Introduction
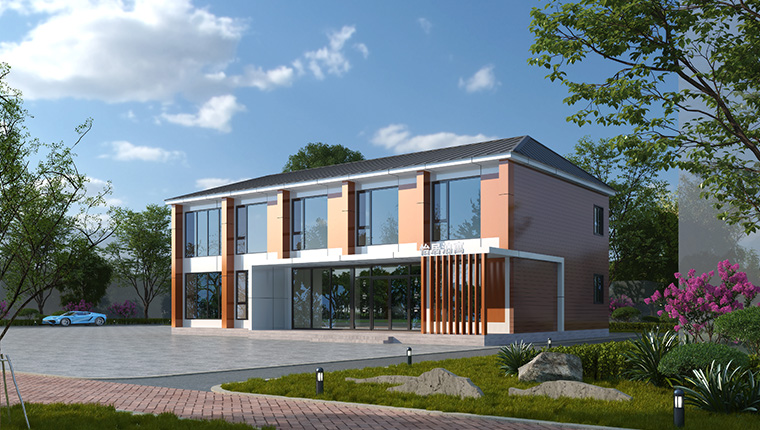
Modular construction has revolutionized how temporary and semi-permanent facilities are deployed across the world's most challenging environments. Unlike traditional construction methods that require extensive on-site building, modular housing provides pre-fabricated, factory-built components that assemble quickly with minimal environmental disruption. The technology has been successfully adapted to extreme climates ranging from equatorial rainforests to Arctic regions and arid deserts.
This comprehensive guide examines real-world modular construction examples and demonstrates how engineering solutions are tailored to specific climate conditions. By understanding these practical applications, project managers, engineers, and facility planners can select appropriate modular solutions for their unique environmental challenges.

What is Modular Construction?
Modular construction refers to a building method where structures are manufactured in controlled factory environments, then transported and assembled on-site. Key advantages include:
Rapid deployment: Assembly in days rather than months
Quality control: Factory conditions ensure precision manufacturing
Portability: Structures can be relocated without major disassembly
Standardization: Modular units follow consistent specifications
Cost efficiency: Reduced transportation and labor expenses for remote sites
Environmental adaptability: Can be engineered for specific climate conditions
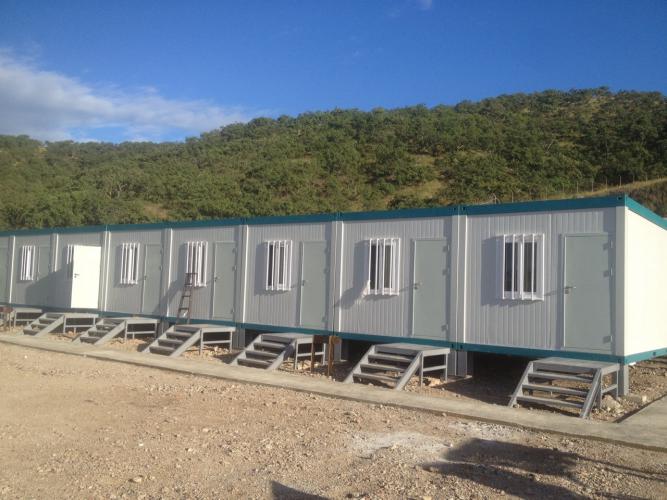
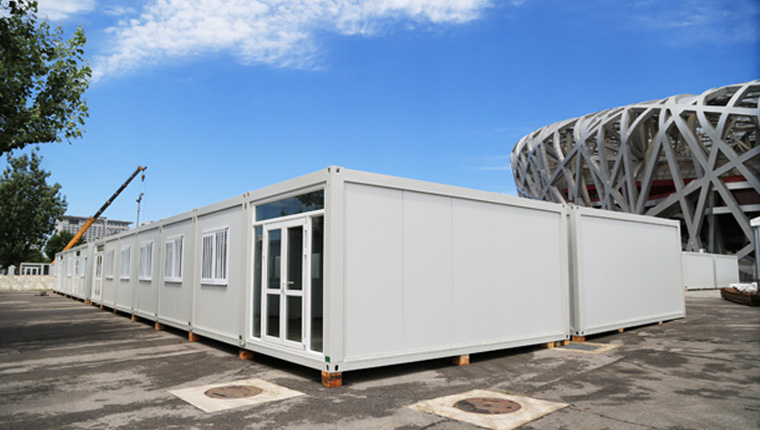
Modular units typically measure 6,055mm in length with 2,990mm width, accommodating standardized dimensions for ocean shipping containers. These dimensions allow for efficient packaging and transportation while maintaining practical internal living and working spaces.
Tropical Rainforest Climate: Papua New Guinea Case Study
Environmental Challenges
Tropical rainforest environments present unique challenges for construction:
Annual rainfall exceeding 3,000-4,000mm
High humidity levels (85-95% relative humidity)
Aggressive corrosion from salt-laden air in coastal regions
Rapid biodegradation of organic materials
Foundation instability from water-saturated soils
Extreme heat combined with moisture
Technical Solution: Galvanized Steel Modular Housing
The Papua New Guinea ORO Province accommodation project demonstrates how modular construction adapts to tropical climates. The project selected ZA-type modular houses—engineering-grade containers built with hot-dip galvanized steel frames.
Key technical specifications:
Material: Hot-dip galvanized cold-formed steel structure
Wall insulation: 75mm rock wool or fiberglass composite panels with color steel cladding
External finish: Decorative boards for enhanced durability
Design life: 5-10 years with proper maintenance
Installation speed: 2-3 days per unit
The galvanizing process applies a protective zinc coating (typically 70-100 microns thick) that sacrificially corrodes before the underlying steel, providing 15-25 years of corrosion protection in tropical environments.
Additional Climate-Adaptive Features
Elevated flooring systems: Rather than placing structures directly on soil, modular units utilize elevated foundations with 300-400mm clearance. This design:
Prevents moisture wicking from saturated ground
Allows air circulation beneath the structure
Reduces termite and pest infiltration
Simplifies drainage around buildings
Enhanced drainage design: Modular camps in tropical regions incorporate:
Sloped roof designs preventing water pooling
Seamless waterproof connections using patented structural designs
Underground drainage networks with sedimentation tanks
Separate systems for greywater and sewage
Environmental materials: The Papua New Guinea project specified zero-formaldehyde materials for interior finishes, critical in tropical regions where high humidity accelerates off-gassing from conventional construction materials.
Humid Coastal Climate: Tanzania Gas Pipeline Camp

Project Overview
The Tanzania gas pipeline project stretched from Mtwara to Dar es Salaam, traversing regions with extreme humidity and salt-air corrosion. The camp covered 10,298m² and required accommodation for 500+ workers.
Technical Approach
This project showcased advanced moisture management in modular construction:
Foundation design:
Fully galvanized elevated floor systems with 300mm overhead clearance
Prevents ground moisture penetration and supports rapid drying
Eliminates need for extensive concrete work on unstable soils
Material specifications:
Hot-dip galvanized structural components throughout
High-quality galvanized profiles with stable surface properties
Resistant to salt-spray corrosion (typically surviving 1,500+ salt-fog hours per ASTM B117 standards)
Installation advantage:
No site concrete construction required
Reduces project timeline significantly
Minimizes environmental damage from concrete production in sensitive coastal areas
The elevated design proved particularly valuable in Tanzania, where seasonal flooding from the Rufiji River and coastal water tables create perpetually damp conditions.
Maldives Airport Expansion: Tropical Island Paradise
Unique Environmental Constraints
The Maldives Velana International Airport reconstruction project presented specific challenges:
Coral island foundation (sandy substrate with minimal bearing capacity)
Intense sun exposure (5,000+ kilowatt-hours per square meter annually)
Annual rainfall: 1,900mm
Proximity to equator (intense UV radiation)
Frequent cyclone activity during monsoon season
Modular Solution: Double-Layer ZA Housing
Camp specifications:
Total area: 15,600m² with 6,800m² construction footprint
Double-layered ZA and ZM barracks
Sandwich color steel plates with enhanced weather sealing
Designed operational life: 3-5 years
Foundation system:
200mm C20 concrete base
Coral sand backfill (100mm layer)
50mm additional coral sand interlayer (locally sourced)
100mm C15 concrete cushion
Paving tiles for interior flooring
This layered foundation approach maximizes stability on sandy soils while utilizing locally available materials, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact.
Special features:
Modular toilet and shower facilities with separate hot water systems
Medical office complex with quarantine capacity
Recreation facilities (basketball courts, badminton, gymnasiums)
Advanced security system integration with airport infrastructure
Cold Climate Adaptation: Astana Light Railway Project, Kazakhstan

Extreme Winter Conditions
Kazakhstan's Astana experiences some of the harshest conditions for modular construction:
Winter temperatures: -52°C minimum
Snow cover duration: 130-140 consecutive days
Snow load: 50+ kg per square meter
Strong wind pressures (15-20 m/s gusts)
Ground freeze depth: 1.5-2.0 meters
Advanced Insulation Strategy
The Astana Light Railway project required housing for 3,000 workers across 18,041m² of camp area with 60 modular units.
Enhanced thermal specifications:
Wall insulation: 150mm rock wool in color steel sandwich panels
Roof insulation: 150mm glass fiber wool with enhanced thickness
Window system: Hollow triple-layer glass casement windows (low-emissivity coatings)
Thermal break design: Structural elements thermally isolated from exterior surfaces
For reference on additional cold-resistant specifications, visit https://www.cdph.net/ for advanced technical documentation on extreme-temperature modular housing.
Cold-bridge elimination:
Engineers at Beijing Chengdong addressed the critical "cold bridge" effect—where structural connections create pathways for heat loss. Solutions included:
Thermally-broken fastener systems
Foam-filled connection details
Sealed joints preventing wind infiltration
Heat-tape systems for plumbing in external walls
Structural loads:
Roof designed for 0.5 kN/m² live load plus snow accumulation
Wind load resistance: 0.45 kN/m² (equivalent to 70+ mph winds)
Foundations extended below frost line with concrete pilings
The project was completed during harsh winter conditions, requiring 4 experienced installation supervisors to oversee assembly. Follow-up inspections three years later confirmed structures remained in excellent condition despite extended sub-zero exposure.
Siberian Extreme Cold: Russia Khabarovsk Two-Story Housing
Technical Challenges
The Khabarovsk project in Russia's far east presented engineering challenges unique to continental climates:
Permafrost presence requiring special foundation design
Temperature swings of 70°C+ between summer and winter
Thermal stress on materials and connections
Potential ground subsidence from thawing permafrost layers
Design Solution: Two-Story Container Housing
Specifications:
Double-story modular container design
Double-slope roof (sheds snow efficiently, distributes loads)
Cold-bridge effect solutions engineered into connections
Thermal-break design throughout structural frame
Installation innovation:
The customer modified design plans during construction, requiring on-site component reworking. The project supervisor redesigned and fabricated replacement components on-site, preventing cost overruns and schedule delays.
Long-term performance:
Three years after completion, inspection confirmed structures remained in "like-new" condition despite:
This case demonstrates how modular construction's prefabricated precision ensures durability in climates where dimensional changes from thermal expansion/contraction could compromise assembled structures.
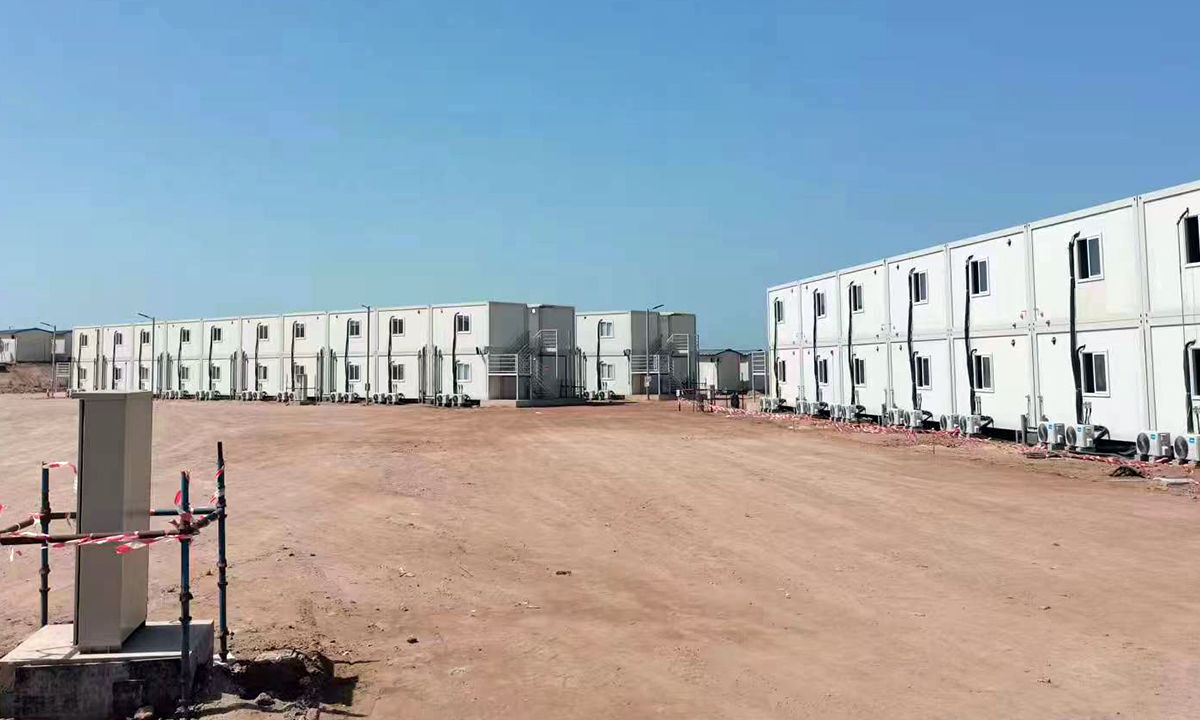
Hot Desert Climate: Ethiopia Industrial Projects

Climate Characteristics
Ethiopia's Adama Industrial Park and highway projects operate in semi-arid conditions:
Annual rainfall: 200-400mm (highly variable)
Summer temperatures: 35-45°C
Low humidity (20-30%)
Intense solar radiation (6,500+ kWh/m² annually)
Dust storms and wind abrasion hazards
Modular Solution: Flatpack Heat-Insulating Containers
Project specifications:
15 Flatpack containers with coupled design
Separate roof systems for modular functionality
Heat-insulating materials throughout
Highly mobile for site relocation
Features for desert environments:
Ventilation: Natural air circulation beneath elevated structures
Solar protection: Reflective color coatings minimize heat absorption
Dust resistance: Sealed connection details prevent infiltration
Thermal mass: Color steel composite panels provide thermal buffer
Easy relocation: Flatpack design allows repositioning to accommodate mining/construction site changes
ZA-type houses selection:
Ethiopian highway projects also employed ZA-type modular houses alongside K-type units for flexibility:
Irregular design accommodations (ZA's flexible design capability)
Rapid installation (K-type's pre-assembled configuration)
Both types stress wind and rain protection
Cold-formed steel structure withstands thermal cycling
The combination approach maximized installation speed while maintaining weather protection in the harsh desert climate.
West African Port Development: Côte d'Ivoire Case Study
Environmental Challenges
The Abidjan Port expansion project combined tropical coastal conditions with intense industrial requirements:
High humidity with salt-air corrosion
Temperature range: 20-35°C year-round
Seasonal rainfall patterns
Heavy equipment operation requiring robust structures
Comprehensive Modular Campus
The camp covered 27 hectares with distinct functional zones:
Office area: 14,000m² with traditional office configurations
Chinese living area: 32,500m² with residential comfort standards
Local worker accommodation: 4,000m² with practical designs
Production facilities: Concrete mixing plant, prefabrication areas
Recreational facilities: Basketball courts, tennis, swimming, football fields
Structural specifications:
ZA-type modular houses for primary accommodation
Light steel villa structures for guesthouses (25+ year design life)
Cold-formed thin-walled steel structure system for safety and stability
Wind resistance: Level 10 (89+ mph)
Galvanizing plus color spray treatment for superior corrosion protection
Innovative waterproofing:
The project implemented patented structural waterproof design (15+ year proven track record):
Eliminates traditional self-tapping screw connections prone to leakage
Proprietary roof connection prevents water penetration during repeated assembly/disassembly
Verified through 10+ disassembly/reassembly cycles with 98%+ success rate
Modular Construction Product Types and Climate Suitability
Best for: High-mobility projects, minimal site preparation
Standardized dimensions: 6,055mm × 2,990mm × 2,896mm
Pre-wired electrical systems
Can be stacked three layers high
Transportation in standard shipping containers
Best for: Diverse climate adaptation (high/low temperature, desert, coastal)
Hot-dip galvanized cold-formed steel frame
Flexible design capability
75-150mm insulation options (adjustable by climate)
Rapid bolted assembly (no site welding)
Design life: 5-10 years
K-Type Houses
Best for: Speed of installation, temporary projects
Pre-assembled configurations
Minimal on-site assembly
Rapid deployment capability
Moderate climate adaptation
Best for: Semi-permanent projects, extended occupancy
Design life: 25+ years
Enhanced aesthetic appeal
Superior thermal performance
Suitable for long-term residential use
Best for: Large-span production facilities
Warehouse and factory construction
Supports heavy equipment and cranes
High structural load capacity
Wide-span capabilities (up to 30m)
Critical Modular Construction Specifications by Climate
Tropical/Humid Environments (Humidity >80%)
| Parameter | Specification |
| Structural material | Hot-dip galvanized steel (70-100 microns) |
| Wall insulation | 75-100mm rock wool or fiberglass |
| Foundation clearance | 300-400mm elevated |
| Drainage system | Independent greywater and sewage lines |
| Design life | 5-10 years |
| Primary corrosion strategy | Galvanization plus ventilation |
Extreme Cold Environments (Below -40°C)
| Parameter | Specification |
| Wall insulation | 130-190mm rock wool (thickness increases with extreme cold) |
| Roof insulation | 150-200mm glass fiber wool |
| Windows | Triple-glazed, low-emissivity coating |
| Thermal breaks | Foam-filled connections throughout |
| Foundation depth | Below frost line (typically 1.5-2.0m) |
| Design snow load | 0.5+ kN/m² with regional adjustment |
Desert/Hot-Dry Environments (Temperature >40°C, Humidity <30%)



More

More

More

More

More
Learn More




























![Top Advantages of Modular Construction Explained [2025]](/uploads/upload/images/20250424/0fb390068474145a09a8c0504c73b1d2.png)





