familiar with the modular process are key. |
| 4. How durable and strong are modular buildings compared to site-built structures? | Modular buildings are often structurally superior to their site-built counterparts. They are designed and engineered to withstand the rigorous forces of transportation, being lifted by cranes, and set onto the foundation. This requires extra bracing, gluing, and structural reinforcement, resulting in a building that is highly durable, better sealed, and often exhibits better seismic and wind-load performance. |
Modular construction merges factory-level efficiency with on-site building flexibility, delivering fast timelines, consistent quality, and sustainable reuse. Whether for remote camps, emergency clinics, schools, apartments, or hotels, it offers a transformative solution for today’s construction challenges—and stands at the forefront of the industry’s future.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More

























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





