Understanding Prefab Accommodation Units
Prefab accommodation units represent a transformative approach to temporary and semi-permanent housing, fundamentally changing how construction companies, mining operations, and infrastructure projects address worker accommodation challenges. These units—also known as modular housing, container houses, or integrated housing systems—are factory-manufactured building components that arrive at project sites substantially pre-assembled, requiring minimal on-site construction work.
The concept of prefabrication has evolved significantly over the past two decades. Unlike traditional site-built structures that demand extensive construction timelines and on-site labor coordination, prefab accommodation units leverage factory-controlled manufacturing environments to ensure consistent quality, precise specifications, and accelerated delivery schedules. This manufacturing paradigm represents a critical competitive advantage in industries where project timelines are measured in weeks rather than months.

Core Components of Modern Prefab Accommodation Units
Contemporary prefab accommodation systems comprise several integrated product categories, each designed to address specific project requirements and environmental conditions. Understanding these product types enables project managers and facility planners to select solutions optimally aligned with their operational needs.
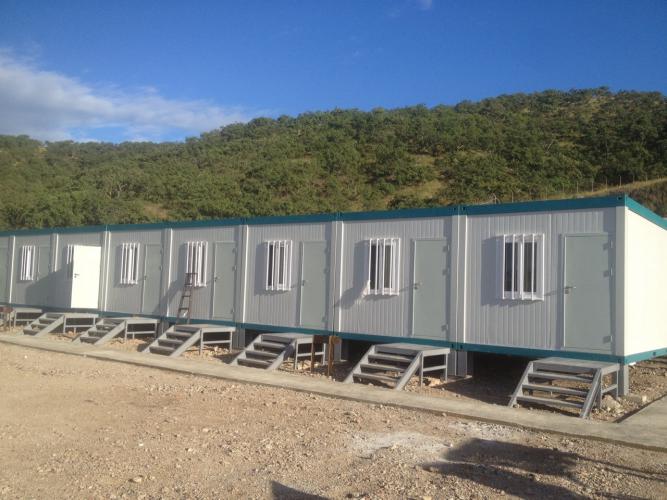
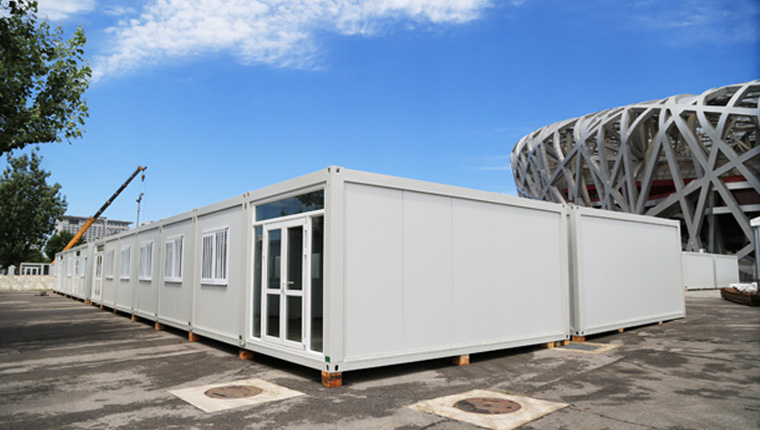
Container Houses function as the foundational modular building block for rapid accommodation deployment. These units utilize standardized steel container frames as structural bases, with dimensions typically measuring 6,055mm in length, 2,990–2,435mm in width, and 2,896mm in height. The design permits single-unit deployment or horizontal and vertical stacking up to three layers, creating flexible spatial configurations. Container houses undergo complete factory prefabrication including electrical systems, water supply infrastructure, and drainage networks, enabling immediate occupancy upon site installation. This standardized approach facilitates mass production economies and significantly reduces per-unit manufacturing costs compared to custom-built alternatives.
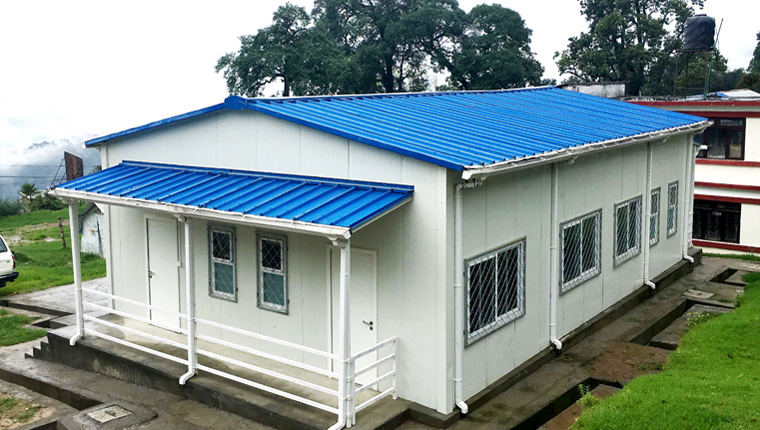
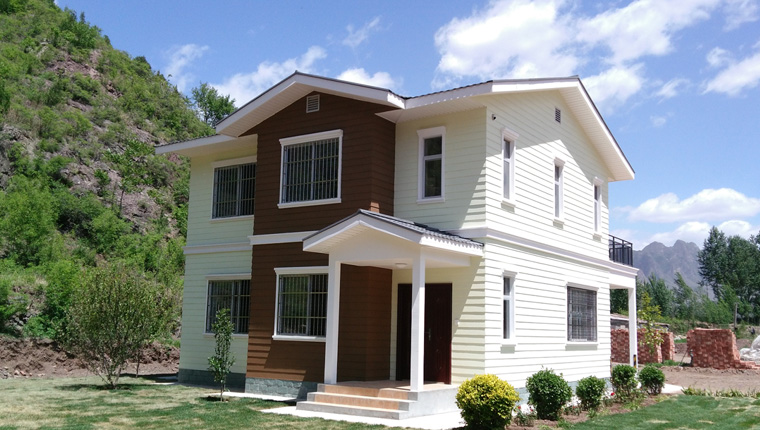
ZA-Type Houses represent an evolution beyond basic container designs, incorporating cold-formed hot-dip galvanized steel structures as primary load-bearing components. These units feature superior corrosion resistance, enhanced thermal insulation with 75–100mm rock wool or glass fiber insulation, and advanced sealing performance through seamless wall-frame connections. ZA-type houses accommodate customized interior layouts including dormitories, offices, dining facilities, and recreational spaces, with eave heights adjustable up to 5 meters depending on functional requirements. Their structural capacity withstands Category 11 wind loads, with specialized treatments enabling resistance to Category 17 hurricane conditions. The flexibility of design combined with robust structural performance makes ZA-type houses particularly suitable for challenging climatic environments.
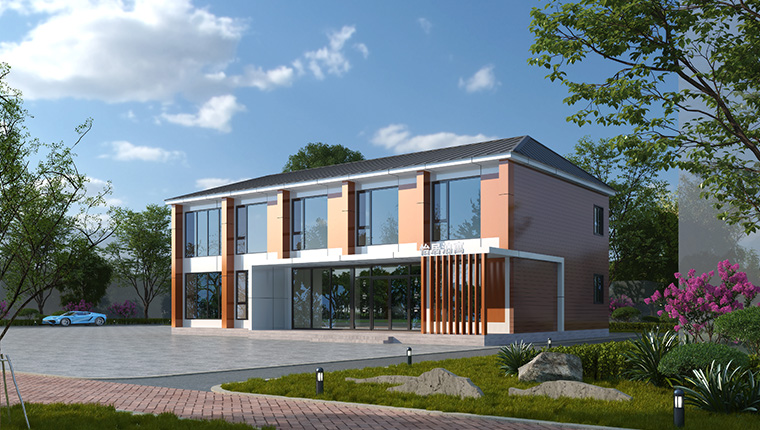
Prefab Houses emphasize modular construction using steel frame integration with composite maintenance boards, creating stable building systems adaptable to diverse environmental conditions. These units feature excellent anti-corrosion properties, superior sealing characteristics, and thermal insulation performance suited to varied climate zones. The integrated design approach eliminates the need for secondary on-site decoration, with interior and exterior finishing completed during factory production phases.
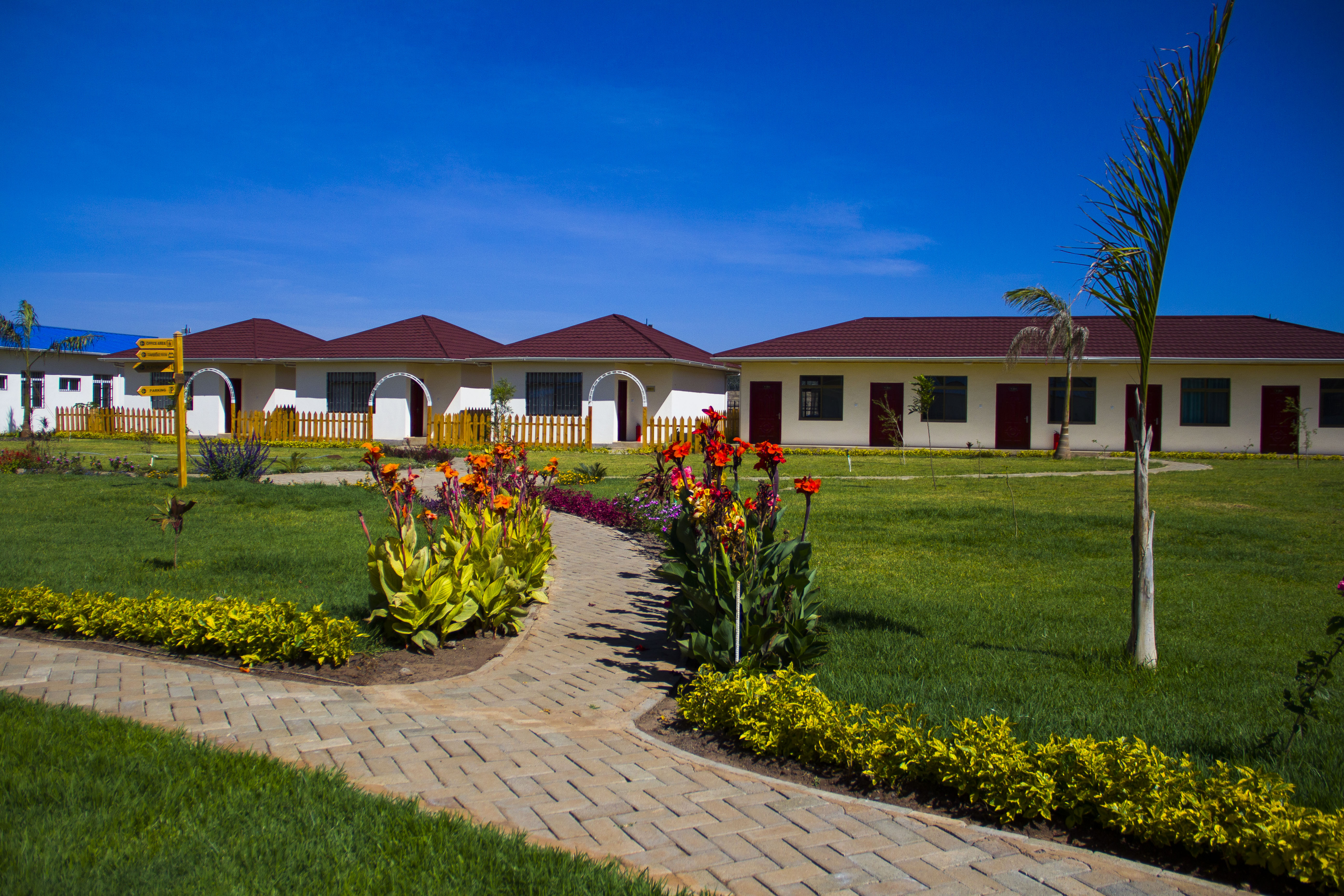
Light Steel Villas address the emerging demand for semi-permanent accommodation offering enhanced aesthetic appeal and residential comfort. Utilizing cold-formed light steel construction enabling mechanical mass production, these units serve dual purposes as both temporary project facilities and longer-term owner accommodation during project operation phases. Service life expectations exceed 25 years, with customizable layouts and climate-responsive material selections enabling deployment across diverse geographic regions.
Operational Advantages of Prefab Accommodation Solutions

The adoption of prefab accommodation units generates substantial competitive advantages across multiple operational dimensions:
Accelerated Installation Timelines represent perhaps the most visible benefit of prefabricated systems. Traditional construction camp development typically requires 60–90 days from site selection through occupancy readiness. Prefab accommodation solutions compress these timelines to 15–30 days through elimination of on-site structural work, interior finishing, and systems integration. This acceleration directly translates to earlier project productivity, reduced mobilization expenses, and improved cash flow management for project owners.
Cost Efficiency derives from multiple sources within the prefab ecosystem. Factory production achieves substantial economies through mechanized manufacturing processes, bulk material procurement, and standardized component production reducing waste. Transportation efficiency improves through containerized packaging of multiple units within standard 20-foot shipping containers—five assembled modular units typically condense into a single 20-foot container, dramatically reducing logistics expenses for international projects. Installation labor requirements decline by approximately 70–80% compared to conventional construction, and elimination of secondary decoration phases further reduces on-site labor costs. The comprehensive cost advantage typically ranges from 25–40% compared to site-built alternatives, with savings scaling proportionally to project size and unit quantity.
Mobility and Reusability distinguish prefab systems from permanent construction. Complete units can be relocated without disassembly as projects progress or conclude, enabling asset redeployment across multiple projects within a single asset lifecycle. This characteristic generates exceptional value in industries characterized by sequential project phases or geographically dispersed operations. A single accommodation unit installed for one project can be relocated and reinstalled elsewhere with minimal efficiency loss, effectively amortizing capital costs across multiple deployments.
Environmental Responsiveness capabilities have evolved substantially as manufacturers developed climate-specific configurations. In arctic regions such as Kazakhstan with winter temperatures reaching -52°C, specialized ZA-type units feature triple-layer hollow glass windows and 150mm rock wool insulation panels engineered for extreme cold performance. Conversely, tropical environments require corrosion-resistant hot-dip galvanized structures with enhanced drainage systems and ventilation provisions. This adaptive capacity eliminates costly project delays caused by climate-related performance failures, a critical consideration in remote location projects where replacement timelines extend months rather than weeks.
Global Applications and Project Diversity
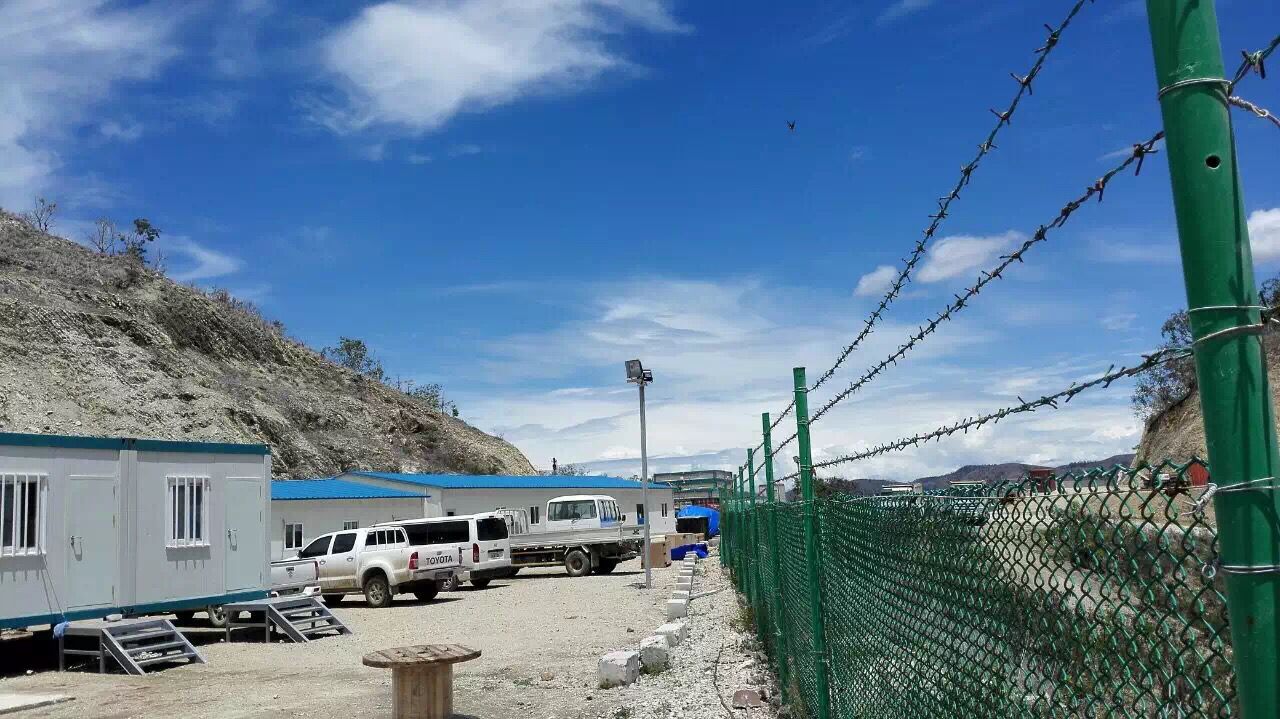
Prefab accommodation units have achieved deployment across virtually every industry requiring temporary or semi-permanent worker housing. Construction projects constitute the primary application domain, with comprehensive camp solutions supporting both site offices and residential facilities for multi-thousand-person workforces. Mining and energy extraction operations particularly benefit from prefab systems given the remote location characteristics and extended project duration requirements typical in these sectors.
Infrastructure development initiatives including railway, highway, and port expansion projects routinely deploy prefab accommodation to support construction workforces. The Astana Light Railway project in Kazakhstan exemplified this application, establishing a 18,041 square-meter accommodation camp housing 3,000 workers through deployment of 60 specialized ZA-type units engineered for sub-zero winter conditions. Educational and healthcare facility expansion projects increasingly leverage prefab accommodation for both administrative staff housing and temporary instructional spaces, with modular designs facilitating curriculum-specific spatial configurations.
Tourism and hospitality applications represent an emerging growth segment, with tourism module houses combining container bases with light steel decoration enabling semi-prefabricated or fully-prefabricated deployment models. These applications serve cultural tourism sites, commercial venues, and event facilities requiring rapid temporary infrastructure. Military and humanitarian applications have similarly expanded, with modular housing providing standardized accommodation for peacekeeping operations, disaster relief efforts, and international assistance initiatives. The compact packaging efficiency—five units condensing into single 20-foot containers—particularly suits international humanitarian deployments where transportation constraints define feasibility parameters.
Technical Specifications and Design Considerations
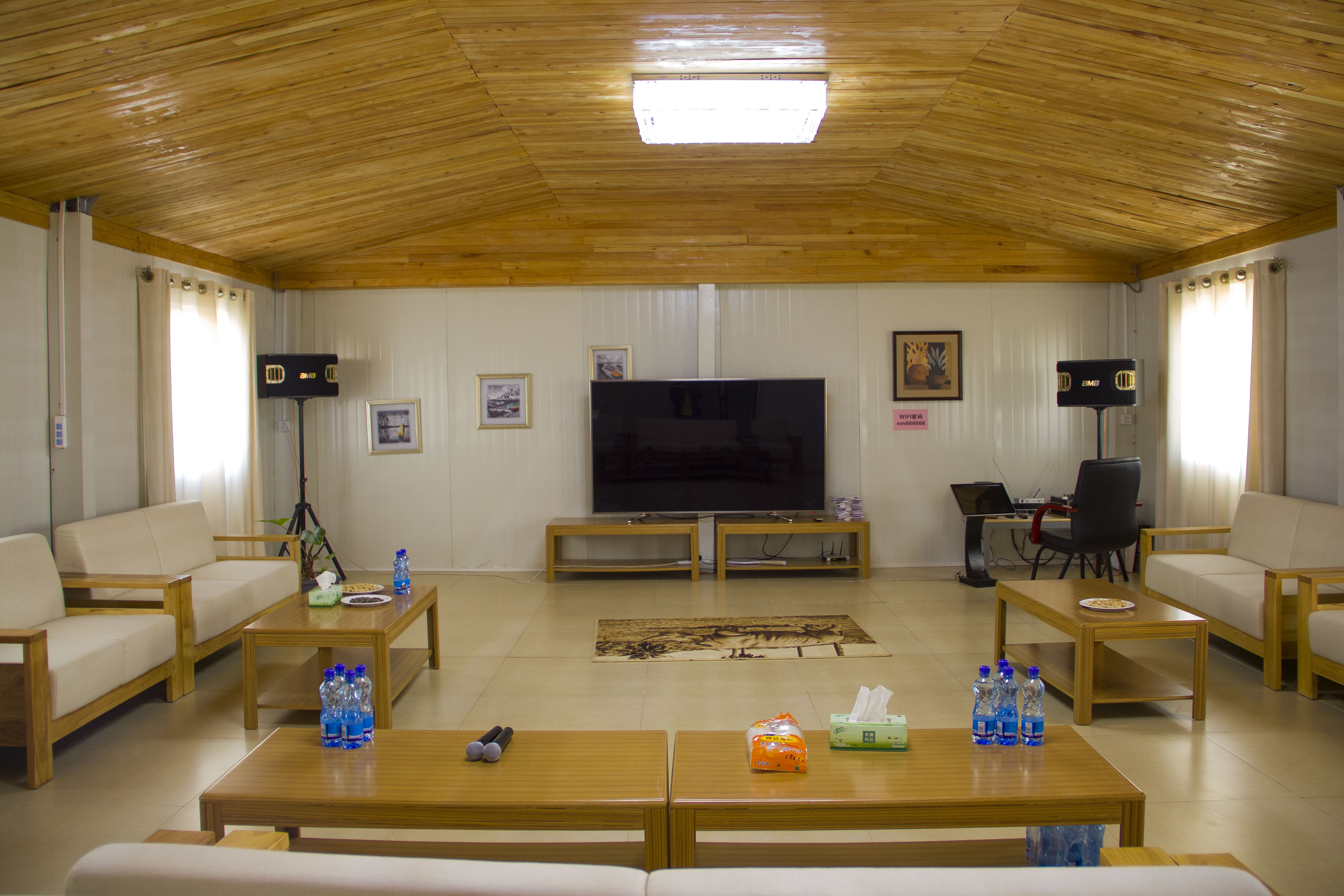

Understanding the technical parameters underlying prefab accommodation systems enables informed procurement decisions and site planning optimization:
Standard container house dimensions accommodate interior net sizes of approximately 5,845mm length and 2,780mm width with 2,500mm interior heights, providing approximately 16–18 square meters of usable floor space per unit. Structural specifications include hot-dip galvanized steel profiles with roof live loads of 0.5 KN/m² and floor live loads of 2.0 KN/m², with wind load resistance of 0.5 KN/m². Thermal performance characteristics feature roof heat transfer coefficients of 0.64 W/K, floor coefficients of 0.46 W/K, and wall coefficients of 0.47 W/K, delivering insulation performance equivalent to permanent residential construction.
Interior configurations support flexible layout implementations including single dormitories, double-occupancy rooms, office spaces with integrated workplace furniture, bathroom facilities with independent toilet and shower provisions, and kitchen support areas with complete electrical and water infrastructure. Color steel sandwich wall panels provide 75mm or optional 50–100mm rock wool or glass wool insulation, with adjustable specifications enabling climate-specific thermal performance optimization.
Electrical infrastructure includes pre-installed rooftop circuit pathways, standardized indoor wiring for 236W fluorescent lighting, comprehensive socket provisions including air conditioning capability, and safety-certified switching systems. Water supply systems feature integrated wall piping with drainage provisions, supporting full bathroom functionality without secondary plumbing work. These integrated infrastructure systems eliminate the principal delays and quality variability associated with on-site mechanical and electrical installations.
Site Installation and Logistics Management
Prefab accommodation deployment requires systematic logistics coordination despite reduced on-site construction requirements. Professional installation teams typically complete basic assembly within 2–5 days following unit delivery, involving roof installation, connection bolting between stacked units, and final utility terminations. The bolted connection methodology—eliminating on-site welding requirements—substantially reduces installation complexity and enables deployment in remote locations lacking welding capabilities or infrastructure support.
Transportation logistics represent critical success factors in international project deployments. Standard container house units divide into disassembled roof, ground, column, and panel components enabling optimal container volume utilization. This modular disassembly approach permits five unit deployments within a single 20-foot shipping container, dramatically reducing ocean freight expenses for global projects. Complex projects across multiple geographic zones benefit from pre-positioned inventory and regional staging facilities, reducing mobilization delays and expediting installation schedules when site conditions achieve readiness.
Industry-Specific Implementation Models
Mining and Energy Sector Applications leverage prefab accommodation to address the particular challenges of remote location operations. Large-scale mining operations deploying multi-thousand worker camps benefit substantially from the modular scalability enabling phased capacity expansion aligned with production ramp-up schedules. The cost efficiency of prefab systems becomes particularly pronounced in mining contexts where alternative permanent structures would require capital investments exceeding project duration value justifications. Energy extraction operations similarly benefit from the mobility characteristics permitting accommodation relocation as extraction sites progress geographically or vertically.
Construction Project Integration increasingly treats accommodation as integrated project infrastructure rather than secondary support functions. Comprehensive camp planning now incorporates accommodation units alongside office facilities, dining services, medical support, and security infrastructure, creating self-contained communities supporting construction workforces. The standardized modular approach enables coordinated master planning with accommodation components scaled and positioned to optimize overall site efficiency. Construction enterprises recognize that quality accommodation directly correlates with workforce retention, productivity, and safety performance—making accommodation investment decisions fundamental to project economics rather than cost-minimization exercises.
Educational and Commercial Facility Expansion represents a distinctive application domain where prefab accommodation units serve dual purposes as both temporary construction camp facilities and permanent post-construction infrastructure. Schools expanding facilities frequently retain modular classroom units following construction completion, capturing residual value and deferring future facility expansion capital requirements. Commercial hospitality and tourism venues similarly utilize modular units through project completion and subsequent permanent deployment, effectively eliminating construction phase accommodation costs.
Comparative Advantages Against Alternative Approaches
The competitive positioning of prefab accommodation units versus alternative housing solutions becomes increasingly apparent as project parameters scale:
Compared to temporary site-built structures constructed from local materials and labor, prefab units deliver superior quality consistency, shortened timelines, enhanced durability, and reduced on-site disruption. Site-built temporary structures typically exhibit variable construction quality, extended deployment timelines, limited reusability, and environmental sensitivity to local labor availability and material supply constraints.
Versus permanent construction alternatives, prefab accommodation dramatically reduces capital requirements, eliminates long-term facility carrying costs post-project completion, and enables rapid redeployment to subsequent projects. Permanent structures remain productive only through extended operational periods justifying high capital investments—prefab units generate competitive returns even for 12–24 month project durations.
Compared to leasing existing structures or securing off-site accommodation, prefab units provide superior site integration, accommodate project-specific functional requirements, reduce relocation and commuting inefficiencies, and typically deliver superior total-cost-of-ownership economics at multi-unit scales.
Quality Assurance and Durability Characteristics
Factory production environments enable quality control standards exceeding typical construction site capabilities. Prefab manufacturers implement systematic material testing, structural verification, and performance validation across entire production runs, generating consistency documentation and quality assurance certifications exceeding industry standards. Factory completion of interior finishing, systems testing, and performance validation eliminates the quality variability associated with site-executed construction work.
Durability performance has been validated across diverse climatic extremes including arctic conditions with -52°C temperatures, tropical environments with intense humidity and salt-air corrosion exposure, and arid regions with extreme temperature diurnal variations. Hot-dip galvanized structural systems demonstrate exceptional longevity in coastal environments and high-moisture conditions, with protective coating systems designed for 20+ year service life expectancies. Roof and wall insulation systems maintain thermal performance across extended operational periods, while structural systems undergo design verification for wind loads, snow loads, and seismic conditions appropriate to deployment regions.
Cost Economics and Financial Analysis
Comprehensive cost analysis demonstrates consistent prefab accommodation advantages across relevant financial dimensions. Capital costs typically range from $8,000–$15,000 per unit for standard configurations, with economy-of-scale advantages reducing unit costs as project volumes expand beyond 50 units. Transportation expenses average $500–$1,200 per unit internationally, with containerization efficiency reducing logistics costs below $200 per unit for large-scale deployments. Installation costs span $1,000–$2,500 per unit, representing a fraction of site-built alternatives requiring $15,000–$25,000 in labor and material investments.
Operating cost advantages accrue through extended asset reusability, with prefab units typically supporting 5–10 project deployments across 15–20 year operational periods. Residual value recovery at final lifecycle completion typically achieves 30–50% of original capital costs, with material content (steel, aluminum, glass) supporting secondary market demand. These economic characteristics generate total-cost-of-ownership advantages particularly pronounced for organizations executing sequential projects within consistent geographic markets.
Strategic Considerations for Project Selection
Organizations evaluating prefab accommodation adoption should assess specific decision parameters including project duration (minimum 6 months recommended for standalone units), workforce scale (economies emerge at 25+ units), geographic location (remote sites amplify logistics and quality control advantages), and accommodation function diversity (multi-purpose requirements favor modular flexibility). Projects with extended labor-intensive phases, difficult site access, or geographic location constraints consistently demonstrate the strongest cost and schedule benefits.
Environmental sensitivity represents an increasingly relevant decision criterion, with prefab systems generating substantially reduced site disturbance, waste generation, and environmental impact compared to site-built alternatives. The controlled factory production environment minimizes material waste through precision manufacturing, and the complete prefabrication approach eliminates construction site environmental hazards including welding fumes, construction dust, and uncontrolled material storage.
Conclusion
Prefab accommodation units have evolved from innovative alternatives to fundamental components of modern construction and project management strategy. The integration of modular design principles, factory-controlled manufacturing, standardized specifications, and systematic logistics creates economic and operational advantages proving increasingly difficult to justify ignoring in competitive project environments.
The technological maturity of contemporary prefab systems, demonstrated through thousands of successful international deployments, has transformed accommodation from a project impediment into a potential competitive advantage. Organizations systematically deploying prefab accommodation across successive projects capture escalating benefits through standardized planning methodologies, optimized logistics networks, experienced installation teams, and amortized capital investments. As project environments grow increasingly dynamic, geographically dispersed, and schedule-constrained, the rapid deployment capability and operational flexibility of prefab accommodation units will continue driving adoption rates across industries dependent on temporary worker housing.
For organizations seeking comprehensive prefab accommodation solutions aligned with specific project requirements, partnering with experienced providers offering integrated design, manufacturing, logistics, and installation services ensures optimization across all success-critical dimensions. The combination of proven technology, established global deployment networks, and expert project integration capabilities enables confident adoption of prefab accommodation as a strategic competitive advantage rather than a commodity procurement decision.
References and Sources:
Information sourced from Chengdong Modular House official documentation (https://www.cdph.net/), including global project footprint data, product specifications for container houses, ZA-type houses, and prefab house systems, as well as detailed case study documentation from international deployment projects.



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More



























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





