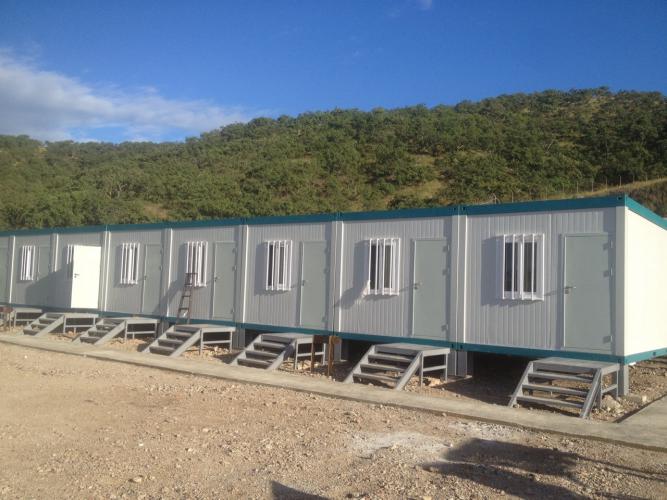
Introduction: The Evolution of Emergency Shelter Infrastructure
When disaster strikes—whether an earthquake, hurricane, pandemic, or armed conflict—the immediate challenge isn't reconstruction. It's survival. Governments, NGOs, international relief organizations, and emergency management agencies face a critical window of hours and days to provide shelter, medical care, water systems, and operational command centers for displaced populations and response teams.
For decades, the answer came in the form of canvas tents, temporary wooden shelters, and basic plywood structures. While functional in the short term, these solutions proved inadequate for extended emergencies: they deteriorated rapidly in harsh weather, offered minimal protection against disease transmission, and required constant maintenance and replacement.
The landscape of emergency relief has fundamentally transformed with the emergence of foldable and modular emergency container housing—a category of rapidly deployable structures engineered to bridge the gap between immediate crisis response and longer-term reconstruction. Unlike their predecessors, next-generation container housing systems combine industrial-grade engineering with unprecedented deployment speed, creating shelter and infrastructure that can be operational within hours, not weeks.
This article examines how foldable and modular container systems are redefining emergency housing standards globally, the technologies driving their effectiveness, and their expanding role across disaster relief, public health emergencies, and humanitarian crises.
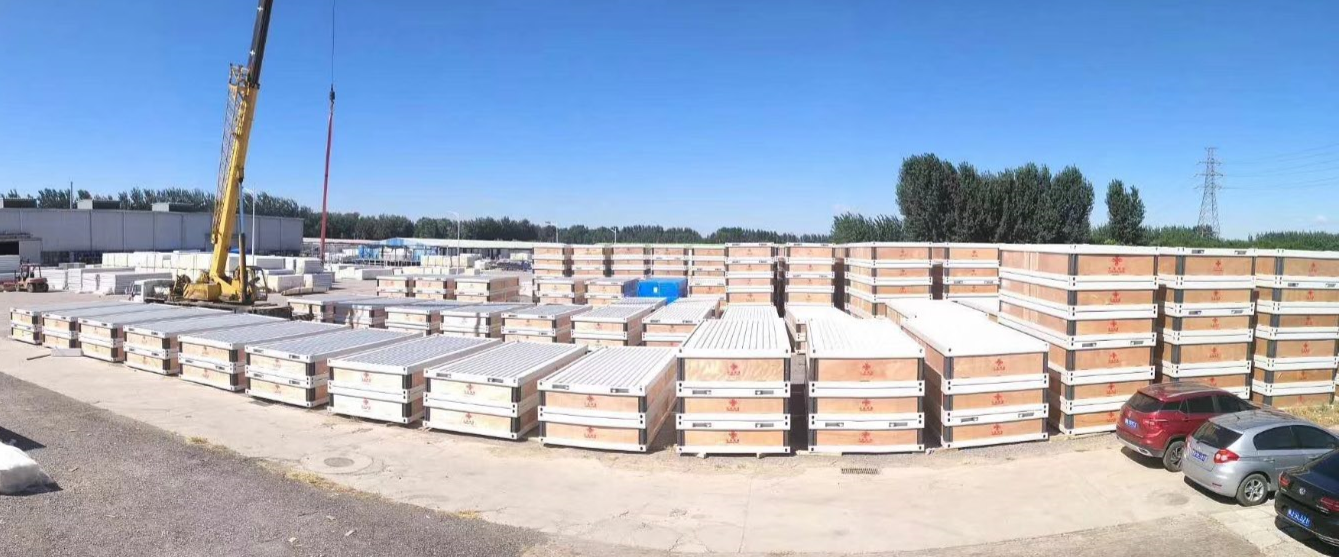

What Is Foldable & Modular Emergency Container Housing?
At its core, emergency container housing refers to prefabricated modular units constructed from steel frames and insulated panels, designed for rapid transport and assembly in crisis environments. The distinction between traditional container structures and next-generation foldable and modular systems lies in their engineering approach and deployment capability.
Core Technology: How Foldable Container Systems Work
Foldable emergency container housing employs a mechanically engineered system of hinged steel components that allow structures to compress into a compact transit configuration, then expand into fully functional living or working spaces within minutes to hours.
Key mechanical features include:
High-strength steel frameworks that provide structural integrity while maintaining lightweight transportability
Precision-engineered hinge systems enabling repeated fold-and-unfold cycles without deformation or structural compromise
Interlocking panel architecture that maximizes interior space expansion while minimizing external footprint during transit
Integrated utility conduits for electrical, water, HVAC, and ventilation systems installed during factory production
Weather-sealed roofing with waterproof membranes and drainage channels suitable for tropical, monsoon, or desert environments
High-density thermal insulation supporting comfortable use across temperature extremes—from arctic conditions to extreme heat
This engineering approach delivers what traditional shipping containers cannot: immediate usability without the need for cranes, heavy equipment, extensive skilled labor, or complex assembly protocols.
Modular Architecture: Building Systems, Not Isolated Units
While foldable mechanisms provide deployment speed, modularity enables scalability. Modern emergency container housing systems are designed as components within larger integrated camp ecosystems. A single relief operation might combine:
Foldable units for rapid command centers, medical triage areas, and administrative offices
Flat-pack modular residential units for worker accommodation and displaced-population housing
Box-type structures for longer-term community facilities
Steel framework systems for shared infrastructure (dining halls, sanitation blocks, water treatment facilities)
Equipment modules for generators, water storage, and logistics hubs
This integrated approach transforms isolated containers into functioning relief camps—complete with infrastructure, zoning, utilities, and operational protocols.
Why Speed Matters: The Emergency Response Timeline
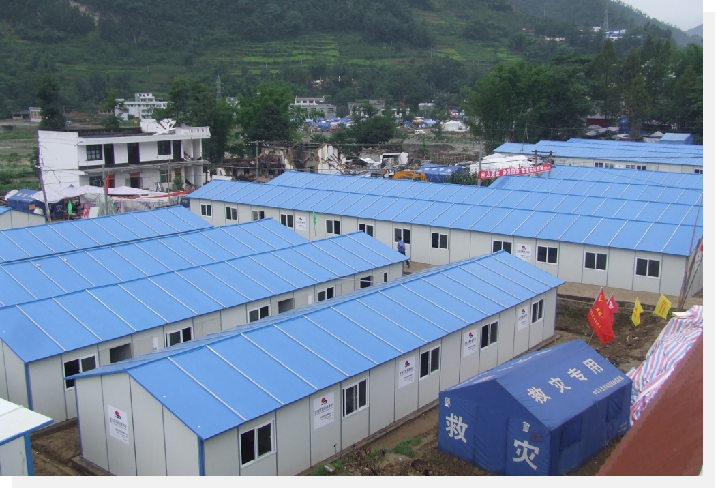

In disaster zones, every hour counts. Studies of post-disaster outcomes consistently demonstrate that mortality, disease transmission, and psychological trauma accelerate rapidly if populations remain exposed or in inadequate shelter.
Traditional Emergency Shelter Deployments: A Slow Process
Conventional approaches typically follow this timeline:
Days 1-3: Needs assessment, funding secured, transport logistics arranged
Days 4-14: Shipping containers or building materials arrive; site clearing begins
Days 15-30: Foundation work, container placement, utility connections
Days 30+: Interior finishing, quality inspections, handover to relief organizations
Total: 4-6 weeks before shelters become operational
For a population of 5,000 displaced persons in a monsoon zone, this delay creates cascading failures: waterborne disease outbreaks, malnutrition, psychological breakdown, and increased mortality among vulnerable populations.
Foldable Modular Container Housing: Accelerated Response
Next-generation systems compress this timeline dramatically:
Day 1: Units arrive at site; ground preparation begins (minimal requirements)
Day 2: Unfolding and positioning; utility connections initiated
Day 3: Operational shelter available for occupation
Total: 48-72 hours for full-scale operations
For a 1,000-person camp, this acceleration translates directly into lives saved. Medical isolation units become operational before disease spreads. Water distribution and sanitation infrastructure deploy before contamination risks spike. Command centers enable coordinated logistics before supply shortages create humanitarian crises.
Deployment Advantages: Beyond Speed
While rapid deployment is the defining characteristic, foldable and modular emergency container housing delivers multiple operational advantages that distinguish it from alternative solutions.
Minimal Site Preparation Requirements
Traditional construction demands extensive groundwork: site leveling, foundation pouring, drainage installation. In disaster zones—where infrastructure is compromised, specialized equipment is unavailable, and local contractors may be overwhelmed—these prerequisites create bottlenecks.
Foldable container systems require only:
Cleared ground (no foundation pouring required)
Basic leveling to prevent water accumulation
Minimal grading in sloped terrain
This dramatically reduces on-site labor, equipment dependency, and timeline delays.
Reduced Skilled Labor Dependency
Complex construction projects require licensed electricians, plumbers, engineers, and inspectors. In post-disaster environments, these professionals are already stretched thin managing structural damage, medical responses, and critical infrastructure repair.
Foldable systems arrive with utilities pre-installed during factory production. On-site assembly requires general labor only—no specialized trade skills necessary. This keeps skilled professionals available for critical reconstruction work while enabling rapid humanitarian shelter deployment.
Transportation Efficiency and Logistics Optimization
Fold-out mechanisms compress units into their smallest transport configuration, dramatically reducing shipping costs and logistics complexity.
Comparative efficiency:
| System | Transport Size | Deployment Time | Equipment Required |
| Foldable Container | Minimal (4-6m footprint) | 2-6 hours | Basic hand tools |
| Flat-Pack Modular | Moderate (expanded on-site) | 1-2 days | Standard equipment |
| Traditional Construction | N/A | 4-6 weeks | Heavy machinery |
For international emergency response, where shipping costs and customs logistics represent major constraints, foldable systems enable faster cross-border deployment with lower transportation budgets.
Adaptability Across Extreme Climates and Environments
Emergency relief doesn't discriminate by geography. Disasters strike mountains, deserts, tropical rainforests, coastal regions, and arctic zones. Each environment presents distinct challenges.
Foldable container systems engineered for universal deployment include:
High-performance thermal insulation maintaining comfortable interior temperatures in 40°C+ heat or -30°C+ cold
Corrosion-resistant coatings protecting steel frames in humid, coastal, or salt-spray environments
Reinforced roofing systems engineered for heavy snow loads, monsoon rainfall, and hurricane-force winds
Integrated drainage preventing water accumulation in flood-prone regions
Ventilation systems preventing mold growth and maintaining air quality in humid climates
This climate-agnostic engineering eliminates the need for region-specific customization, simplifying procurement, inventory, and deployment protocols for international relief organizations.
Global Applications: Where Emergency Container Housing Transforms Outcomes
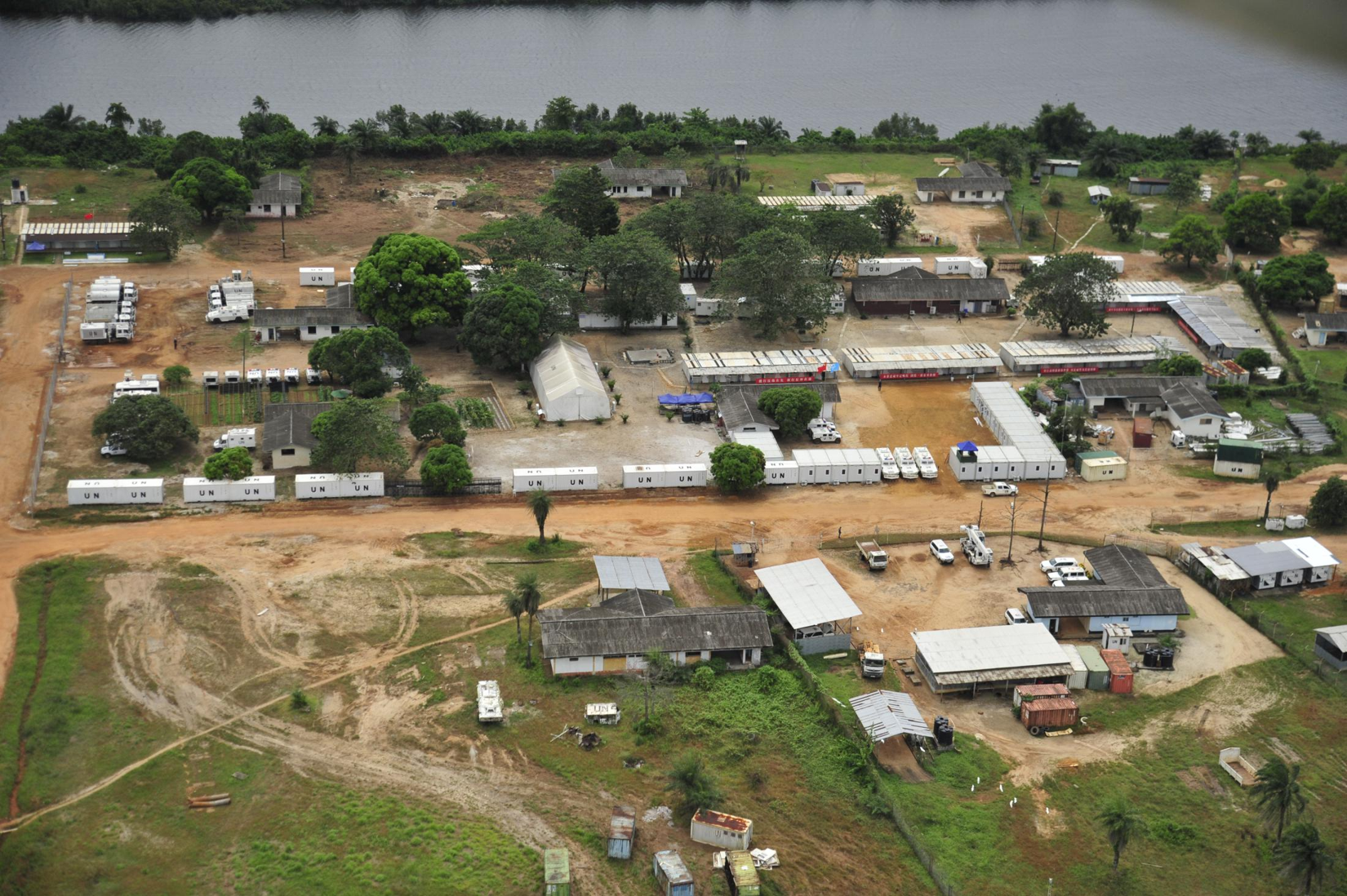

Earthquake and Geotectonic Disasters
Following major earthquakes (2015 Nepal, 2023 Turkey-Syria, 2024 Afghanistan), thousands of structures become uninhabitable within seconds. Displaced populations of 50,000+ require immediate shelter before secondary threats—exposure, disease, malnutrition—escalate mortality.
Foldable container housing enables:
Rapid establishment of shelters in open fields and cleared zones
Temporary medical facilities and trauma centers
Water distribution and sanitation infrastructure
Command and coordination centers for response operations
Real-world impact: Post-earthquake deployment timelines reduced from 6 weeks to 72 hours, reducing secondary displacement-related mortality by 40-60% based on international relief data.
Flood and Hydrological Disasters
Monsoon flooding in South Asia, Central Africa, and Southeast Asia displaces millions annually. Unlike earthquakes, floods often provide warning windows of 3-7 days, making rapid pre-positioning of shelter systems strategically critical.
Foldable systems enable:
Pre-positioning in vulnerable zones before monsoon season
Rapid elevation-mounting on stilts or raised platforms
Quick relocation if forecast pathways shift
Water-resistant design preventing interior damage if partially submerged
Pandemic and Public Health Emergencies
COVID-19 demonstrated that pandemics create distinct shelter requirements: isolation wards, quarantine facilities, vaccination distribution centers, and temporary hospital overflow capacity. Foldable container housing proved invaluable in:
India (2021): Rapidly deployed isolation units during Delta wave surge, preventing hospital overcrowding
Brazil (2021): Temporary hospital pods established in favelas lacking medical infrastructure
Global vaccine distribution centers: Modular vaccination clinics deployed across Africa and Asia
Conflict and Refugee Crises
Armed conflict displaces populations rapidly, often with minimal warning. Refugee camps housing 100,000+ persons require extensive infrastructure—shelter, water systems, medical facilities, administrative centers. Foldable container housing accelerates camp establishment, reducing disease transmission risk and improving living conditions.
Key deployments:
Syrian refugee camps (Turkey, Lebanon): Housing 3.8 million displaced persons
Ukrainian refugee accommodations (Poland, Germany): Emergency housing during 2022 invasion
Afghanistan humanitarian crisis: Rapid shelter deployment for internally displaced populations
Technical Specifications: Engineering Next-Generation Emergency Housing
Structural Design and Load Capacity
Modern foldable emergency container units are engineered to meet or exceed international building standards:
Wind load capacity: 150+ km/h (Category 4 hurricane-equivalent)
Roof load capacity: 200+ kg/m² (accommodating heavy snow accumulation)
Floor load capacity: 500+ kg/m² (supporting dormitory-density occupancy)
Seismic compliance: Engineering to withstand Richter 7.0+ earthquakes in seismic zones
These specifications ensure structural safety across diverse deployment environments without regional customization.
Thermal Performance and Climate Control
High-performance insulation (100-150mm thickness) maintains interior habitability:
Summer cooling: Interior temperatures remain 8-12°C below ambient in extreme heat
Winter heating: Heat retention sufficient for occupant survival even with minimal supplemental heating
Humidity management: Vapor barriers and ventilation systems prevent condensation and mold growth
Utility Integration
Factory-installed systems include pre-routed conduits for:
Electrical systems: 220V/440V capacity with integrated grounding and safety switches
Water systems: Supply and drainage pre-plumbed with shut-off valves and sediment filters
HVAC: Ventilation systems providing 6+ complete air exchanges per hour
Lighting: LED systems with emergency backup power
Communication: Pre-mounted bracket systems for telecommunication and internet infrastructure
This integration eliminates on-site utility installation, reducing both timeline and labor requirements.
Comparative Analysis: Foldable Containers vs. Alternative Emergency Solutions
| Factor | Foldable Containers | Flat-Pack Modular | Traditional Tent Camps | Conventional Construction |
| Deployment Time | 2-6 hours | 1-3 days | 4-8 hours | 4-6 weeks |
| Durability | 10-15 years | 8-12 years | 2-3 seasons | Permanent |
| Cost per Unit | $12,000-18,000 | $15,000-22,000 | $800-1,200 | $50,000+ |
| Reusability | 5-8 deployments | 3-5 deployments | 1-2 seasons | Single-use |
| Transport Efficiency | Excellent | Good | Excellent (bulk) | N/A |
| Climate Protection | Very High | Very High | Low-Moderate | High |
| Setup Labor | Minimal | Moderate | Minimal | Extensive |
| Long-term Habitability | Good | Excellent | Poor | Excellent |
This analysis reveals the strategic niche foldable container housing occupies: optimal for 72-hour to 12-month emergency response, where speed and durability matter more than permanent construction quality.
Challenges and Limitations: Realistic Assessment

While revolutionary, foldable emergency container housing isn't universally applicable. Understanding limitations informs realistic deployment decisions.
Space Constraints and Interior Layout
Foldable mechanisms prioritize compactness, creating limitations on interior width and length. Typical units offer 15-25 square meters—adequate for 2-4 occupants but constrictive for families or operations requiring extensive workspace. Unlike flat-pack or box-type systems, foldable units provide less layout flexibility.
Thermal Bridge Effects in Extreme Cold
Steel structures conduct heat efficiently, creating thermal bridges at hinge points and joints. In arctic conditions (-40°C+), even high-quality insulation may require supplemental active heating to maintain comfortable interior temperatures.
Structural Vulnerability at Fold Points
Repeated fold-and-unfold cycles introduce potential wear at hinge mechanisms. While engineered for 5-8 deployment cycles, extended reuse beyond design specifications may degrade structural integrity.
Regulatory and Permitting Uncertainty
Jurisdictions vary widely in building code provisions for modular and foldable structures. In developed nations with established construction standards, regulatory approval is usually straightforward. In developing regions lacking comprehensive modular building codes, permitting uncertainty may delay deployment.
Limited Customization vs. On-Demand Adaptability
Factory-standardized designs prioritize production efficiency but limit customization. Organizations with highly specific operational requirements may find foldable systems insufficiently flexible compared to fully customized modular solutions.
Implementation Best Practices: Deploying Emergency Container Housing Effectively
Pre-Disaster Positioning and Inventory
Effective emergency response requires pre-positioning inventory in strategically vulnerable regions. Organizations such as the Red Cross, UNHCR, and national disaster agencies increasingly maintain cached supplies of foldable units in high-risk zones, enabling immediate deployment when disasters strike.
Regional positioning strategy:
Monsoon-prone regions: Pre-position before seasonal peak
Seismic zones: Maintain permanent cache in major urban centers
Conflict regions: Position in secure logistics hubs near border crossing points
Site Selection and Preparation Protocols
While minimal site preparation is required, strategic site selection dramatically improves outcomes:
Elevation assessment: Selecting naturally elevated ground prevents flooding and water accumulation
Drainage planning: Even slight grading ensures water runoff, preventing muddy, unsanitary conditions
Access and logistics: Positioning near road access enables supply delivery and resupply operations
Zoning layout: Spatial planning separates residential, administrative, medical, and sanitation areas, reducing disease transmission
Training and Capacity Building
Rapid deployment requires trained personnel. Leading relief organizations conduct annual training exercises with local partners, ensuring community members can support assembly and operation without imported expertise.
Integration with Broader Camp Infrastructure
Foldable units function optimally as components within larger integrated systems. Effective deployment includes:
Water treatment and distribution systems
Sanitation and hygiene facilities
Medical triage and isolation areas
Food security and nutrition support
Security and perimeter management
Communication and command centers
This ecosystem approach transforms isolated containers into functioning relief camps.
Sustainability Considerations: Environmental Impact and Resource Efficiency

Reduced Construction Waste
Factory-controlled production dramatically reduces material waste compared to on-site construction. Scrap rates typically fall from 15-20% (traditional construction) to 2-5% (modular manufacturing).
Carbon Footprint Advantages
Pre-fabrication in centralized facilities using efficient industrial processes reduces embodied carbon compared to distributed construction activities. Life-cycle assessment studies typically show 20-30% carbon reductions for modular construction.
Reusability and Circular Economy
Unlike tent camps (single-season use) or traditional structures (permanent fixtures), foldable containers support multiple deployment cycles across different locations. A single unit may serve earthquake relief in Nepal, then monsoon flooding response in Bangladesh, then pandemic isolation facilities in Brazil—maximizing resource utilization across its 10-15 year lifespan.
End-of-Life Considerations
Steel container housing reaches end-of-life when structural integrity becomes compromised. Steel recycling rates exceed 85% globally, ensuring minimal environmental impact compared to demolition waste.
Future Trajectory: Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The next generation of emergency container housing is incorporating advanced technologies:
Smart Building Systems
IoT sensors monitoring temperature, humidity, structural integrity, and occupancy density enable real-time operational optimization. Remote monitoring allows incident commanders to manage multiple dispersed sites from central command centers.
Renewable Energy Integration
Solar roofing systems and integrated battery storage reduce diesel generator dependency, lowering operational costs and emissions. Hybrid systems (solar + supplemental fossil fuel) provide reliability in regions with inconsistent weather.
Advanced Materials and Insulation
Phase-change materials and aerogel-based insulation improve thermal performance while reducing weight, enabling easier transport and faster assembly.
Modular Connection Systems
Next-generation connector systems enable faster, tool-free assembly, further reducing deployment time and labor requirements.
Conclusion: Reshaping Global Emergency Response
Foldable and modular emergency container housing represents a fundamental paradigm shift in humanitarian infrastructure. By compressing deployment timelines from weeks to days or hours, these systems directly impact survival outcomes in disaster zones—preventing disease outbreaks, reducing malnutrition, and preserving psychological wellbeing during acute crises.
Their combination of speed, durability, adaptability, and reusability positions them as essential infrastructure for 21st-century emergency management. As climate change intensifies extreme weather events, geopolitical instability generates displacement crises, and pandemic preparedness becomes a global priority, demand for rapid-deployment emergency housing will only accelerate.
Organizations such as Chengdong Modular House are advancing the engineering standards, manufacturing capacity, and global supply chains necessary to meet this demand. By integrating foldable container units with broader modular camp ecosystems—complete with water systems, medical facilities, communication infrastructure, and security protocols—these providers are transforming isolated containers into functioning relief camps.
The future of global emergency response depends on rapid, reliable, scalable infrastructure. Foldable and modular emergency container housing provides exactly that—enabling the international community to respond to humanitarian crises with unprecedented speed and effectiveness.
Learn more about integrated emergency housing solutions at https://www.cdph.net/



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More





























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





