Introduction
Prefabricated construction has revolutionized the building industry by enabling faster project timelines, reduced waste, and improved quality control. At the heart of this transformation lies the careful selection and integration of specialized prefab construction materials. Unlike traditional on-site construction, prefab buildings depend entirely on engineered materials that are manufactured in controlled factory environments and assembled with precision. This comprehensive guide explores the essential components, specifications, and performance characteristics of modern prefab construction materials, providing builders, developers, and project managers with actionable insights for selecting the right materials for their projects.
The global shift toward prefabrication reflects growing demand for sustainable, cost-effective construction solutions. Prefab materials must meet stringent engineering requirements while remaining cost-competitive and compatible with factory production processes. Understanding these materials—and how they contribute to the overall performance of modular structures—is critical for anyone involved in construction camp development, emergency housing, or large-scale infrastructure projects.

Understanding Prefab Construction Materials: Definition and Scope
Prefab construction materials are engineered components manufactured off-site in factory conditions and transported to construction sites for rapid assembly. These materials are fundamentally different from traditional building components because they are designed for:
Factory prefabrication with precision tolerances
Transportation over long distances, including international shipping
Rapid on-site assembly with minimal welding or specialized labor
Reusability and modularity across multiple projects
Durability under variable climate conditions (extreme heat, cold, humidity, and wind)
The scope of prefab materials encompasses structural frameworks, insulation systems, wall and roof panels, flooring, doors, windows, drainage systems, and electrical components. Each element is engineered to integrate seamlessly while maintaining structural integrity, thermal performance, and long-term durability.
Primary Structural Materials: Steel Frameworks and Load-Bearing Systems

Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel: The Foundation of Durability
The most critical component of prefab construction is the structural steel frame. Hot-dip galvanized steel has emerged as the industry standard because it provides exceptional corrosion resistance combined with structural strength. The hot-dip galvanization process involves immersing steel profiles in molten zinc, creating a protective barrier that prevents rust and degradation even in harsh environments.
Container houses typically utilize hot-dip galvanized steel frames manufactured to precise specifications. Standard container house frames are constructed using:
Q235 hot-dip galvanized steel strip as the primary structural material
Factory-prefabricated profiles with fixed cooling and bending
Bolted connections throughout, eliminating the need for on-site welding
Overall frame weight of approximately 800 kg per standard unit, providing rigidity without excessive mass
The heat transfer coefficients for galvanized steel structures are precisely calculated to ensure thermal efficiency:
| Component | Heat Transfer Coefficient (W/m²K) |
| Roof | 0.64 |
| Ground | 0.46 |
| Wallboard | 0.47 |
This standardized approach ensures that prefab buildings maintain consistent thermal performance across different climates and geographic locations.
Cold-Formed Steel Structures: Innovation for Complex Designs
Cold-formed steel represents an advancement in prefab materials technology. Unlike traditional hot-rolled H-shaped steel, cold-formed steel profiles are manufactured through mechanical processes that allow mass production while reducing transportation costs. These profiles can be:
Customized for specific spans and eave heights
Mechanized for rapid factory production
Fitted with bolted connections for field assembly
Designed for long-span structures like warehouses and production facilities
The ZA type house system exemplifies this innovation. Built from thin-walled, hot-dip galvanized cold-formed steel, these structures offer:
Structural safety capable of withstanding Category 11 winds (and Category 17 hurricane-force winds with special treatment)
Superior corrosion resistance in coastal and humid environments
Shorter processing cycles through mechanized production
Fully bolted assembly eliminating on-site welding
Flexible design allowing customization up to 11-meter spans with eave heights to 5 meters
Insulation and Thermal Materials: Maintaining Energy Efficiency
Insulation performance is critical in prefab construction, particularly for structures deployed in extreme climates—from arctic regions with temperatures dropping to -52°C to tropical areas with intense solar radiation and humidity. Modern prefab buildings utilize multiple insulation strategies:
Glass Fiber Wool and Rockwool Insulation
Standard insulation specifications in prefab container houses typically include:
Roof insulation: 100mm glass fiber wool or equivalent
Floor insulation: 100mm glass fiber wool or equivalent
Optional wall insulation: 50-100mm rockwool or glass wool composite panels
For extreme climate applications, insulation thickness can be increased significantly. Projects deployed in regions with severe winters specify 150mm thick rockwool color steel composite panels to ensure superior thermal resistance and minimize heat loss through walls and roofs.
Glass fiber wool offers several advantages in prefab applications:
Lightweight (approximately 80 kg/m³ bulk density for standard rockwool)
Excellent thermal insulation reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling
Fire-resistant properties meeting Class A fire safety standards
Moisture-resistant preventing degradation in humid environments
Easy installation during factory assembly
Thermal Performance Standards
Prefab buildings designed for diverse climates must achieve specific thermal performance standards. Heat transfer coefficients are engineered to minimize thermal bridging, which occurs at structural connections and material junctions. The integrated design of steel frames with thick insulation layers ensures:
Consistent internal temperatures regardless of external weather
Reduced HVAC load lowering operational costs
Improved occupant comfort maintaining stable, healthy indoor environments
Compliance with international building standards for energy efficiency
Composite Wall and Roof Panels: Durability and Aesthetics
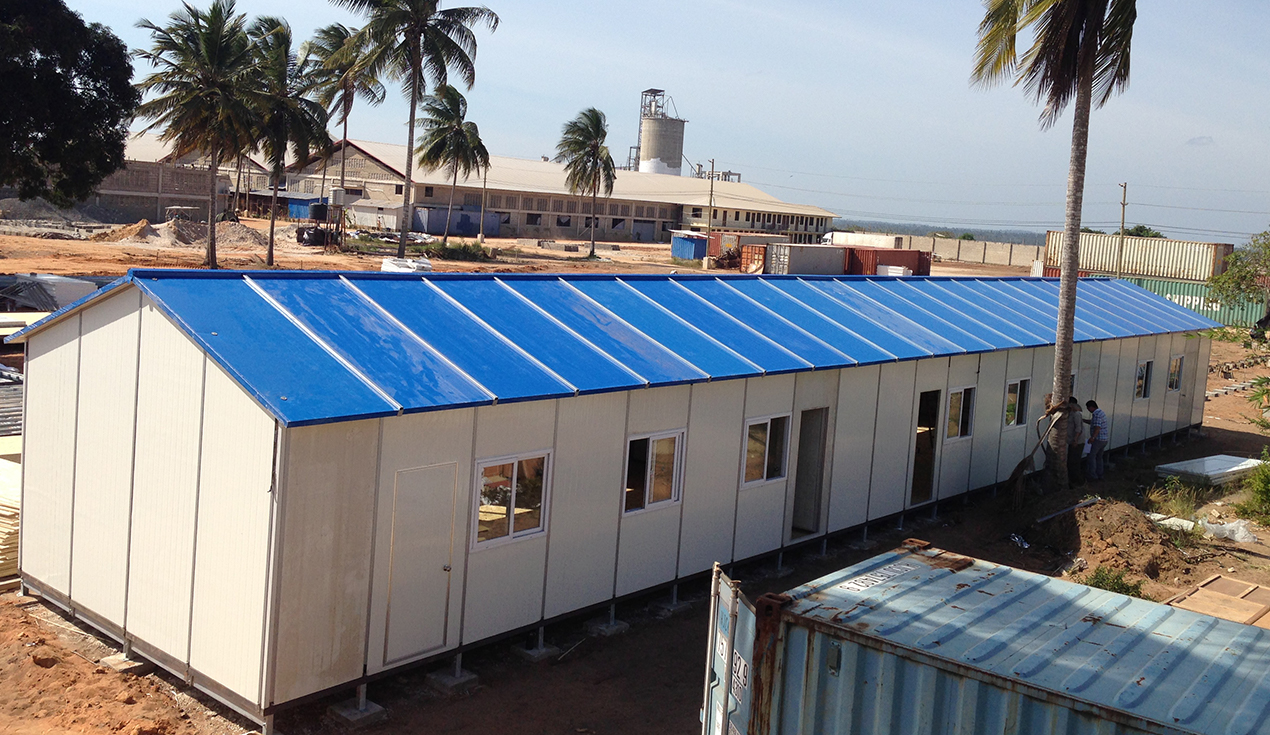

Color Steel Sandwich Composite Boards
The exterior envelope of prefab buildings relies on color steel sandwich composite boards, which are engineered assemblies combining multiple materials into a single, high-performance panel. Standard specifications include:
Standard Configuration:
Overall thickness: 75mm
Color-coated steel plate thickness: 0.4mm (outer and inner surfaces)
Core material: Rockwool with bulk density of 80 kg/m³
Texture: Orange peel grain on outer surface
Color options: Grey and white standard colors with custom options available
Enhanced Configuration for Extreme Climates:
Overall thickness: 150mm (double standard thickness)
Core material: 150mm continuous rockwool insulation
Enhanced fire resistance: Class A fire-resistant materials
Superior thermal performance: Appropriate for arctic and high-altitude deployments
These composite panels offer integrated advantages:
Structural contribution to the overall building rigidity
Thermal insulation eliminating separate insulation layers
Weather protection with sealed color-coated surfaces
Fire resistance meeting international safety standards
Aesthetic appeal with finished exterior appearance
Wall Panel Specifications and Customization
Prefab construction materials allow extensive customization while maintaining manufacturing efficiency. Wall panel options include:
75mm glass fiber wool/polystyrene color steel composite boards (standard specification)
50-100mm rockwool/glass wool composite boards (medium duty)
150mm enhanced composite panels (extreme climate applications)
Alternative materials including calcium silicate board ceilings for humid environments
This material flexibility ensures that prefab buildings can be optimized for specific environmental conditions while maintaining standardized production processes.
Flooring and Foundation Materials: Structural Support and Moisture Control
Advanced Flooring Systems
Prefab flooring systems are engineered assemblies providing:
Structural rigidity (floor live load: 2.0 KN/m²)
Moisture protection through elevated or fully sealed designs
Ease of installation with factory-installed systems
Standard prefab floor specifications include:
1.8mm thick rubber and plastic flooring providing durable, stain-resistant surfaces
Cement fiberboard underlayment (18mm thickness) supporting floor finishes
Optional elevated flooring with 300mm air gap for moisture control in high-humidity environments
For projects in humid or coastal regions, elevated flooring with ventilation gaps prevents ground moisture from compromising structural integrity while reducing reliance on vapor barriers and additional moisture barriers.
Foundation and Ground Preparation
While prefab building components are factory-manufactured, foundation design remains site-specific. Standard practice includes:
Concrete foundations (typically C15-C20 grade)
Backfill materials including sand and compacted soil
Fine stone concrete cushioning layers (100mm C15 grade)
Drainage provisions with 50mm PVC drain pipes and post-drainage systems
This foundation approach allows rapid site preparation while ensuring long-term structural stability.
Doors, Windows, and Building Envelope Components
Door Systems in Prefab Construction
Standard prefab door specifications include:
Material: Steel security doors or composite panel flat doors
Dimensions: Typically 840mm width × 2035mm height
Opening options: Inward or outward swing configurations
Security features: Anti-theft capabilities with reinforced frames
Steel doors provide superior security and durability in challenging environments, while composite doors offer lighter weight and modern aesthetics for hospitality and commercial applications.
Window Systems and Glazing
Windows in prefab buildings must balance thermal performance with safety and durability:
Material: Plastic-steel frames (PVC-aluminum hybrid) or aluminum alloy
Glazing: 4mm-9mm insulating glass configurations
Common sizes: 500×500mm, 800×500mm, 1100×1120mm, and custom dimensions
Operation: Push-pull (sliding) or casement styles
Enhanced specification: Hollow three-layer glass for extreme cold climates (arctic deployments)
Accessories: Window screens and anti-theft guardrails
Triple-glazed windows represent the highest thermal performance standard, reducing heat loss in ultra-cold environments while maintaining transparency and visibility.
Electrical and Plumbing Integration: Factory Assembly Advantages
One of the critical advantages of prefab construction materials is the integration of utilities during factory assembly. Prefab electrical and plumbing systems are pre-installed, pressure-tested, and certified before shipping, eliminating on-site utility work.
Electrical Systems
Standard electrical specifications in prefab containers include:
Prefabricated roof circuits with integrated wiring
Outdoor connection: 2P ground 32A industrial plug
Indoor lighting: 2×36W single-tube fluorescent lamps
Power outlets: Three five-hole sockets plus dedicated air-conditioning socket
Control systems: Single-open large key switch for master control
Plumbing and Drainage
Prefab plumbing systems feature:
Wall-mounted water supply lines (pressure-tested)
Wall-side and post-drainage systems with 50mm PVC downspouts
Pre-installed fixtures ready for connection at site
Sloped drainage for gravity-fed systems minimizing reliance on pumped drainage
Material Standards and Quality Assurance
Prefab construction materials must meet international standards ensuring safety, durability, and performance consistency. Leading manufacturers comply with:
European standards including CPR EU 305/2011 and EN 1090-1:2009
International certification registrars verifying conformity with building codes
CE marking requirements for modular housing products exported to EU markets
Environmental compliance standards ensuring sustainable material sourcing
These certifications validate that prefab construction materials meet rigorous requirements for structural integrity, fire resistance, thermal performance, and environmental impact.
Material Selection for Specialized Applications
Prefab construction materials must address diverse environmental challenges:
Coastal and High-Humidity Environments
Projects in coastal regions require materials with exceptional corrosion resistance:
100% hot-dip galvanized steel structures for maximum protection
150mm insulation panels for tropical heat and humidity
Elevated flooring systems with ventilation gaps preventing moisture accumulation
Class A fire-resistant composite panels meeting maritime safety standards
Arctic and High-Cold Climates
Arctic deployments demand enhanced thermal performance:
Upgraded insulation to 150mm in walls and roofs
Triple-glazed windows with advanced sealing
Continuous thermal barrier design eliminating cold bridges
Elevated flooring preventing ground freeze cycles from affecting structures
High-Wind and Seismic Regions
Structures in hurricane and seismic zones require enhanced structural materials:
Category 17 hurricane-rated galvanized steel structures with special treatment
Fully bolted assembly allowing load distribution without rigid welding
Flexible foundation systems accommodating ground movement
Continuous reinforcement at structural connections
Conclusion: The Future of Prefab Construction Materials
Prefab construction materials represent a convergence of engineering innovation, manufacturing efficiency, and sustainable building practices. From hot-dip galvanized steel frames providing corrosion resistance to advanced insulation systems maintaining thermal comfort across diverse climates, these materials enable rapid deployment of high-quality, durable structures.
The selection of appropriate prefab materials depends on understanding project-specific requirements—climate conditions, deployment duration, occupancy needs, and operational budgets. Modern prefab construction materials offer unprecedented flexibility, allowing customization while maintaining the factory-controlled quality and rapid deployment that define the prefab advantage.
Whether for temporary engineering camps, permanent residential communities, or emergency housing, the carefully engineered integration of structural steel, insulation systems, composite panels, and building envelope components creates buildings that outperform traditional construction in speed, quality, and long-term durability. As global construction demands intensify and climate variability increases, prefab construction materials will continue driving industry innovation toward more efficient, sustainable, and resilient building solutions.
For comprehensive information about prefab construction materials and modular housing solutions, visit https://www.cdph.net/ to explore integrated housing products and engineering camp construction services.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More



























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





