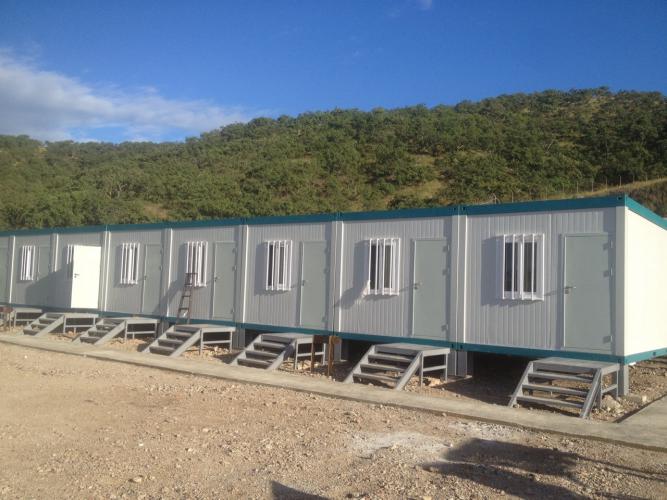
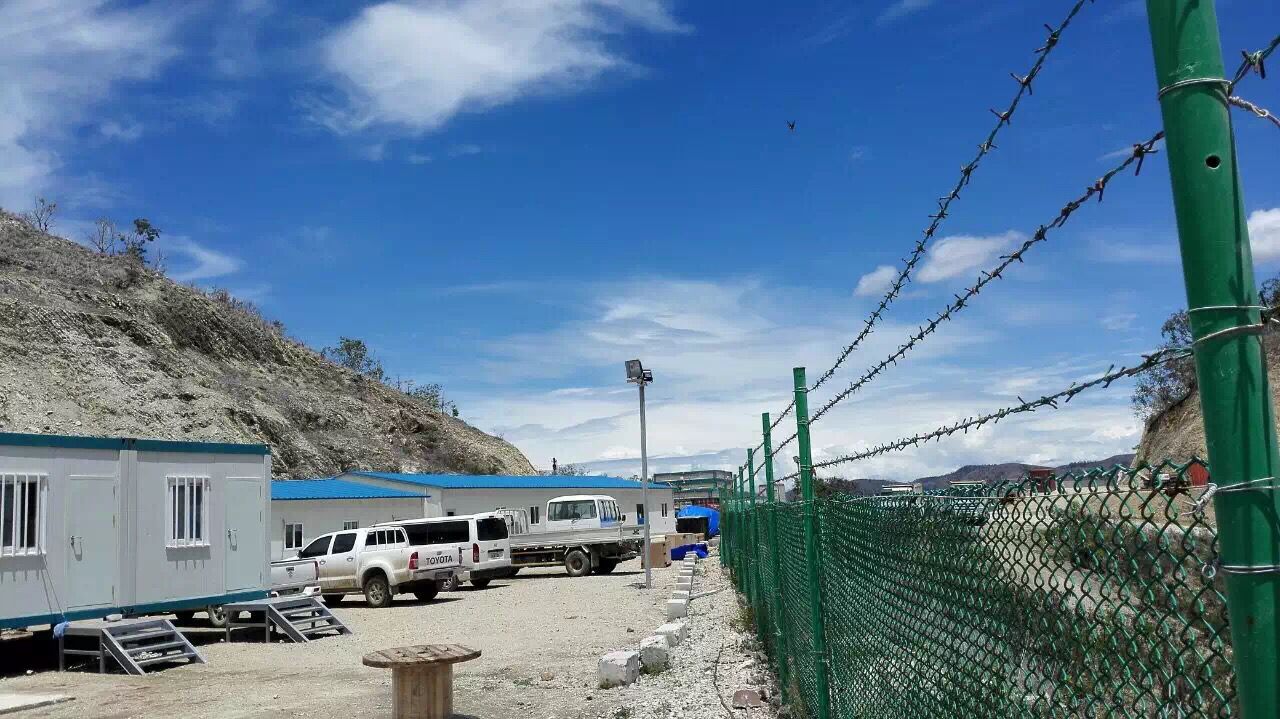
What Is Modular Construction? A Comprehensive Definition
Modular construction, also referred to as prefabricated or modular building, represents a revolutionary approach to modern construction where buildings are designed, manufactured, and assembled off-site in a controlled factory environment. Unlike traditional on-site construction methods, modular construction involves creating standardized building components or modules that are then transported and assembled at the final destination. This contemporary construction methodology has transformed the way we build, combining efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness into a single comprehensive building solution.
The fundamental principle underlying modular construction is the use of standardized, repeatable modules that can be combined in virtually unlimited configurations to meet specific project requirements. These modules—whether container houses, prefabricated panels, or steel structural components—are manufactured with precision in controlled factory settings before being transported to the construction site. Once delivered, the modules can be rapidly installed, configured, and connected through bolted or welded connections, significantly reducing on-site construction time and labor expenses.
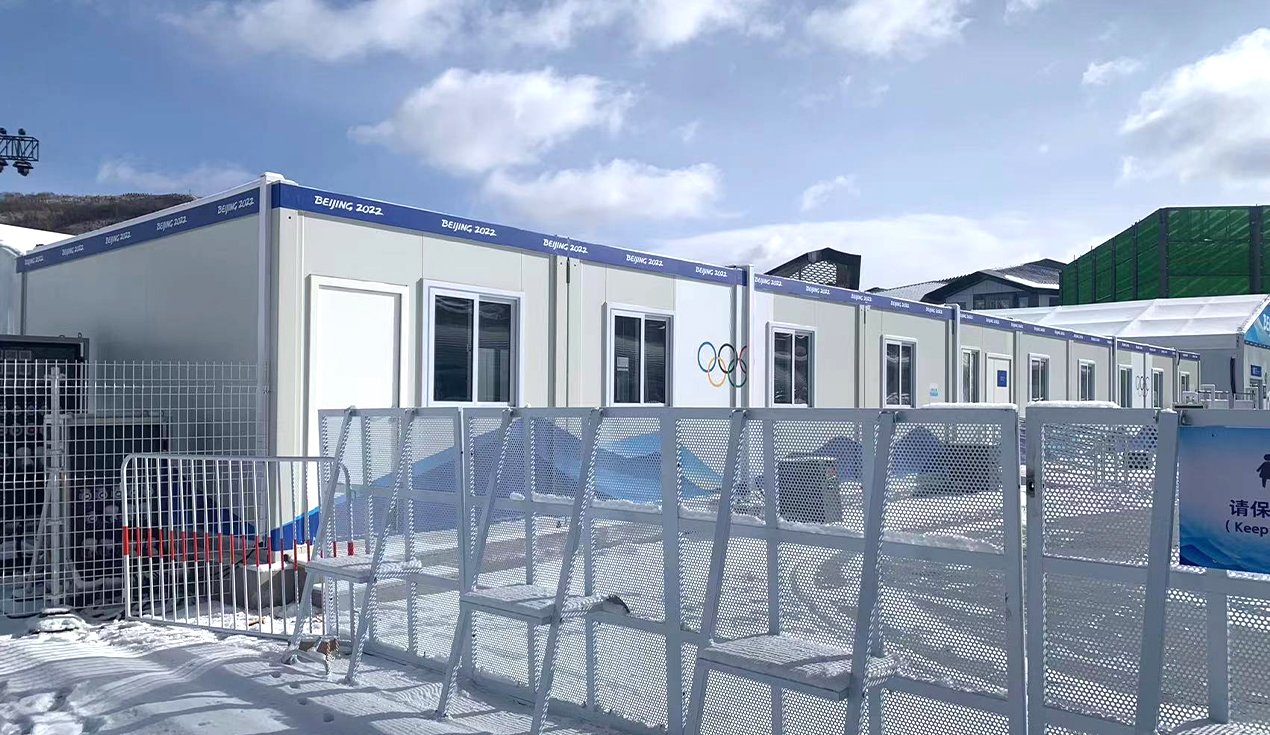

Historical Development and Evolution of Modular Construction
The concept of modular construction is not entirely new, but its modern implementation represents a significant technological advancement. The modular building industry has evolved dramatically over the past two decades, with companies pioneering innovative approaches to temporary and semi-permanent structures for engineering camps, disaster relief, and commercial applications.
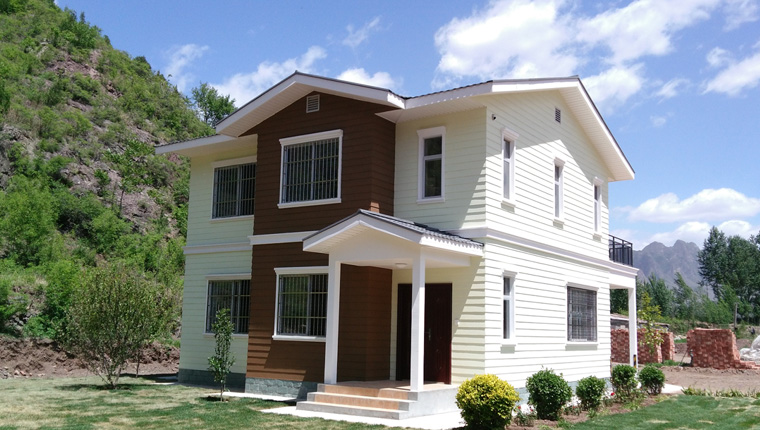
Early modular construction primarily utilized container houses—converted shipping containers adapted for human habitation. These container-based structures provided a practical solution for quickly establishing temporary housing in remote locations, mining operations, and construction sites. As technology advanced and manufacturing processes improved, the industry expanded beyond simple container conversions to include sophisticated prefabricated housing systems incorporating advanced materials, insulation technologies, and customizable interior configurations.
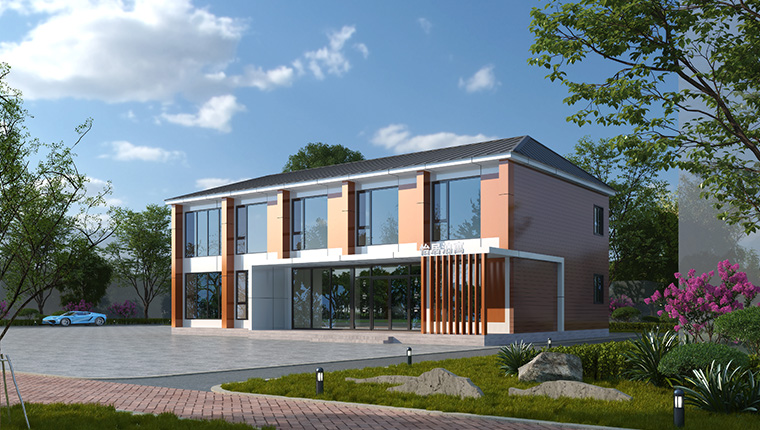
Today's modular construction encompasses multiple product categories, including container houses, prefabricated houses, light steel villas, steel structures, and expandable modular units. Each category serves specific purposes while maintaining the core principle of factory-based manufacturing and rapid on-site assembly.
Modern modular construction systems comprise several essential components that work together to create functional, durable buildings:
Structural Framework
The foundation of any modular unit begins with its structural framework. Most contemporary modular buildings utilize hot-dip galvanized steel profiles that are cold-formed and mechanically mass-produced in factories. This approach offers superior durability, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity compared to traditional construction methods. The galvanized steel framework can withstand Category 11 winds under standard conditions, with enhanced versions capable of withstanding Category 17 hurricane-force winds after specialized treatment.
Insulation and Thermal Properties
Modular construction emphasizes thermal efficiency through high-quality insulation materials. Standard configurations typically include 100mm glass fiber wool or polyurethane insulation in both roof and floor sections, with optional thicker insulation available for extreme climate applications. This superior insulation significantly reduces heating and cooling costs while improving occupant comfort, making modular buildings suitable for deployment in diverse climate zones—from tropical regions to sub-zero environments.
Interior Finishes and Materials
Factory manufacturing allows for precise application of interior finishes and materials. Modular units feature suspended ceilings made from color steel composite materials, durable rubber-plastic flooring with thickness specifications of 1.8mm or greater, and professionally installed electrical and plumbing systems. Interior materials are often selected for environmental friendliness, creating zero-formaldehyde living environments that prioritize occupant health and wellbeing.
Connectivity and Assembly Systems
One of the defining characteristics of modular construction is the use of standardized connection systems. Modules connect through bolted connections rather than welding, allowing for rapid on-site assembly without requiring specialized welding equipment or skilled trades. This bolt-connection approach dramatically accelerates installation timelines while improving assembly accuracy and structural reliability.
Key Advantages and Benefits of Modular Construction
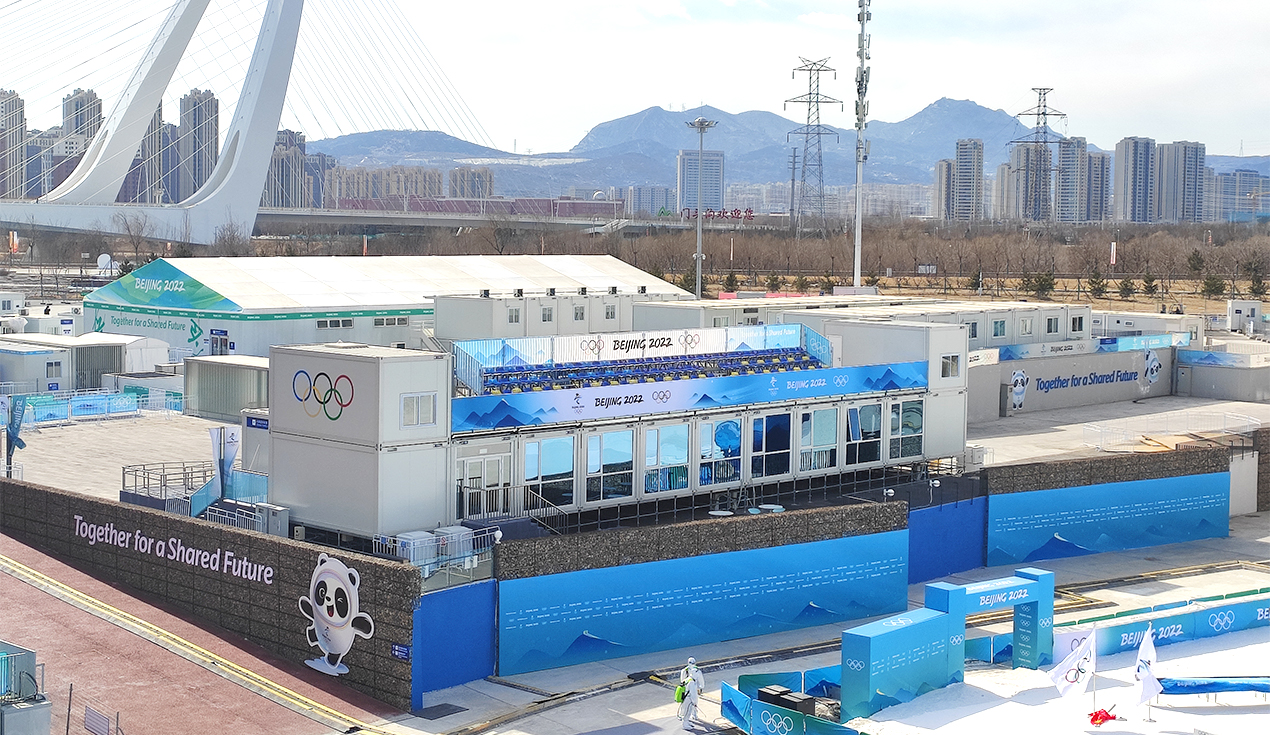

The widespread adoption of modular construction across industries stems from its numerous advantages over traditional building methods:
Accelerated Construction Timeline
Perhaps the most significant benefit of modular construction is dramatically reduced project timelines. By manufacturing building components in parallel within factory environments while site preparation occurs simultaneously, modular projects can be completed in a fraction of the time required for conventional construction. Complex engineering camp projects that might require 12-18 months using traditional methods can be completed in 120 days or less with modular solutions.
Cost Efficiency and Reduced Overhead
Factory-controlled manufacturing minimizes waste, reduces labor costs, and improves material efficiency. Standardized production processes enable economies of scale, while reduced on-site labor requirements lower overall project expenses. Lower transportation costs result from optimized packaging—multiple modular units can be nested and containerized for efficient ocean freight, reducing shipping expenses by up to 60% compared to traditional building materials.
Superior Quality Control
Controlled factory environments enable consistent quality standards that exceed typical on-site construction practices. Each module undergoes rigorous inspection and testing before leaving the factory, ensuring compliance with international building codes and customer specifications. This quality-first approach dramatically reduces defects, rework requirements, and warranty claims.
Environmental Sustainability
Modular construction significantly reduces environmental impact through reduced material waste, lower energy consumption during manufacturing, and minimized on-site disruption. Factory-based manufacturing enables precise material calculation, reducing surplus waste by up to 90% compared to traditional construction. Additionally, the mobility of modular structures allows for site reclamation and environmental restoration without permanent landscape alteration.
Flexibility and Customization
Despite standardized manufacturing processes, modular construction offers remarkable flexibility. Modules can be configured horizontally and vertically to create varied floor plans and building heights. Container-based units can stack up to three layers, while prefabricated house systems can achieve unlimited horizontal combinations. Custom interior layouts, material selections, and finish options ensure that each project meets specific client requirements while maintaining production efficiency.
Reusability and Asset Lifecycle Extension
Unlike traditional buildings designed for permanent installation, modular structures are inherently reusable. Modules can be disassembled and relocated to new sites, extending asset lifecycles and maximizing return on investment. This reusability is particularly valuable for companies managing multiple projects across different geographic locations, as module inventories can be rotated among active projects.
Applications of Modular Construction Across Industries
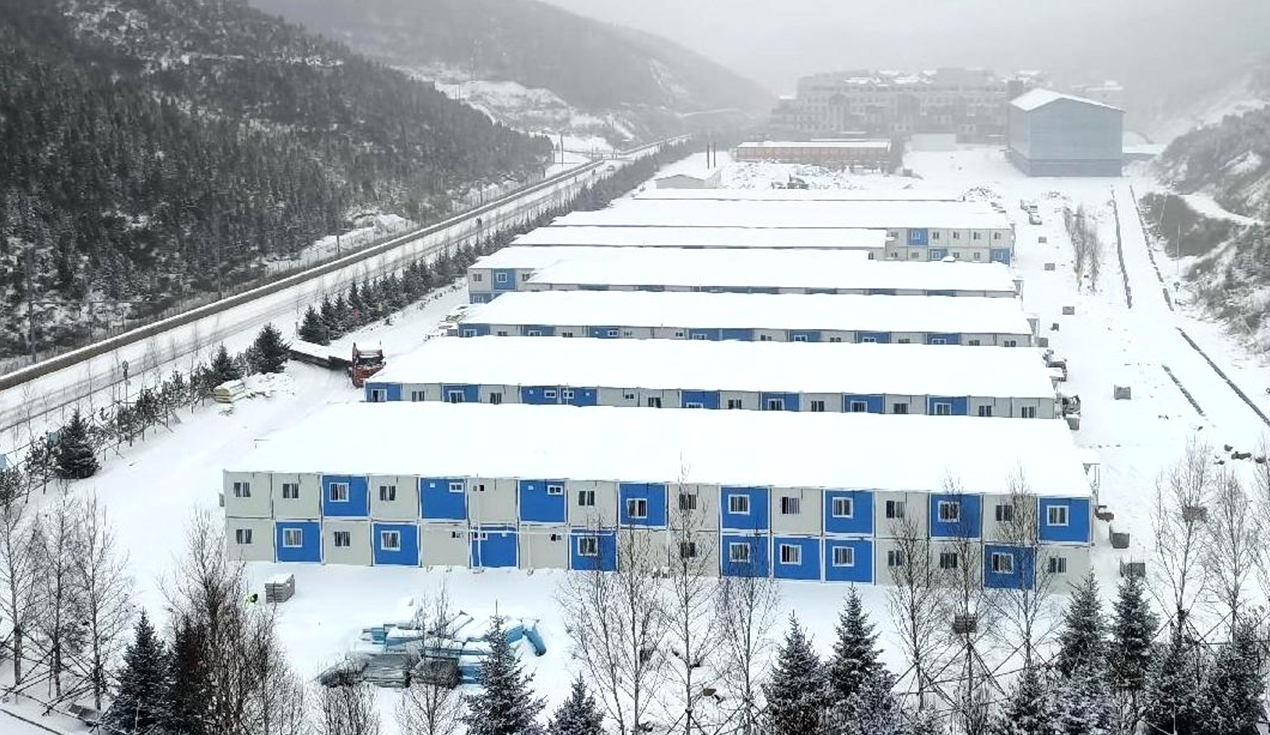

Modern modular construction serves diverse applications across multiple sectors:
Engineering and Construction Camps
Engineering camps represent the primary application for modular construction systems. These temporary or semi-permanent establishments support specific construction projects, mining operations, and infrastructure development initiatives. Modular camps typically include accommodation facilities, office spaces, storage areas, catering services, and supporting infrastructure. The rapid deployment capability of modular construction makes it ideal for remote project sites where traditional construction logistics present significant challenges.
Mining and Energy Extraction Operations
In mining and petroleum extraction industries, modular camps provide critical worker accommodation in remote, often inhospitable locations. The durability, mobility, and rapid installation characteristics of modular housing address the unique demands of these industries while providing workers with safe, comfortable living environments equipped with essential amenities.
Transportation and Infrastructure Projects
Railway, highway, and major infrastructure projects employ modular construction for worker accommodation and project support facilities. The ability to rapidly establish camps at new project locations and quickly dismantle facilities upon project completion makes modular solutions ideal for linear infrastructure projects spanning multiple geographic regions.
Educational and Healthcare Facilities
Modular construction has gained significant traction in education and healthcare sectors. Schools and medical facilities can be rapidly established using modular components, providing controlled environments with superior sound insulation, natural lighting, and environmentally friendly materials that prioritize occupant safety and wellbeing. The flexibility of modular systems allows educational institutions and healthcare providers to expand capacity without permanent structural commitments.
Commercial and Hospitality Applications
Tourism and commercial applications increasingly utilize modular construction for hotels, resorts, restaurants, and retail facilities. Customized modular designs enable hospitality operators to create premium accommodation experiences while maintaining rapid deployment timelines and cost efficiency. Semi-permanent light steel villa components offer aesthetic appeal combined with functional durability suitable for upscale commercial applications.
Military and Humanitarian Assistance
Military applications particularly benefit from modular construction's transportability and rapid assembly characteristics. Standard modular units can be integrated into compact 20-foot containers, with five housing units condensing to a single container size. This efficiency reduces transportation costs while accelerating deployment timelines for military personnel assignments and humanitarian relief operations.
Sports and Event Management
Event venues and temporary sports facilities utilize modular construction for spectator seating, broadcast facilities, and operational support buildings. The modular design enables flexible configurations supporting various event requirements while maintaining installation speed and cost efficiency.
Modular Construction vs. Traditional Building Methods
The distinction between modular construction and traditional building approaches reflects fundamental differences in methodology, timeline, and quality outcomes:
| Aspect | Modular Construction | Traditional Construction |
| Manufacturing Location | Controlled factory environment | On-site construction |
| Quality Control | Rigorous factory-based testing | Variable on-site oversight |
| Installation Timeline | 30-50% reduction in project duration | Standard 12-24 month timelines |
| Labor Requirements | Reduced on-site labor needs | Higher labor-intensive processes |
| Weather Dependency | Minimal weather impact | Significant weather delays |
| Cost Predictability | Fixed manufacturing costs | Variable on-site expenses |
| Material Waste | Minimized through precision manufacturing | 10-20% waste typical |
| Customization | Flexible within modular framework | Unlimited customization options |
| Asset Reusability | High—modules relocatable | Fixed permanent structures |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced site disruption | Significant site alteration |
Technical Specifications and Standards for Modular Buildings
Contemporary modular construction adheres to rigorous technical specifications ensuring structural integrity, safety, and performance:
Structural Load Capacities
Standard modular housing units accommodate roof live loads of 0.5 kN/m², floor loads of 2.0 kN/m², and wind loads of 0.45-0.5 kN/m². Enhanced structural designs support heavier live loads for specialized applications requiring additional capacity. Heat transfer coefficients range from 0.46-0.64 W/K across roofing, flooring, and wall components, providing superior thermal efficiency.
Dimensional Standardization
Container-based modular units typically feature outer dimensions of 6055mm length × 2990mm width × 2896mm height, with interior net dimensions of 5845mm × 2780-2435mm × 2500mm. These standardized dimensions correspond to international shipping container specifications, optimizing transportation efficiency while maintaining functional interior space.
Material Composition and Durability
Modern modular units utilize Q235 hot-dip galvanized steel strips for structural components, 75mm rock wool or glass wool insulation in walls, and color steel sandwich panels for exterior surfaces. Internal flooring typically consists of 18mm cement fiberboard with 1.8mm rubber-plastic surface finishes. These material specifications ensure corrosion resistance, thermal performance, and durability extending 25+ years for light steel villa components.
International Compliance and Certification
Leading modular construction manufacturers maintain CE certification and compliance with international standards including EU CPR 305/2011 and EN 1090-1:2009+A1:2011. These certifications validate structural safety, material quality, and manufacturing processes meeting stringent European and global building code requirements.
The Future of Modular Construction
The modular construction industry continues evolving with technological innovations and expanded applications. Emerging trends include integration of smart building technologies, sustainable material development, digital design and prefabrication systems, and expanded use of modular methods in permanent residential and commercial construction.
Advanced manufacturing technologies including computer numerical control (CNC) machining and robotic assembly are improving precision while reducing manufacturing costs. Building Information Modeling (BIM) enables sophisticated 3D design, accurate material estimation, and seamless coordination between manufacturing and installation phases. Sustainability initiatives increasingly incorporate recycled materials, renewable energy integration, and circular economy principles enabling modular buildings to achieve environmental certifications and reduced operational carbon footprints.
Conclusion
Modular construction represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how buildings are designed, manufactured, and assembled. By combining factory-controlled manufacturing with standardized design principles and rapid on-site assembly, modular construction delivers significant advantages in project timeline, cost efficiency, quality consistency, and environmental sustainability. From engineering camps supporting major infrastructure projects to educational facilities and humanitarian relief applications, modular construction has proven its versatility and effectiveness across diverse sectors and geographic regions.
As construction industries worldwide seek solutions addressing labor shortages, sustainability requirements, and accelerated project timelines, modular construction methodologies will continue gaining prominence. The combination of technological advancement, proven cost-effectiveness, and demonstrated durability ensures that modular construction will remain an essential component of contemporary building practices for decades to come.
For organizations seeking reliable modular construction solutions backed by decades of industry experience, comprehensive service offerings, and a proven track record in complex international projects, https://www.cdph.net/ provides comprehensive information about advanced modular housing systems and engineering camp construction services.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More



























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





