Introduction
In an era where efficiency, cost - effectiveness, and sustainability are highly prized in the construction industry, prefabricated housing has emerged as a popular solution. But what exactly constitutes prefabricated housing? This article will delve into the details, exploring its definition, types, benefits, and considerations.
Defining Prefabricated Housing
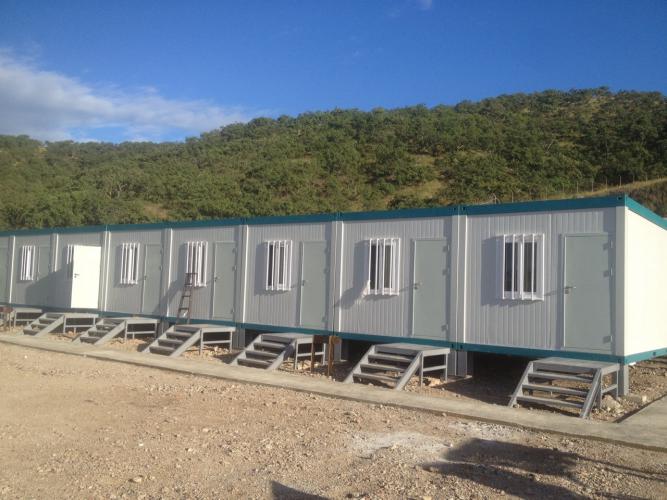
Prefabricated housing refers to houses that are constructed off - site, in a factory or a manufacturing facility, and then transported to the building location for final assembly. Unlike traditional on - site construction, where the house is built piece - by - piece at the actual building site, prefabricated housing components are manufactured in a controlled environment. These components can range from individual wall panels, floor sections, and roof trusses to entire modules that are nearly complete living units.
Types of Prefabricated Housing
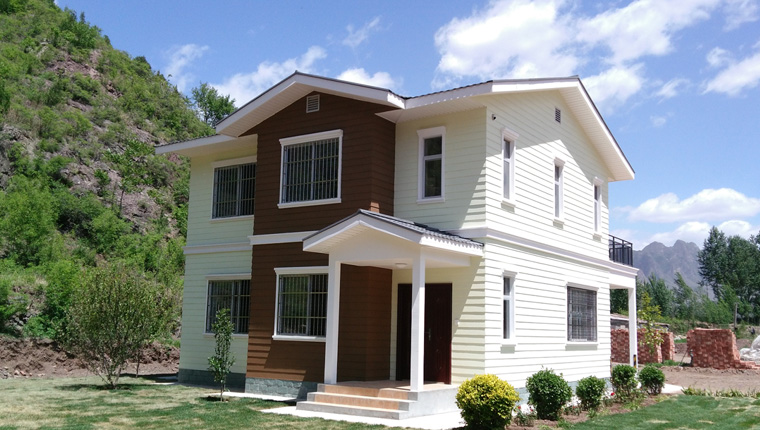
Panelized Houses
Manufacturing Process
Panelized houses are built by manufacturing individual wall, floor, and roof panels in a factory. These panels are cut, assembled, and sometimes pre - finished in the factory. For example, wall panels may have the studs, sheathing, insulation, and even the interior drywall and exterior siding already installed. The panels are then numbered and transported to the building site, where they are lifted into place and joined together using bolts, nails, or other fastening methods.
Advantages
Panelized houses offer a relatively high level of customization. Since each panel is fabricated separately, it's easier to adjust the design to fit specific site requirements or owner preferences. They also allow for a quicker construction process compared to traditional houses, as the panels can be assembled on - site more rapidly. Additionally, the factory - controlled environment ensures consistent quality in the manufacturing of each panel.
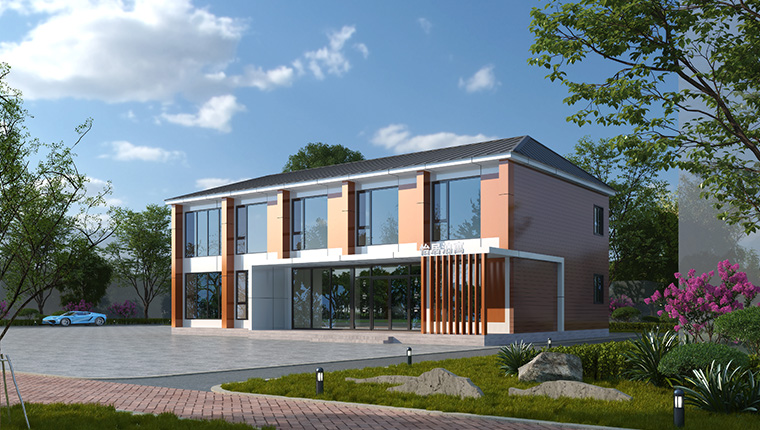
Manufacturing Process
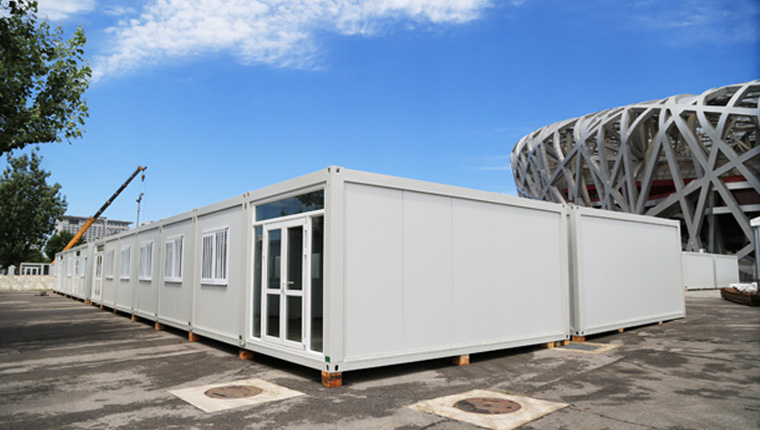
Modular houses are constructed in larger, self - contained modules in a factory. These modules can be entire rooms or sections of the house, such as a complete kitchen - living room combination or a bedroom - bathroom unit. The modules are fully or partially finished in the factory, including plumbing, electrical wiring, and interior finishes. Once transported to the site, the modules are placed on a pre - prepared foundation and connected to form the complete house. Cranes are often used to lift and position the modules accurately.
Advantages
Modular houses are known for their speed of construction. Since a significant portion of the house is already built in the factory, the on - site assembly time is greatly reduced. They also offer a high level of quality control, as the manufacturing process is closely monitored in the factory. Moreover, modular houses can be designed to meet a wide range of architectural styles, from modern and contemporary to traditional and rustic.
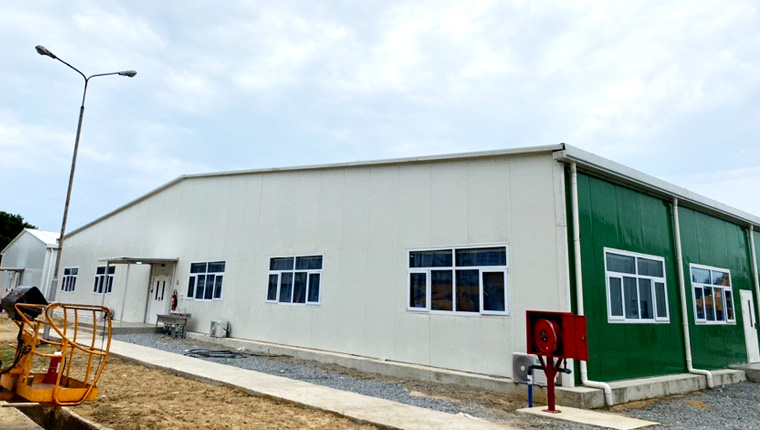
Manufactured Houses
Manufacturing Process
Manufactured houses, also known as mobile houses in some regions, are built entirely in a factory on a permanent chassis. They are designed to be transported to the site on their own wheels and then set in place. These houses are often mass - produced and come in a variety of standard floor plans. The manufacturing process involves building the entire house structure, including the frame, walls, roof, and interior finishes, within the factory.
Advantages
Manufactured houses are highly cost - effective. Their mass - production nature allows for economies of scale, reducing the overall cost. They are also relatively quick to install on - site, as they are essentially a complete unit that only needs to be connected to utilities. Manufactured houses are a popular option for those looking for affordable housing, such as first - time buyers or retirees on a budget.
Benefits of Prefabricated Housing
Cost - Efficiency
Economies of Scale
Factory - based production of prefabricated housing enables economies of scale. Manufacturers can purchase materials in bulk, resulting in lower costs per unit. For example, a prefabricated house factory can buy lumber, drywall, and plumbing fixtures at a discounted rate due to the large quantities they order. This cost savings is often passed on to the consumer, making prefabricated housing an attractive option for budget - conscious individuals.
Reduced Labor Costs
The construction process of prefabricated housing is more efficient, which leads to reduced labor costs. In a factory, workers can specialize in specific tasks, increasing productivity. Additionally, the on - site assembly of prefabricated components is quicker, requiring fewer man - hours compared to traditional construction. This not only saves on labor expenses but also reduces the overall cost of the project.
Quality Control
Controlled Environment
The factory environment provides a high level of quality control. The manufacturing process is carried out under consistent conditions, free from weather - related disruptions. This allows for strict adherence to quality standards. For instance, in a prefabricated housing factory, the installation of insulation can be carefully monitored to ensure proper coverage and R - value, something that may be more difficult to achieve on a traditional construction site.
Standardized Processes
Prefabricated housing manufacturers follow standardized production processes. This means that each component or module is built to the same high - quality specifications. The use of modern manufacturing techniques and machinery ensures precision in cutting, joining, and finishing. As a result, prefabricated houses often have fewer defects and a more consistent level of quality compared to traditionally built houses.
Speed of Construction
Parallel Processes
One of the significant advantages of prefabricated housing is the ability to carry out parallel processes. While the components are being manufactured in the factory, site - preparation work, such as land clearing, foundation pouring, and utility connections, can be taking place at the building site. This parallel approach significantly reduces the overall construction time. For example, a prefabricated house that might take several months to build traditionally could be completed in a matter of weeks.
Quick Assembly
The pre - fabricated components of prefabricated housing are designed for easy and quick assembly. The panels or modules fit together like pieces of a puzzle, with pre - drilled holes and pre - cut joints. This simplifies the on - site construction process, allowing for a faster completion of the house. For a panelized house, the wall panels can be erected in a relatively short time, followed by the installation of the roof and interior finishes.
Considerations for Prefabricated Housing
Site - Specific Requirements
Foundation Compatibility
Prefabricated housing has specific foundation requirements. The type of foundation needed depends on the type of prefabricated house. For example, modular houses may require a more substantial foundation, such as a slab or a basement foundation, while manufactured houses can be placed on a simpler foundation or even a gravel pad. It's essential to have the building site evaluated by a professional to determine the appropriate foundation type to ensure the stability of the house.
Accessibility
The location of the building site should be accessible for the transportation of prefabricated components. Narrow roads, low - hanging power lines, or difficult - to - navigate terrain can pose challenges. In some cases, special permits may be required to transport large modular units. owners need to consider these factors when choosing a building site for their prefabricated house.
Design Limitations
Standardization vs. Customization
While prefabricated housing offers some level of customization, it may have more design limitations compared to traditional construction. Some prefabricated house manufacturers offer a range of standard floor plans and design options, but significant departures from these standards may be more difficult or costly to achieve. For example, if a owner wants a highly unique architectural feature, such as a circular room or a very large, open - span living area, it may not be easily incorporated into a prefabricated house design.
Aesthetic Constraints
In some cases, prefabricated housing may be associated with certain aesthetic styles due to the manufacturing process. For example, manufactured houses may have a more uniform or "cookie - cutter" appearance. However, this is changing as manufacturers are increasingly offering more diverse aesthetic options, including different exterior finishes, roof styles, and interior design choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are prefabricated houses as durable as traditionally built houses?
Yes, prefabricated houses can be as durable as traditionally built houses. The factory - controlled manufacturing process often results in high - quality construction. The use of modern building materials and techniques, along with strict quality control measures, ensures that prefabricated houses are built to last. However, like any house, proper maintenance is essential to ensure long - term durability.
How energy - efficient are prefabricated houses?
Many prefabricated houses are designed to be energy - efficient. The factory - controlled manufacturing process allows for better insulation installation, air - sealing, and the use of energy - efficient appliances and fixtures. Additionally, some prefabricated house manufacturers incorporate sustainable building practices, such as the use of solar - ready designs or energy - efficient lighting systems. However, the energy efficiency of a prefabricated house can also depend on the specific design and features chosen by the owner.
Conclusion
Prefabricated housing offers a viable and attractive alternative to traditional house building. With its cost - efficiency, high - quality construction, and speed of completion, it has the potential to meet the housing needs of a wide range of individuals. However, it's important to carefully consider the site - specific requirements, design limitations, and other factors before choosing prefabricated housing. By doing so, owners can make an informed decision and enjoy the many benefits that prefabricated housing has to offer.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More
























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





